ICND2 – InterVLAN Questions
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
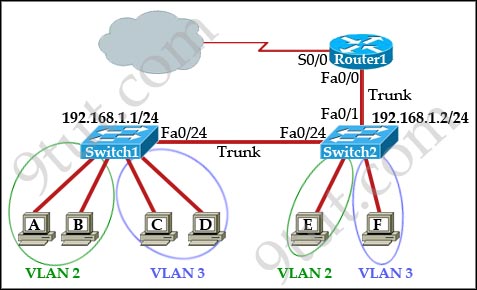
Which two statements are true about interVLAN routing in the topology that is shown in the exhibit? (Choose two)
A. Host E and host F use the same IP gateway address.
B. Routed and Switch2 should be connected via a crossover cable.
C. Router1 will not play a role in communications between host A and host D.
D. The FastEthernet 0/0 interface on Router1 must be configured with subinterfaces.
E. Router1 needs more LAN interfaces to accommodate the VLANs that are shown in the exhibit.
F. The FastEthernet 0/0 interface on Router1 and Switch2 trunk ports must be configured using the same encapsulation type.
Answer: D F[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about slow inter VLAN forwarding is true?
A. The VLAN is experiencing slowness in the point-to-point collisionless connection.
B. The VLANs are experiencing slowness because multiple devices are connected to the same hub.
C. The local VLAN is working normally, but traffic to the alternate VLAN is forwarded slower than expected.
D. The entire VLAN is experiencing slowness.
E. The VLANs are experiencing slowness due to a duplex mismatch.
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The causes of slow interVLAN are usually duplex mismatch or collision domain issues, user misconfiguration. For more information please read: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/virtual-lans-vlan-trunking-protocol-vlans-vtp/23637-slow-int-vlan-connect.html#troubleshoot_slow_interv
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which configuration can you apply to enable encapsulation on a subinterface?
A. interface FastEthernet 0/0
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ip address 10.1.1.30 255.255.255.0
B. interface FastEthernet 0/0.30
ip address 10.1.1.30 255.255.255.0
C. interface FastEthernet 0/0.30
description subinterface vlan 30
D. interface FastEthernet 0/0.30
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ip address 10.1.1.30 255.255.255.0
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
To enabe encapsulation on a subinterface we have type the “encapsulation” command under that subinterface, not the main interface. An example of configuring encapsulation on subinterface of Fa0/1 is shown below:
|
Router(config)#interface f0/0 (Note: The main interface f0/0 doesn’t need an IP address but it must be turned on) Router(config)#interface f0/0.0 |
Note: In the “encapsulation dot1q 10”, number 10 is the VLAN applied to that subinterface. Or you can understand that the subinterface belongs to that VLAN.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
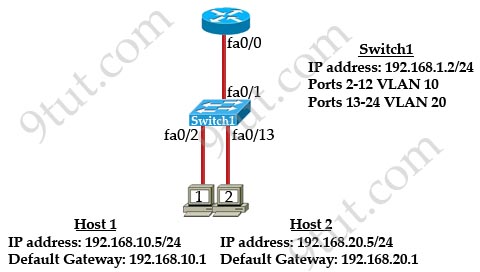
What commands must be configured on the 2950 switch and the router to allow communication between host 1 and host 2? (Choose two)
A. Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut down
B. Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0.1
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10
Router(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-subif)#interface fastethernet 0/0.2
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 20
Router(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
C. Router (config)#router eigrp 100
Router(config-router)#network 192.168.10.0
Router(config-router)#network 192.168.20.0
D. Switch1(config)# vlan database
Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp domain XYZ
Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp server
E. Switch1(config) # interface fastEthernet 0/1
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
F. Switch1(config)# interface vlan 1
Switch1(config-if)# ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:

C-router is to be used as a “router-on-a-stick” to route between the VLANs. All the interfaces have been properly configured and IP routing is operational. The hosts in the VLANs have been configured with the appropriate default gateway. What can be said about this configuration?
A. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router eigrp 123
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
B. No further routing configuration is required.
C. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router ospf 1
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
D. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router rip
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
Answer: B[/am4show]


On Q2, what the question actually asking? ask about the reason of slowness or the definition of slow inter vlan? If reason, answer will be E but if definition will be C. Which one?
kariya