ICND2v3 – New Questions Part 4
Note: These new questions have not been classified into specific topics so please practice them separately.
Premium Members: You can practice these questions with our quizzes first at:
+ Question 1 to 20
+ Question 21 to 40
+ Question 41 to 60
Question 1
In the Software-Defined Networking model, where is the interface between the control plane and the data plane?
A. between the control layer and the infrastructure layer
B. between the collocated layer and the dislocated layer
C. between the control layer and application layer
D. between the application layer and the infrastructure layer
Answer: A
Question 2
Which function is performed by a TACACS+ server?
A. It hosts an access list that permits or denies IP traffic to the control plane of a device.
B. It provides external AAA verification.
C. It filters usernames and passwords for Telnet and SSH.
D. It serves as a database for line passwords.
Answer: B
Question 3
Which option is the master redundancy scheme for stacked switches?
A. 1:N
B. 1:1
C. N:1
D. 1+N
Answer: A
Question 4
Which Cisco IOS feature can you use to dynamically identify a connectivity problem between a Cisco device and a designated endpoint?
A. traceroute
B. ICMP Echo IP SLAs
C. IP SLAs threshold monitoring
D. Multi Operation Scheduler IP SLAs
Answer: B
Question 5
Drag and drop the SDN components from the left onto the correct API types on the right.
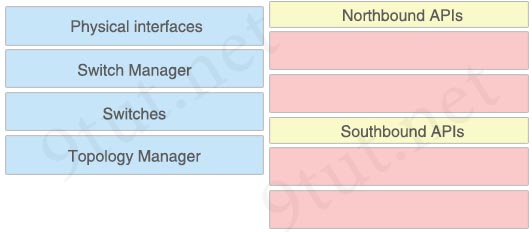
Answer:
Northbound APIs:
+ Switch Manager
+ Topology Manager
Southbound APIs:
+ Physical interfaces
+ Switches
Question 6
Which two benefits of using MPLS for WAN access are true? (Choose two)
A. It supports hub-and-spoke connectivity.
B. It supports CoS.
C. It provides VPN support.
D. It provides payload security with ESP.
E. It supports Authentication Header.
Answer: B C
Question 7
Which two statements about MPLS are true? (Choose two)
A. It encapsulates all traffic in an IPv4 header
B. It provides automatic authentication
C. It uses labels to separate and forward customer traffic
D. It can carry multiple protocols, including IPv4 and IPv6
E. It tags customer traffic using 802.1Q
Answer: C D
Question 8
Which three statements about the ACEs that are matched by a Cisco APIC-EM ACL path are true? (Choose three)
A. If the trace fails to find a matching ACE in an ACL, it is reported as implicitly permitted.
B. If an optional criterion is omitted from the trace, the results include all possible ACE matches.
C. If the trace fails to find a matching ACE in an ACL, it is reported as implicitly denied.
D. ACEs are reported only if they match.
E. All ACEs found by the trace are reported, including those that fail to match.
F. If an optional criterion is omitted from the trace, the results are reported as if the default value was specified.
Answer: B C D
Explanation
An ACL path trace shows whether the traffic matching your criteria would be permitted or denied based on the ACLs configured on the path.
The following rules effect the ACL path trace results:
+ Only matching access control entries (ACEs) are reported.
+ If you leave out the protocol, source port, or destination port when defining a path trace, the results include ACE matches for all possible values for these fields.
+ If no matching ACEs exists in the ACL, the flow is reported to be implicitly denied.
Note:
Question 9
Which three protocols does APIC-EM support with Path Trace? (Choose three)
A. HSRP
B. ECMP
C. WLC
D. SNMP
E. SMTP
F. ECMP/TR
Answer: A B F
Explanation
Path Trace Supported Device Protocols and Network Connections:
Access Control List (ACL)
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN)
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
Equal Cost Multipath/Trace Route (ECMP/TR)
Equal Cost Multi Path (ECMP)
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Protocol
…
For more information about these supported protocols and network connections, please visit https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/cloud-systems-management/application-policy-infrastructure-controller-enterprise-module/1-3-x/config-guide/b_apic-em_config_guide_v_1-3-x/b_apic-em_config_guide_v_1-3-x_chapter_0111.html
Question 10
Where must you configure switch-level global features on a switch stack?
A. on the stack master
B. on the stack master and each individual stack member
C. on the stack master or any individual stack member
D. on each individual stack member
Answer: A
Question 11
Which two statements about the Cisco APIC-EM ACL Path Trace feature are true? (Choose two)
A. Higher-priority ACEs override lower-priority ACEs in the same ACL.
B. The trace analyzes only the egress interface of all devices in the path.
C. The trace analyzes the ingress interface and the egress interface of all devices in the path.
D. The trace analysis stops as soon as the trace encounters a deny entry on the path.
E. The trace analyzes only the ingress interface of all devices in the path.
Answer: A C
Explanation
Access Control List (ACL) Trace analyzes how a flow is affected by ACLs programmed on the path. After the path is calculated between the source and the destination, the ACL Trace analyzes both ingress and egress interfaces of all devices on the path -> C is correct.
Analysis of entries within an individual ACL is cumulative. That is, if a higher priority ACE is a match, lower-priority ACEs are ignored -> A is correct.
Question 12
Which two data integrity algorithms are commonly used in VPN solutions? (Choose two)
A. DH1
B. DH2
C. HMAC-MD5
D. HMAC-SHA-1
E. RSA
Answer: C D
Explanation
Two popular algorithms a VPN gateway uses for verifying integrity of data are HMAC-Message Digest 5 (HMAC-MD5) and HMAC-Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (HMAC-SHA1)
+ HMAC-MD5 uses a 128-bit shared-secret key of any size. The variable-length message and shared-secret key are combined and run through the HMAC-MD5 hash algorithm. The output is a 128-bit hash. The hash is appended to the original message and is forwarded to the remote end.
+ HMAC-SHA-1 uses a secret key of any size. The variable-length message and the shared-secret key are combined and run through the HMAC-SHA-1 hash algorithm. The output is a 160-bit hash. The hash is appended to the original message and is forwarded to the remote end.
Diffie-Hellman Group 1 (DH-1) & Diffie-Hellman Group 2 (DH-2) are two encryption algorithms for VPN, not data integrity algorithms.
RSA is also an encryption algorithm, not data integrity algorithm.
Question 13
Which component of VPN technology ensures that data is unaltered between the sender and recipient?
A. encryption
B. authentication
C. key exchange
D. data integrity
Answer: D
Question 14
In which three circumstances may your organization require a high-bandwidth Internet connection? (Choose three)
A. It uses cloud computing
B. It uses network devices that require frequent IOS upgrades
C. It uses peer-to-peer file sharing
D. It is undergoing a SAN expansion
E. It uses Infrastructure as a Service
F. It uses resource-intensive applications
Answer: A C E
Question 15
Which tool or utility can report whether traffic matching specific criteria can reach a specified destination on the ACLs along the path?
A. Cisco Security Device Manager
B. Cisco Prime
C. APIC-EM
D. Cisco Network Assistant
Answer: C
Explanation
If you performed an ACL trace, the devices show whether the traffic matching your criteria would be permitted or denied based on the ACLs configured on the interfaces.
Question 16
Which three features are QoS congestion-management tools? (Choose three)
A. PPPoE
B. PQ
C. FIFO
D. PPP
E. PDQ
F. WFQ
Answer: B C F
Explanation
Good reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/qos_conmgt/configuration/xe-3s/qos-conmgt-xe-3s-book/qos-conmgt-oview.html
Question 17
For which two reasons might you choose chassis aggregation instead of stacking switches? (Choose two)
A. to avoid the use of a centralized configuration manager
B. to avoid relying solely on Ethernet interfaces
C. to allow hot-swapping modules
D. to increase the number of devices in use
E. to increase the maximum port count
Answer: B C
Explanation
Chassis aggregation is a Cisco technology to make multiple switches operate as a single switch. It is similar to stacking but meant for powerful switches (like the 6500 and 6800 series switches). Chassis aggregation is often used in the core layer and distribution layer (while switching stacking is used for access layer). Chassis aggregation refers to a technology implemented on modular switches (like Catalyst 6500 and 4500s). The modules can be hot-swapped on these switches.
With switch stacking, the switches that are added to or removed from the switch stack must be powered off -> Answer C is correct.
A switch stack is a set of up to nine Cisco EtherSwitch service modules or Catalyst 3750 switches connected through their Cisco StackWise ports while Chassis aggregation is a Cisco technology to make two switches operate as a single logical switch. Therefore stacking switches have more ports than chassis aggregation -> Answer E is not correct.
Both chassis aggregation and switch stacking increase the number of devices in use and they also use a centralized conf -> Answer D is not correct.
Switch stacking elects a master switch to control the configuration and administration of the stack. Chassis aggregation also uses a single Supervisor module to control all of the Spanning-Tree protocol running in both switches that were bundled together. Therefore we can consider both of them use a centralized manager -> Answer A is not correct.
Chassis aggregation is used for high-end switches (like cat6500s and Cat4500s) which support many types of linecards/modules other than Ethernet while switch stacking only supports Ethernet interfaces -> Answer B is correct.
Question 18
Which option is the master redundancy scheme for stacked switches?
A. 1:N
B. N:1
C. 1:1
D. 1+N
E. N+1
Answer: A
Explanation
1:N master redundancy: Every switch in the stack can act as the master. If the current master fails, another master is elected from the stack.
1:N master redundancy allows each stack member to serve as a master, providing the highest reliability for forwarding. Each switch in the stack can serve as a master, creating a 1:N availability scheme for network control. In the unlikely event of a single unit failure, all other units continue to forward traffic and maintain operation.
Note:
N+1 simply means that there is a power backup in place should any single system component fail. The ‘N’ in this equation stands for the number of components necessary to run your system. The ‘+1’ means there is one independent backup should a component of that system fail. An example of “N+1” is your family has 5 members, so you need 5 cups to drink. But you have one extra cup for redundancy (6 cups in total) so that if any cup breaks, you still have enough cups for the family.
Question 19
Which three statements about QoS policing are true? (Choose three)
A. It can be applied to outbound traffic only.
B. It avoids queuing delays.
C. It drops excess packets.
D. It can be applied to inbound and outbound traffic.
E. It queues excess traffic.
F. It is configured in bits per second.
Answer: B C D
Explanation
Unlike traffic shaping, QoS policing avoids delays due to queuing.
QoS policing drops (or remarks) excess packets above the committed rates. Does not buffer.
QoS policing is configured in bytes (while QoS traffic shaping is configured in bits per second)
QoS policing can be applied to both inbound and outbound traffic (while QoS shaping can only be applied to outbound traffic)
Question 20
Which switch architecture is scalable, flexible, resilient, and relatively inexpensive?
A. aggregate switch
B. single switch
C. stacked switch
D. modular-chassis switch
Answer: C
Question 21
Which device might be installed at a branch office to enable and manage an IPsec site-to-site VPN?
A. Cisco IOS IPsec/SSL VPN client
B. Cisco VPN Client
C. ISDN terminal adapter
D. Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance
Answer: D
Explanation
An example of IPsec site-to-site VPN is your corporation has departments in many countries which need to communicate with each other. A popular solution is site-to-site (LAN-to-LAN) VPN to create private networks through the Internet. But as we know, Internet is not a safe environment for important data to be transferred. That is the reason why we need IPsec, a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol (IP) communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session.
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) supports IPsec, that’s all I can say! If you wish to learn more about the configuration, please read http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps5855/products_configuration_example09186a0080a9a7a3.shtml
Question 22
Which option is the main function of congestion management?
A. discarding excess traffic
B. queuing traffic based on priority
C. classifying traffic
D. providing long-term storage of buffered data
Answer: B
Question 23
Which IPv6 address is the all-router multicast group?
A. FF02::1
B. FF02::2
C. FF02::3
D. FF02::4
Answer: B
Explanation
A packet sent to an all-router multicast group is received and processed by all IPv6 routers on the link or network
Question 24
Which IPv6 routing protocol uses multicast group FF02::9 to send updates?
A. static
B. RIPng
C. OSPFv3
D. IS-IS for IPv6
Answer: B
Explanation
Some special IPv6 addresses:
FF02::5 – OSPFv3 All SPF routers
FF02::6 – OSPFv3 All DR routers
FF02::9 – All routing information protocol (RIP) routers on a link
FF02::A – EIGRP routers
Question 25
Drag and drop the BGP components from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
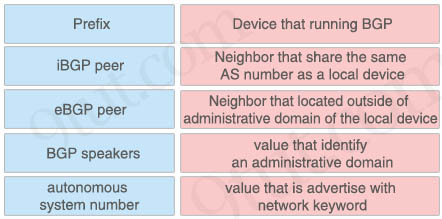
Answer:
+ Device that running BGP: BGP speakers
+ Neighbor that share the same AS number as a local device: iBGP peer
+ Neighbor that located outside of AD domain of the local device: eBGP peer
+ Value that identify an administrative domain: Autonomous system number
+ Value that is advertise with network keyword: Prefix
Question 26
Which two statements about switch stacking are true? (Choose two)
A. The stack is powered by a single power cable
B. The switches are connected in a daisy-chain fashion
C. The first and last switch in the stack must be connected to one another
D. The switches are connected by crossover cables
E. The switches must be fully meshed
Answer: B C
Question 27
Which name describes an IPv6 host-enabled tunneling technique that uses IPv4 UDP, does not require dedicated gateway tunnels, and can pass through existing IPv4 NAT gateways?
A. manual 6to4
B. dual stack
C. dynamic
D. Teredo
Answer: D
Question 28
Which two steps must you perform on each device that is configured for IPv4 routing before you implement OSPFv3? (Choose two)
A. configure an autonomous system number
B. configure a loopback interface
C. configure a router ID
D. enable IPv6 on an interface
E. enable IPv6 unicast routing
Answer: C E
Question 29
What is the alternative notation for the IPV6 address B514:82C3:0000:0000:0029:EC7A:0000:EC72?
A. B514:82C3:0029::EC7A:0000:EC72
B. B514:82C3:0029:EC7A:EC72
C. B514:82C3::0029:EC7A:0:EC72
D. B514:82C3::0029:EC7A:EC72
Answer: C
Question 30
Refer to the exhibit.
|
R1 interface FastEthernet0/0 ipv6 router ospf 1 |
R2 interface FastEthernet0/0 ipv6 router ospf 1 |
After you apply the give configurations to R1 and R2 you notice that OSPFv3 fails to start. Which reason for the problem is most likely true?
A. The area numbers on R1 and R2 are mismatched
B. The IPv6 network addresses on R1 and R2 are mismatched
C. The autonomous system numbers on R1 and R2 are mismatched
D. The router ids on R1 and R2 are mismatched
Answer: A
Question 31
Which two of these statements are true of IPv6 address representation? (Choose two)
A. There are four types of IPv6 addresses: unicast, multicast, anycast, and broadcast
B. A single interface may be assigned multiple IPv6 addresses of any type.
C. Every IPv6 interface contains at least one loopback address.
D. The first 64 bits represent the dynamically created interface ID.
E. Leading zeros in an IPv6 16 bit hexadecimal field are mandatory.
Answer: B C
Explanation
A single interface may be assigned multiple IPv6 addresses of any type (unicast, anycast, and multicast).
Every IPv6-enabled interface must contain at least one loopback (::1/128) and one link-local address. Optionally, an interface may have multiple unique local and global addresses.
Leading zeros in IPv6 are optional do that 05C7 equals 5C7 and 0000 equals 0 -> E is not correct.
Question 32
Which two statements describe characteristics of IPv6 unicast addressing? (Choose two)
A. Global addresses start with 2000::/3
B. Link-local addresses start with FE00:/12
C. Link-local addresses start with FF00::/10
D. There is only one loopback address and it is ::1
E. If a global address is assigned to an interface, then that is the only allowable address for the interface.
Answer: A D
Explanation
Below is the list of common kinds of IPv6 addresses:
| Loopback address | ::1 |
| Link-local address | FE80::/10 |
| Site-local address | FEC0::/10 |
| Global address | 2000::/3 |
| Multicast address | FF00::/8 |
From the above table, we learn that A and D are correct while B and C are incorrect. Notice that the IPv6 unicast loopback address is equivalent to the IPv4 loopback address, 127.0.0.1. The IPv6 loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, or ::1.
E is not correct because of anycast addresses which are indistinguishable from normal unicast addresses. You can think of anycast addresses like this: “send it to nearest one which have this address”. An anycast address can be assigned to many interfaces and the first interface receives the packet destined for this anycast address will proceed the packet. A benefit of anycast addressing is the capability to share load to multiple hosts. An example of this benefit is if you are a Television provider with multiple servers and you want your users to use the nearest server to them then you can use anycast addressing for your servers. When the user initiates a connection to the anycast address, the packet will be routed to the nearest server (the user does not have to specify which server they want to use).
Question 33
Which address is the IPv6 all-RIP-routers multicast group address that is used by RIPng as the destination address for RIP updates?
A. FF02::6
B. FF02::9
C. FF05::101
D. FF02::A
Answer: B
Question 34
Which value must you configure on a device before EIGRP for IPv6 can start running?
A. public IP address
B. loopback interface
C. router ID
D. process ID
Answer: C
Question 35
Which component of an IPv6 OSPFv3 connection must be configured in IPv4 format?
A. Router ID
B. Primary interface
C. Neighbor address
D. Secondary interface
Answer: A
Question 36
Which IPv6 address is the equivalent of the IPv4 interface loopback address 127.0.0.1?
A. ::1
B. ::
C. 2000::/3
D. 0::/10
Answer: A
Question 37
Which three are characteristics of an IPv6 anycast address? (Choose three)
A. one-to-many communication model
B. one-to-nearest communication model
C. any-to-many communication model
D. a unique IPv6 address for each device in the group
E. the same address for multiple devices in the group
F. delivery of packets to the group interface that is closest to the sending device
Answer: B E F
Question 38
You enter the show ipv6 route command on an OSPF device and the device displays a remote route. Which conclusion can you draw about the environment?
A. OSPF is distributing IPv6 routes to BGP.
B. The router is designated as an ABR.
C. The router is designated as totally stubby.
D. OSPFv3 is in use.
Answer: D
Question 39
Which command do you enter to permit IPv6 functionality on an EIGRPv3 interface?
A. Router1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
B. Router1(config-rf)#ipv6 router eigrp 1
C. Router1(config-if)#ipv6 enable
D. Router1(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 1
Answer: D
Question 40
What are three features of the IPv6 protocol? (Choose three)
A. complicated header
B. plug-and-play
C. no broadcasts
D. checksums
E. optional IPsec
F. autoconfiguration
Answer: B C F
Question 41
Which three checks must you perform when troubleshooting EIGRPv6 adjacencies? (Choose three)
A. Verify that IPv6 is enabled.
B. Verify that the network command has been configured.
C. Verify that auto summary is enabled.
D. Verify that the interface is up.
E. Verify that an IPv4 address has been configured.
F. Verify that the router ID has been configured.
Answer: A D F
Question 42
Which of these represents an IPv6 link-local address?
A. FE08::280e:611:a:f14f.3d69
B. FE81::280f.512b:e14f:3d69
C. FE80::380e:611a:e14f:3d69
D. FEFE:0345:5f1b::e14d:3d69
Answer: C
Explanation
The range of IPv6 link-local address (similar to the Windows auto-configuration IP address of 169.254.x.x.) is FE80::/10. For more information about IPv6, please read my IPv6 tutorial.
Question 43
Identify the four valid IPv6 addresses. (Choose four)
A. ::
B. ::192:168:0:1
C. 2000::
D. 2001:3452:4952:2837::
E. 2002:c0a8:101::42
F. 2003:dead:beef:4dad:23:46:bb:101
Answer: A B E F
Explanation
Answers B E F are correct because A and B are the short form of 0:0:0:0:192:168:0:1 and 2002:c0a8:0101:0:0:0:0:0042 while C are normal IPv6 address.
Answer A is correct because “::” is named the “unspecified” address and is typically used in the source field of a datagram that is sent by a device that seeks to have its IP address configured.
Answer C is not correct because a global-unicast IPv6 address is started with binary 001, denoted as 2000::/3 in IPv6 and it also known as an aggregatable global unicast address. The 2000:: (in particular, 2000::/3) is just a prefix and is not a valid IPv6 address.
In fact answer D is acceptable but it is considered the network portion of an IPv6 address so it is a worse choice than others.
The entire global-unicast IPv6 address range is from 2000::/128 to 3FFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/128, resulting in a total usable space of over 42,535,295,865,117,307,932,921,825,928,971,000,000 addresses, which is only 1/8th of the entire IPv6 address space!
Question 44
Which type of IPv6 ACL is applied first in the order of precedence?
A. TCAM
B. router ACLs
C. Fragmented frames
D. Port ACLs
Answer: D
Question 45
Which IPv6 address is valid?
A. 2031:0:130F::9C0:876A:130B
B. 2001:0DB8:0000:130F:0000:0000:08GC:140B
C. 2001:0DB8:0:130H::87C:140B
D. 2031::130F::9C0:876A:130B
Answer: A
Explanation
Answer B is not correct because it has a letter “G”.
Answer C is not correct because it has a letter “H”.
Answer D is not correct because it has two “::”.
Question 46
Which step must you perform first to enable OSPFv3 process 20 for IPv6?
A. Enter the ipv6 router ospf 20 command to enable OSPFv3.
B. Enter the ip routing command to enable IPv4 unicast routing.
C. Enter the router ospf 20 commands to enable OSPF.
D. Enter the ipv6 unicast-routing command to enable IPv6 unicast routing.
Answer: D
Question 47
Which two are features of IPv6? (Choose two)
A. multicast
B. broadcast
C. allcast
D. podcast
E. anycast
Answer: A E
Explanation
Anycast IPv6 addresses are 128-bit identifiers for interfaces and sets of interfaces. A packet sent to an anycast address is delivered to one of the interfaces identified by that address (the “nearest” one, according to the routing protocols’ measure of distance)
Question 48
Which BGP command do you enter to allow a device to exchange IPv6 prefixes with its neighbor?
A. neighbor ip-address activate
B. neighbor ip-address remote-as ASN
C. router bgp ASN
D. show ip bgp neighbors
Answer: A
Question 49
Which protocol can be used between administrative domains?
A. IS-IS
B. EIGRP
C. BGP
D. OSPF
Answer: C
Question 50
Which two statements about eBGP neighbor relationships are true? (Choose two)
A. The two devices must reside in different autonomous systems
B. Neighbors must be specifically declared in the configuration of each device
C. They can be created dynamically after the network statement is con-figured.
D. The two devices must reside in the same autonomous system
E. The two devices must have matching timer settings
Answer: A B
Question 51
What does it take for BGP to establish connection? (Choose two)
A. Enable CDP
B. AS number on local router
C. AS number on remote router
D. IGP
E. EGP
Answer: B C
Question 52
A security administrator wants to profile endpoints and gain visibility into attempted authentications. Which 802.1x mode allows these actions?
A. Monitor mode
B. High-Security mode
C. Low-impact mode
D. Closed mode
Answer: A
Explanation
There are three authentication and authorization modes for 802.1x:
+ Monitor mode
+ Low impact mode
+ High security mode
Monitor mode allows for the deployment of the authentication methods IEEE 802.1X without any effect to user or endpoint access to the network. Monitor mode is basically like placing a security camera at the door to monitor and record port access behavior.
With AAA RADIUS accounting enabled, you can log authentication attempts and gain visibility into who and what is connecting to your network with an audit trail. You can discover the following:
+ Which endpoints such as PCs, printers, cameras, and so on, are connecting to your network
+ Where these endpoints connected
+ Whether they are 802.1X capable or not
+ Whether they have valid credentials
+ In the event of failed MAB attempts, whether the endpoints have known, valid MAC addresses
Monitor mode is enabled using 802.1X with the open access and multiauth mode Cisco IOS Software features enabled, as follows:
sw(config-if)#authentication open
sw(config-if)#authentication host-mode multi-auth
For more information about each mode, please read this article: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Security/TrustSec_1-99/Phased_Deploy/Phased_Dep_Guide.html
Question 53
Refer to the exhibit.
| R1 interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.1.33 255.255.255.224 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 router bgp 100 neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 100 |
Which command do you enter so that R1 advertises the loopback0 interface to the BGP Peers?
A. Network 172.16.1.32 mask 255.255.255.224
B. Network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
C. Network 172.16.1.32 255.255.255.224
D. Network 172.16.1.33 mask 255.255.255.224
E. Network 172.16.1.32 mask 0.0.0.31
F. Network 172.16.1.32 0.0.0.31
Answer: A
Question 54
Drag and drop the DHCP snooping terms from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
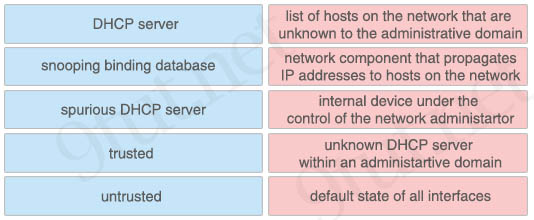
Answer:
+ DHCP server: network component that propagates IP addresses to hosts on the network
+ snooping binding database: list of hosts on the network that are unknown to the administrative domain
+ spurious DHCP server: unknown DHCP server within an administrative domain
+ trusted: internal device under the control of the network administrator
+ untrusted: default state of all interfaces
Question 55
Drag and drop the network programmability features from the left onto the correct description on the right.
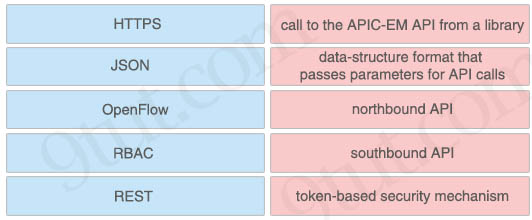
Answer:
+ HTTPS: call to the APIC-EM API from a library
+ JSON: data-structure format that passes parameters for API calls
+ OpenFlow: southbound API
+ RBAC: token-based security mechanism
+ REST: northbound API
Explanation
What is the data format used to send/receive data when making REST calls for APIC-EM?
Javascript Object Notation (JSON) is used to pass parameters when making API calls and is also the returned data format.
What’s RBAC?
The Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) mechanism utilizes security tokens that the controller issues upon successful authentication of a user of the APIC-EM controller. All subsequent requests from the authenticated user must provide a valid token.
Reference: https://communities.cisco.com/docs/DOC-60530#q16
Question 56
Drag drop about characteristics of a cloud environment.
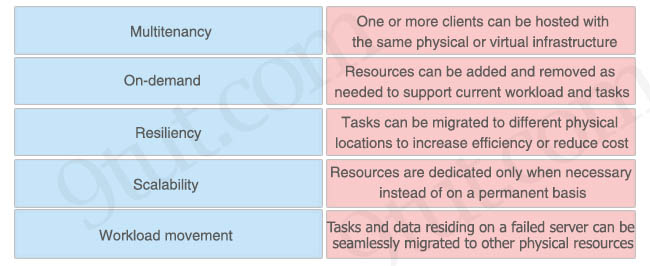
Answer:
+ Multitenancy: One or more clients can be hosted with the same physical or virtual infrastructure
+ Scalability: Resources can be added and removed as needed to support current workload and tasks
+ Workload movement: Tasks can be migrated to different physical locations to increase efficiency or reduce cost
+ On-demand: Resources are dedicated only when necessary instead of on a permanent basis
+ Resiliency: Tasks and data residing on a failed server can be seamlessly migrated to other physical resources
Question 57
Which two statements about exterior gateway routing protocols are true? (Choose two)
A. BGP is considered to be a path-vector protocol.
B. They can be used to connect to another AS across the Internet as a virtual instance.
C. eBGP is considered to be a distance-vector protocol.
D. EGP is considered to be a path-vector protocol.
E. They can be used to connect to the Internet
Answer: A E
Question 58
Drag and drop the BGP components from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.

Answer:
+ autonomous system number: Value that identifies an administrative domain
+ BGP Speaker: device that is running BGP
+ eBGP: Peer neighbor that located outside of administrative domain of the local device
+ BGP Peer: neighbor device that shares the same AS number as the local device
+ Prefix: value that is advertised with the network keyword
Question 59
Which routing protocol is most appropriate for sending and receiving routes directly to and from the Internet?
A. RIP
B. BGP
C. EIGRP
D. OSPF
Answer: B
Question 60
Drag and drop the descriptions of performing an initial device configuration from the left onto the correct features or components on the right.
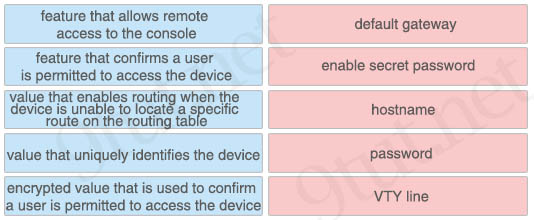
Answer:
+ feature that allows remote access to the console: VTY line
+ feature that confirms a user is permitted to access the device: password
+ value that enables routing when the device is unable to locate a specific route on the routing table: default gateway
+ value that uniquely identifies the device: hostname
+ encrypted value that is used to confirm a user is permitted to access the device: enable secret password


There’s no way I just paid for the membership to see you posted 11 questions. You have got to be kidding me. 9tut is becoming a major scam.
@Anonymous: We are still updating the questions when we have information about the questions. Please wait for some time.
ok, can you just tell for how much we must wait?
I know better answer is ‘we don’t know’, but could you just zoom in this? 24 horus, 1 week, 1 month?
A lot of people say, they changed everything, maybe it’s ICNDV4 now?
Now Cisco updates their questions frequently so we can only say that we will update this site as soon as we have new information about them.
@9tut: I understand. You can delete my comment please.
@9tut: Can you please upload more new questions in here especially the new drag and drops, I have my 2nd attempt tomorrow. Thanks
@GCP: The drag and drops are what screwed me. They are never easy for any test you take.
Just took the exam and passed. The simulators were the same but the drag and drop were not. I was in my own for most of the test. I got luck.
All I used was 9tut so it’s possible to pass with just this information..
I just passed ICND2 and seen a few questions from the composite quizzes, some from the new questions, and some that were not in the 9tut material. I used a combination of the Cisco Press book, 9tut, YouTube videos, and labs to study. I had the OSPF and EIGRP sims and the questions were the same concepts as seen here, but different questions. As others have said, do NOT memorize the answers, but instead make sure you understand the concepts behind the questions.
@up Next,CCNP could you please share the new question i am giving the exam this monday
understanding the concepts, gives you 50/50, shot , but you have to know your cli show commands, acls, bgp peering, , and sim on, PPP,MPPPP, PAP CHAP, failed test on nov,2 by less than 10 points, had i known more about BGP PEERING and WAN, i would have been fine, re_take in december,,
Is there still new questions for ICND2 or thats enough?
Just failed my test 767 same SIMs a few new questions new drag and drop. Six new drag and drop not one from 9tut OSPFv3, cloud computing, different north and south API and more. I still think 9tut is better than most.
i failed to, infrastructure question and bgp question are to much changed.
Hi,
when are new questions out?
thank
when you add new questions?
@9tut
When post new questions?
drag and drops …are a must…now bgp peering!! and how to configure, BGP AND ACL’s….failed by less by one question
Do you rembember what you had from ACL?
@s.ajdcvhsekjb
I have passed Today! They changed almost everything, you should learn from cisco press and dont Focus on 9tut a lot.
9 tut when post new question ?
failed, 9tut is horrible
9tut I failed today, come on update the latest exam. U haven’t updated in over a month
The exam had a boat load in next questions and only 10% was on this site
I have passed my icnd2 exam today but there alot of new questions on the exam.the questions that come out from here is not up to 5 questions
ify did u use dumps?
New questions?
@9tut : when are you going to release the new questions? Thanks.
Seems like @9tut is no longer bothered to post new questions. Sad
Passed my icnd2 exam today. Between 9tut, Press and common sense it helped me pass with a score of 823.
why is the answer to Q.53 A? why not D? Anyone?
Thanks 9tut for a great website!! Best $15 i spent in a long time
j22 which parts were most on exam from 1-7, and what of the simulations were they similar or very different?