ICND2v3 – New Questions Part 6
Premium Members: You can practice these questions with our quizzes first at:
+ Question 1 to 10
+ Question 11 to 26
+ Question 27 to 50
+ Question 51 to 70
+ Question 71 to 90
+ Question 91 to 100
Question 1
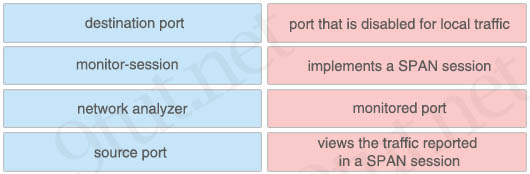
Drag and drop the SPAN terms from the left onto the correct description on the right.
Answer:
+ port that is disabled for local traffic: destination port
+ implements a SPAN session: monitor-session
+ monitored port: source port
+ views the traffic reported in a SPAN session: network analyzer
Question 2
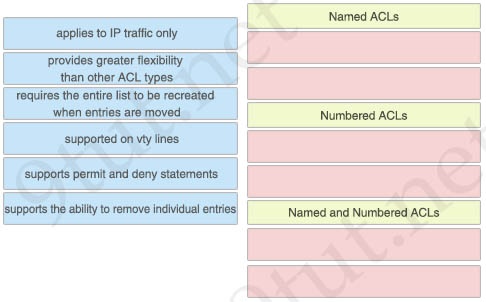
Drag and drop the descriptions of ACLs from the left onto the correct ACL types on the right.
Answer:
Named ACLs:
+ supports the ability to remove individual entries
+ provides greater flexibility than other ACL types
Numbered ACLs:
+ requires the entire list to be recreated when entries are moved
+ supported on vty lines
Named and Numbered ACLs:
+ supports permit and deny statements
+ applies to IP traffic only
Explanation
When you apply an access list to a vty (by using the access-class command), the access list must be a numbered access list, not a named access list.
With named ACL, we can easily remove an individual entry. For example:
R1# show access-list
Standard IP access list nat_traffic
10 permit 10.1.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255
20 permit 10.2.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255
30 permit 10.3.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255
Then to remove the second statement (the line “20 permit 10.2.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255”) we just need to type “no 20”:
R1(config)#ip access-list standard nat_traffic
R1(config-std-nacl)#no 20
Question 3
Drag and drop the terms associated with a hub-and-spoke topology from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.

Answer:
+ central router: hub
+ circuit that connects remote locations: WAN
+ network design that connects all remote sites to a central location: star
+ remote router: spoke
Question 4
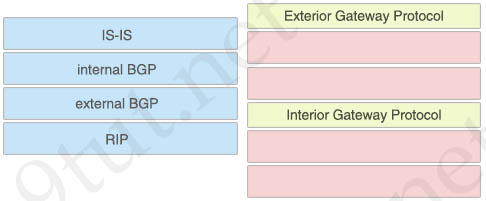
Drag and drop the routing protocols from the left onto the correct routing protocol types on the right.
Answer:
Exterior Gateway Protocol:
+ internal BGP
+ external BGP
Interior Gateway Protocol:
+ IS-IS
+ RIP
Question 5
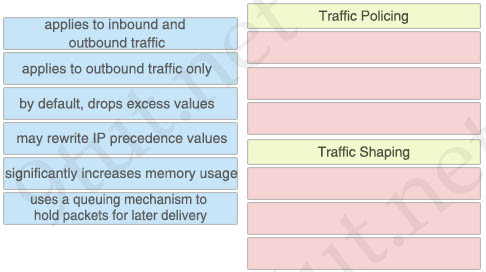
Drag and drop the descriptions of traffic shaping and policing from the left onto the correct categories on the right.
Answer:
Traffic Policing:
+ applies to inbound and outbound traffic
+ by default, drops excess values
+ may rewrite IP precedence values
Traffic Shaping:
+ applies to outbound traffic only
+ uses a queuing mechanism to hold packets for later delivery
+ significantly increases memory usage
Explanation
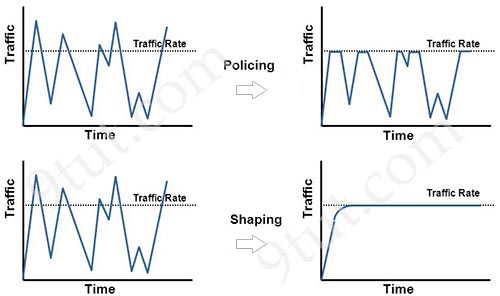
Traffic policing propagates bursts. When the traffic rate reaches the configured maximum rate, excess traffic is dropped (or remarked). The result is an output rate that appears as a saw-tooth with crests and troughs. In contrast to policing, traffic shaping retains excess packets in a queue and then schedules the excess for later transmission over increments of time. The result of traffic shaping is a smoothed packet output rate.
Shaping implies the existence of a queue and of sufficient memory to buffer delayed packets, while policing does not. Queueing is an outbound concept; packets going out an interface get queued and can be shaped. Only policing can be applied to inbound traffic on an interface.
With policing, the token bucket determines whether a packet exceeds or conforms to the applied rate. In either case, policing implements a configurable action, which includes setting the IP precedence or Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP).
Question 6
Two EIGRP routers have failed to establish a neighbor relationship. Drag and drop the configuration parameters from the left onto the categories on the right.
Answer:
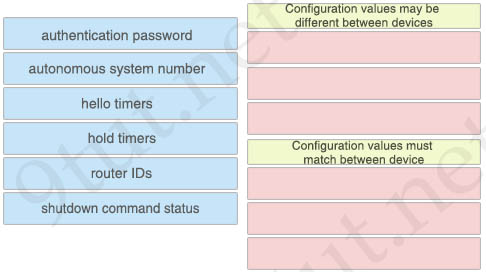
Configuration values may be different between devices:
+ hello timers
+ hold timers
+ router IDs
Configuration values must match between device:
+ authentication password
+ autonomous system number
+ shutdown command status
Question 7
Drag and drop the steps in the process of establishing an OSPFv3 neighbor relationship from the left onto the correct sequence on the right.
Answer:
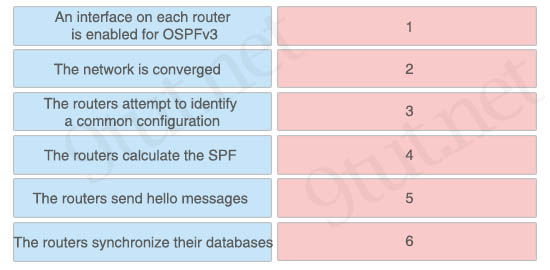
1: An interface on each router is enabled for OSPFv3
2: The routers send hello messages
3: The routers attempt to identify a common configuration
4: The routers calculate the SPF
5: The routers synchronize their databases
6: The network is converged
Explanation
An OSPFv3 router sends a special message, called a hello packet, out each OSPF-enabled interface to discover other OSPFv3 neighbor routers. Once a neighbor is discovered, the two routers compare information in the Hello packet to determine if the routers have compatible configurations. The neighbor routers attempt to establish adjacency, which means that the routers synchronize their link-state databases to ensure that they have identical OSPFv3 routing information. Adjacent routers share link-state advertisements (LSAs) that include information about the operational state of each link, the cost of the link, and any other neighbor information. The routers then flood these received LSAs out every OSPF-enabled interface so that all OSPFv3 routers eventually have identical link-state databases. When all OSPFv3 routers have identical link-state databases, the network is converged
Question 8
Drag and drop the EIGRP K values from the left onto the correct metric components on the right.
Answer:
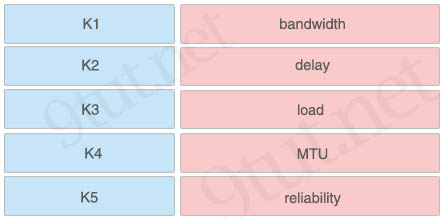
K1 – bandwidth
K2 – load
K3 – delay
K4 – Reliability
K5 – MTU
Question 9
You recently configured your enterprise network to use resources in a public cloud. Drag and drop the steps in the end-user process to access the cloud resources from the left onto the correct sequence on the right. Not all steps are used.
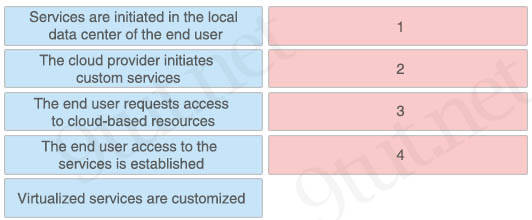
Answer:
1: The end user requests access to cloud-based resources
2: The cloud provider initiates custom services
3: Virtualized services are customized
4: The end user access to the services is established
Question 10
Drag and drop the descriptions if EtherChannel protocols from the left onto the correct protocols on the right.
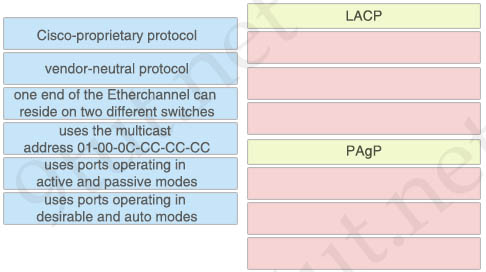
Answer:
LACP:
+ vendor-neutral protocol
+ one end of the Etherchannel can reside on two different switches
+ uses ports operating in active and passive modes
PAgP:
+ Cisco-proprietary protocol
+ uses the multicast address 01-00-0C-CC-CC-CC
+ uses ports operating in desirable and auto modes
Question 11
You are troubleshooting a variety of Layer 3 connectivity issues on your network. Drag and drop the issues from the left onto the location where you will start troubleshooting the issue on the right.
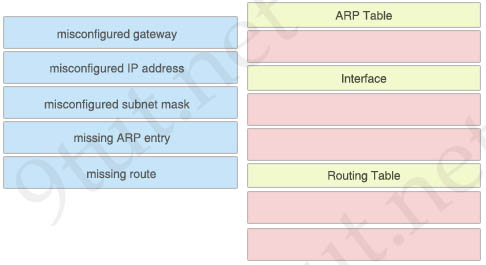
Answer:
ARP Table:
+ missing ARP entry
Interface:
+ misconfigured IP address
+ misconfigured subnet mask
Routing Table:
+ misconfigured gateway
+ missing route
Question 12
Drag and drop the BGP peering states from the left onto the correct statements on the right.
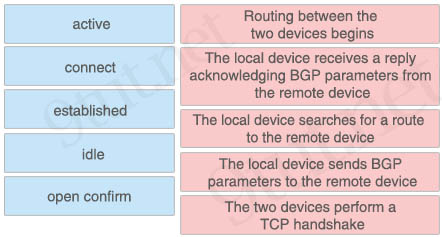
Answer:
+ Routing between the two devices begins: established
+ The local device receives a reply acknowledging BGP parameters from the remote device: open confirm
+ The local device searches for a route to the remote device: idle
+ The local device sends BGP parameters to the remote device: active
+ The two devices perform a TCP handshake: connect
Explanation
Below is the list of BGP states in order, from startup to peering:
1 – Idle: the initial state of a BGP connection. In this state, the BGP speaker is waiting for a BGP start event, generally either the establishment of a TCP connection or the re-establishment of a previous connection. Once the connection is established, BGP moves to the next state.
2 – Connect: In this state, BGP is waiting for the TCP connection to be formed. If the TCP connection completes, BGP will move to the OpenSent stage; if the connection cannot complete, BGP goes to Active
3 – Active: In the Active state, the BGP speaker is attempting to initiate a TCP session with the BGP speaker it wants to peer with. If this can be done, the BGP state goes to OpenSent state.
4 – OpenSent: the BGP speaker is waiting to receive an OPEN message from the remote BGP speaker
5 – OpenConfirm: Once the BGP speaker receives the OPEN message and no error is detected, the BGP speaker sends a KEEPALIVE message to the remote BGP speaker
6 – Established: All of the neighbor negotiations are complete. You will see a number, which tells us the number of prefixes the router has received from a neighbor or peer group.
Question 13
Drag and drop the components of an inter-switch connection from the left onto the correct descriptions in the right.
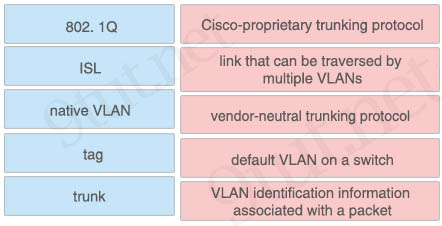
Answer:
+ Cisco-proprietary trunking protocol: ISL
+ link that can be traversed by multiple VLANs: trunk
+ vendor-neutral trunking protocol: 802. 1Q
+ default VLAN on a switch: native VLAN
+ VLAN identification information associated with a packet: tag
Question 14
Drag and drop the STP features from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
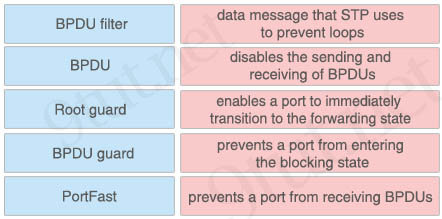
Answer:
+ data message that STP uses to prevent loops: BPDU
+ disables the sending and receiving of BPDUs: BPDU filter
+ enables a port to immediately transition to the forwarding state: PortFast
+ prevents a port from entering the blocking state: Root guard
+ prevents a port from receiving BPDUs: BPDU guard
Explanation
If a BPDU is received on a port where BPDU guard is configured, that port is put into errdisable state (nearly the same as shutdown state) immediately.
Root Guard ensures that the port on which root guard is enabled is the designated port. If the bridge receives superior BPDUs on a root guard-enabled port, root guard moves this port to a root-inconsistent STP state (which is equal to STP listening state). No traffic is forwarded across this port. In this way, the root guard enforces the position of the root bridge.
When BPDU filtering is enabled on a specific port, it prevents this port from sending or receiving BPDUs (so if BPDUs are seen, they will be dropped)
Question 15
Drag and drop the cloud-based resources from the left onto the correct definitions on the right.
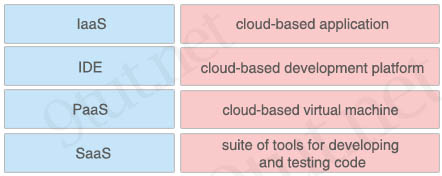
Answer:
cloud-based application: SaaS
cloud-based development platform: PaaS
cloud-based virtual machine: IaaS
suite of tools for developing and testing code: IDE
Explanation
Below are the 3 cloud supporting services cloud providers provide to customer:
+ SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS uses the web to deliver applications that are managed by a third-party vendor and whose interface is accessed on the clients’ side. Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations required, although some require plugins.
+ PaaS (Platform as a Service): are used for applications, and other development, while providing cloud components to software. What developers gain with PaaS is a framework they can build upon to develop or customize applications. PaaS makes the development, testing, and deployment of applications quick, simple, and cost-effective. With this technology, enterprise operations, or a third-party provider, can manage OSes, virtualization, servers, storage, networking, and the PaaS software itself. Developers, however, manage the applications.
+ IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): self-service models for accessing, monitoring, and managing remote datacenter infrastructures, such as compute (virtualized or bare metal), storage, networking, and networking services (e.g. firewalls). Instead of having to purchase hardware outright, users can purchase IaaS based on consumption, similar to electricity or other utility billing.
Reference: https://apprenda.com/library/paas/iaas-paas-saas-explained-compared/
Question 16
Drag and drop the features of an Ethernet interface from the left onto the correct statements on the right.
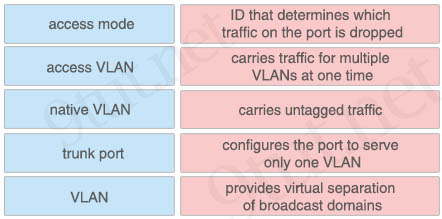
Answer:
ID that determines which traffic on the port is dropped: access VLAN
carries traffic for multiple VLANs at one time: trunk port
carries untagged traffic: native VLAN
configures the port to serve only one VLAN: access mode
provides virtual separation of broadcast domains: VLAN
Question 17
Drag and drop the descriptions of AAA device-security protocols from the left onto the correct protocols on the right.
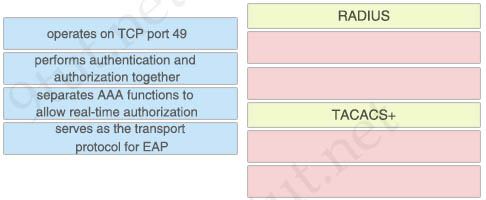
Answer:
RADIUS:
+ performs authentication and authorization together
+ serves as the transport protocol for EAP
TACACS+:
+ operates on TCP port 49
+ separates AAA functions to allow real-time authorization
Explanation
The comparison of two protocols is listed below:
| RADIUS | TACACS+ | |
| Transportation & Ports |
UDP port 1812/1645 (Authentication) 1813/1646 (Accounting) |
TCP port 49 |
| Encryption | only passwords | entire payload of each packet (leaving only the TACACS+ header in cleartext) |
| Standards | Open standard | Cisco proprietary (but actually now it is an open standard defined by RFC1492) |
| Operation | Authentication and authorization are combined in one function | authentication, authorization and accounting are separated |
| Logging | No command logging | Full command logging (commands typed by users can be recorded on the servers) |
Note: In fact both RADIUS and TACACS+ support Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP), which is an authentication framework frequently used in wireless networks and point-to-point connections
Question 18
Which two steps must occur before two routers can become BGP peers? (Choose two)
A. The routers must establish a TCP connection to one another
B. The routers must exchange BGP version information
C. The routers must receive multicast hello packets from one another
D. The routers must receive more than one BGP routing update from one another
E. Each router must reset its BGP timers to their default settings
Answer: A B
Explanation
In order to become BGP peers, the two routers must establish a TCP connection (via a three-way TCP handshake) in the “Connect” state.
In the OpenSent state, an Open message has been sent from the originating router and is awaiting an Open message from the other router. After the originating router receives the OPEN message from the other router, both OPEN messages are checked for errors. The following items are being compared:
+ BGP Versions must match.
+ The source IP address of the OPEN message must match the IP address that is configured for the neighbor.
+ The AS number in the OPEN message must match what is configured for the neighbor.
+ BGP Identifiers (RID) must be unique. If a RID does not exist, this condition is not met.
+ Security Parameters (Password, TTL, and the like).
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2756480&seqNum=4
Question 19
Which two actions must you take to configure a static EtherChannel between two switches, S1 and S2? (Choose two)
A. Configure the channel-group 1 mode auto command on S2
B. Configure the channel-group 1 mode active command on S2
C. Configure the channel-group 1 mode on command on S1
D. Configure the channel-group 1 mode active command on S1
E. Configure the channel-group 1 mode on command on S2
F. Configure the channel-group 1 mode auto command on S1
Answer: C E
Explanation
To configure a static EtherChannel (not LACP or PAgP mode), the only way we can configure is to configure mode “on” on both ends.
Question 20
Which QoS prioritization method is most appropriate for interactive voice and video?
A. policing
B. low-latency queuing
C. round-robin scheduling
D. expedited forwarding
Answer: D
Explanation
There are three standard service classes defined for DiffServ: the default Best-Effort (BE), Expedited Forwarding (EF) and Assured Forwarding (AF).
EF minimizes delay, jitter and loss, hence making it suitable for real-time services e.g. interactive voice, video etc.
Reference: Next Generation Mobile Networks and Ubiquitous Computing Book
Note: Interactive Video has the same service level requirements as VoIP because a voice call is embedded within the video stream.
Question 21
Which port type is used in a stacked deployment?
A. StackWise ports
B. uplinks
C. Ethernet ports
D. console ports
Answer: A
Explanation
A stack port is a port on the switch that is used to communicate with other switches in the stack. Depending on the model, a switch can have either preconfigured or user-defined stack ports.
Question 22
What is the effect of the switchport access vlan 300 command?
A. It configures the interface to perform Layer 2 switching
B. It displays the VLAN configuration of the interface
C. It configures the interface as an access port
D. It assigns the interface to a VLAN
Answer: D
Explanation
The example below configures a port on a switch to access mode and assign VLAN 300 to it:
Switch(config)#interface fa0/1
Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access
Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 300
Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
Question 23
Which two statements about access ports are true? (Choose two)
A. VLANs must be in the VLAN database before they can be assigned to an access port
B. They are configured with 802.1Q encapsulation
C. A device must have at least one access port configured for each trunk port
D. They are assigned to VLAN 1 by default
E. They record all MAC addresses they receive
Answer: A D
Explanation
Answer A is correct but in practical we can assign an access port to a non-existent VLAN because the switch will create it automatically before assign this access port to this VLAN.
By default all access ports belong to VLAN 1. If we want to assign a new VLAN, we have to use the command “switchport access vlan <vlan-id>” under interface mode.
Question 24
Which programming language do you use to script interactions between Cisco devices and network controllers such as APIC-EM?
A. POSIX
B. Python
C. Java
D. C++
Answer: B
Question 25
Which two functions are performed by DHCP snooping? (Choose two)
A. It determines which DHCP messages are valid
B. It hands out DHCP IP addresses to clients requesting access to the network
C. It rate-limits certain traffic
D. It listens to multicast traffic to support packet forwarding
E. It propagates VLAN information between switches
F. It provides DDoS mitigation
Answer: A C
Explanation
DHCP snooping is a security feature that acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and trusted DHCP servers. The DHCP snooping feature performs the following activities:
+ Validates DHCP messages received from untrusted sources and filters out invalid messages.
+ Rate-limits DHCP traffic from trusted and untrusted sources.
+ Builds and maintains the DHCP snooping binding database, which contains information about untrusted hosts with leased IP addresses.
+ Utilizes the DHCP snooping binding database to validate subsequent requests from untrusted hosts.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/Test/dwerblo/broken_guide/snoodhcp.html
Question 26
For which two reasons do you implement a PAgP EtherChannel? (Choose two)
A. to dynamically assign VLANs to a trunk port
B. to increase bandwidth
C. to provide redundancy
D. to exchange VLAN information
E. to dynamically determine whether a port is an access port or trunk port
Answer: B C
Question 27
Which three components must you configure to establish a GRE tunnel? (Choose three)
A. BGP autonomous system number
B. authentication mode
C. tunnel destination IP address
D. IGP type at each site
E. tunnel source IP address
F. logical tunnel interface
Answer: C E F
Explanation
The below example shows how to configure a GRE tunnel at one end:
| R1 interface tunnel0 ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.252 tunnel mode gre ip //this command can be ignored tunnel source 192.168.13.1 tunnel destination 192.168.23.2 |
Question 28
Which two statements about CHAP authentication are true? (Choose two)
A. The called router sends a challenge packet to the calling router
B. It is by definition a one-way authentication method
C. PPP authentication is performed after the CHAP process is complete
D. CHAP authentication can only be used in one direction
E. By default, the calling router authenticates the called router
F. It is by definition a two-way authentication method
Answer: A B
Explanation
CHAP is defined as a one-way authentication method. However, you use CHAP in both directions to create a two-way authentication. Hence, with two-way CHAP, a separate three-way handshake is initiated by each side.
In the Cisco CHAP implementation, by default, the called party must authenticate the calling party (unless authentication is completely turned off) (-> answer B is correct while answer F is not correct). Therefore, a one-way authentication initiated by the called party is the minimum possible authentication. However, the calling party can also verify the identity of the called party, and this results in a two-way authentication ( -> answer D is not correct). Hence, with two-way CHAP, a separate three-way handshake is initiated by each side.
With CHAP, the protocol begins with a random text (called a challenge) sent from the Server, which asks the Client to authenticate. After receiving the challenge, the Client uses its password to perform a one-way hash algorithm (MD5) to encrypt the random text received from the server. The result is then sent back to the Server. Therefore even if someone can capture the messages between client and server, he cannot know what the password is. At the Server side, the same algorithm is used to generate its own result. If the two results match, the passwords must match too.
Question 29
Which type of routing protocol uses the Bellman-Ford algorithm?
A. path-vector
B. link-state
C. distance-vector
D. hybrid routing
Answer: C
Explanation
Distance Vector routing protocols use the Bellman-Ford algorithm for exchanging routing information.
Question 30
Which technology supports fast provisioning for cloud resources?
A. static routing
B. IPS
C. DHCP
D. HSRP
Answer: C
Question 31
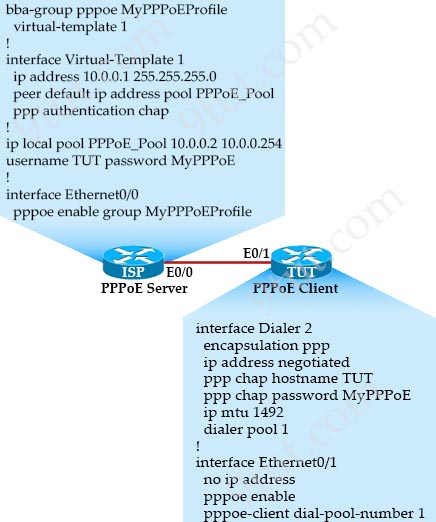
Which two statements about the PPPoE client physical interface configuration are true? (Choose two)
A. It must be physically connected to an ATM switch
B. It must be linked to a dialer interface
C. It must be in shutdown mode while the PPPoE configuration is enabled
D. It must be configured without an IP address
E. It must be configured as a trunk port
Answer: B D
Explanation
The picture below shows all configuration needed for PPPoE. Notice that under PPPoE client physical interface Ethernet0/1 there is no IP address configured and it is linked to the Dialer pool 1 (with the dialer pool 1 command.)
Question 32
Which result occurs when you configure the standby preempt command on an HSRP router that has the same priority as the active router and a higher IP
address?
A. The router becomes the active router only when the current active router fails
B. The router fails to become the active router under any circumstances
C. The router immediately becomes the active router because it has the highest configured IP address
D. The router becomes the active router only when another router triggers renegotiation of the active router
Answer: A
Explanation
In earlier versions, a standby router with the same priority and higher IP address than the active HSRP router will immediately become the active router. But with newer IOS versions, the standby router only becomes the active router only when the current active router fails.
Also in an expired Cisco document, it also said “A standby router with equal priority but a higher IP address will not preempt the active router”
Question 33
Which two values can HSRP use to determine the device with the highest priority? (Choose two)
A. highest configured IP address
B. lowest root bridge ID
C. lowest port ID
D. highest configured priority value
E. highest interface MA C address
Answer: A D
Question 34
Which two features are compatible with SPAN sessions? (Choose two)
A. using private VLANs to identify SPAN destination ports
B. source ports configured as routed ports
C. port security
D. using active port channels as source ports
E. destination ports configured as trunk ports
Answer: D E
Question 35
Which two characteristics of eBGP peers are true? (Choose two)
A. They must be directly connected
B. They must reside in different IP subnets
C. They must reside in the same autonomous system
D. They must reside in the same IP subnet
E. They must reside in two different autonomous systems
Answer: A E
Explanation
eBGP (external BGP) requires two peers must belong to two different AS while iBGP (internal BGP) requires two peers must belong to the same AS.
Unlike iBGP, iBGP requires two peers must be directly connected but they can still use their loopback interfaces for the connection
Question 36
Which feature would prevent a workstation from receiving a DHCP address?
A. STP
B. 802.1Q
C. VTP
D. DTP
Answer: A
Explanation
When a host is connected to a switchport, we have to wait about 50 seconds in order to STP to turn on the port. In this time DHCP cannot assign an IP address for the host. If we want STP to transit to forwarding state immediately we need to issue the “switchport portfast” command.
Question 37
What is the effect of the switchport voice vlan 20 command?
A. It assigns the interface to a voice VLAN
B. It displays the voice VLAN configuration of the interface
C. It configures priority tagging for voice traffic on VLAN 20
D. It configures the interface as an access port
Answer: A
Question 38
Refer to the output. Applying this configuration will result in which outcome?
username CISCO secret Str0ng50690847! aaa authentication login default group tacacs+ group radius local-case aaa authorization exec login default group tacacs+ aaa authorization network login default group tacacs+ aaa accounting exec default start-stop group tacacs+ aaa accounting exec network start-stop group tacacs+ tacacs server Server1 address ipv4 192.168.10.1 key TACACSserver radius server Server2 address ipv4 192.168.20.1 key RADIUSserver
A. Command starting with aaa are rejected because the aaa new-model command is missing
B. The user is authenticated against the configured RADIUS server
C. The user is authenticated against the local database
D. When the enable secret password is entered the user will gain access to the device
Answer: A
Question 39
Which two protocols can support trunking? (Choose two)
A. LACP
B. 802.1Q
C. ISL
D. VTP
E. PAgP
Answer: B C
Explanation
Cisco switches support two trunking protocols 802.1q & ISL. 802.1q is an open standard and is thus compatible between most vendors’ equipment while Inter-Switch Link (ISL) is Cisco proprietary.
Question 40
Which two values can a standard IPv6 ACL use to identify traffic? (Choose two)
A. UDP header
B. TCP header
C. source IPv6 address
D. DSCP value for QoS
E. destination IPv6 address
Answer: C E
Explanation
IPv6 supports only extended ACLs so we always have to specify both the source and destination IPv6 addresses. An example of a standard IPv6 ACL is shown below:
ipv6 access-list Deny_Subnet
deny ipv6 2001:DB8:0:12::/64 any
permit ipv6 any any
Question 41
Which QoS feature can change the value of the IPv4 Type of Service and the IPv6 Traffic Class header fields?
A. shaping
B. marking
C. prioritization
D. policing
Answer: B
Explanation
The IPv6 Traffic Class header field is equivalent to the IPv4 Type of Service field.
Traffic marking allows you to mark (that is, set or change) a value (attribute) for the traffic belonging to a specific class. Attributes that can be set and modified include the DSCP value in the type of service (ToS) byte.
Note: Traffic policing is used to control the rate of traffic flowing across an interface. Traffic shaping retains excess packets in a queue and then schedules the excess for later transmission over increments of time.
Question 42
On which port type is the spanning-tree portfast command supported without additional configuration?
A. access ports
B. Layer 3 subinterfaces
C. Layer 3 main interfaces
D. trunk ports
Answer: A
Explanation
The “spanning-tree portfast” command has no effect on trunk ports (we have to use “spanning-tree portfast trunk” command instead). It is only effective on access ports. This command cannot be used on a Layer 3 interface.
Question 43
How does an IP SLA ICMP Echo operation measure response time?
A. It checks the timestamp on source and destination ICMP Time Exceeded messages
B. It checks the timestamp on ICMP Echo messages
C. It calculates the time that elapses from when the device sends an ICMP Echo request to when it receives an ICMP Echo reply
D. It checks the one-way delay of each ICMP Echo packet received
Answer: B
Explanation
In ICMP operations, the source IP SLA device sends several ICMP packets to the destination. The destination device, which is any IP device, echoes with replies. The source IP SLA device uses the sent and received time stamps to calculate the response time.
Question 44
Refer to the exhibit. All three PCs on the network are in different VLANs. If you want to permit PC A to communicate with PC C, but prevent communications from PC B to PC C, where on this network do you place a standard ACL?
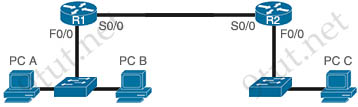
A. on interface S0/0 on R2
B. on interface F0/0 on R1
C. on interface F0/0 on R2
D. on interface S0/0 on R1
Answer: A
Explanation
Standard Access Control List (ACL) filters the traffic based on source IP address. Therefore a standard ACL should be placed on the router which is near to the destination network/host where it is denied. If we place the standard ACL near to source of the traffic, there is a chance for denial or other legitimate traffic from the source network to some other network.
Therefore in this case we should place the ACL on R2 which near the destination PC C. We should place on S0/0 interface as the traffic should be checked first before making any routing decision to save R2’s resource.
Another reason we should not place the ACL on R1 is PC A and PC B belong to different VLANs so we may have subinterfaces on Fa0/0 of R1. As the result of this, we have to apply ACL to two subinterfaces and it is not effective. Please notice that ACL applied to the main interface does not affect the traffic of subinterfaces.
Question 45
When you configure a new switch interface, to which VLAN it is automatically assigned?
A. VLAN with the lowest ID
B. default VLAN
C. management VLAN
D. native VLAN
Answer: B
Explanation
If we configure an access port as follows:
| Switch(config)#interface fa0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access |
Then this interface, by default, will belong to VLAN 1 (the default VLAN). Of course we can assign another VLAN to this port via the “switchport access vlan {vlan-number}” command.
Question 46
Which two functions of the APIC-EM Path Trace ACL Analysis tool are true? (Choose two)
A. It can identify the path between two specified IP addresses
B. It can determine whether traffic along a specific path will be filtered
C. It can manage access lists in an SDN environment
D. It can create and modify access lists in a private cloud infrastructure
E. It applies the ACLs from a specified path to permit and deny incoming traffic
Answer: A B
Explanation
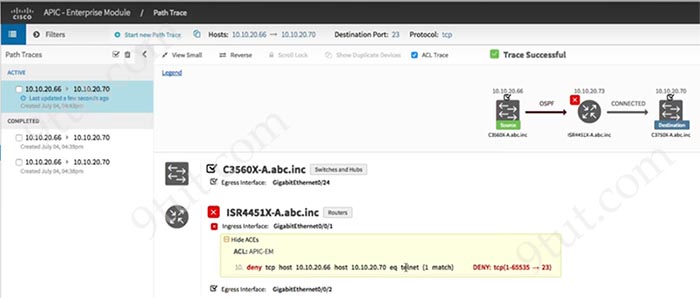
In the APIC-EM Path Trace ACL Analysis tool, we can identify the path between the source and destination IP addresses.
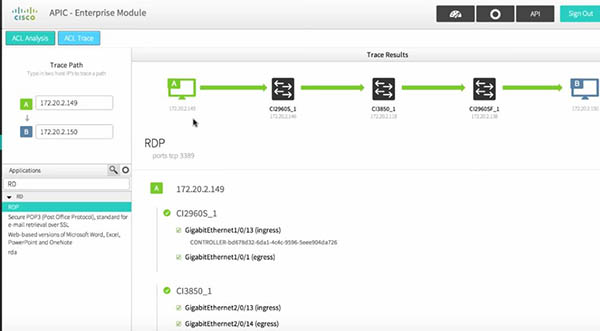
The APIC-EM Path Trace ACL Analysis Tool can display the ACLs that are using (by downloading the configurations after a specific period of time and shows them when we do a path trace). Therefore it helps verify the ACLs more easily.
Question 47
Which two statements about the BGP network command are true? (Choose two)
A. It must be configured to enable BGP between neighbors
B. It references a connected interface
C. It must match the subnet and mask of a route in the routing table
D. It references the routing table
E. It can specify a different subnet mask than the mask configured on the interface
Answer: C D
Explanation
For example we have the following topology and config in R1:

| R1(config)#interface fastethernet0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 11.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown |
With BGP, we must advertise the correct network and subnet mask in the “network” command. (in this case network 11.0.0.0/24). BGP is very strict in the routing advertisements. In other words, BGP only advertises the network which exists exactly in the routing table (in this case network 11.0.0.0/24 exists in the routing table). If you put the command “network 11.0.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0” or “network 11.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0” or “network 11.0.0.1 mask 255.255.255.255” then BGP will not advertise anything.
Question 48
Which networking function occurs on the data plane?
A. forwarding remote client/server traffic
B. sending and receiving OSPF Hello packets
C. spanning-tree election
D. processing inbound SSH management traffic
Answer: A
Explanation
The control plane: The control plane is the brain of the router. It consists of dynamic IP routing protocols (that is OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, and so on), the RIB, routing updates, in addition to other protocols such as PIM, IGMP, ICMP, ARP, BFD, LACP, and so on. In short, the control plane is responsible for maintaining sessions and exchanging protocol information with other router or network devices.
The data plane: The data plane is the forwarding plane, which is responsible for the switching of packets through the router (that is, process switching and CEF switching). In the data plane, there could be features that could affect packet forwarding such as quality of service (QoS) and access control lists (ACLs).
Question 49
What is the maximum bandwidth of a T1 point-to-point connection?
A. 1.544 Mbps
B. 2.048 Mbps
C. 34.368 Mbps
D. 43.7 Mbps
Answer: A
Question 50
According to Cisco best practices, which two tasks must you perform to support a voice VLAN? (Choose two)
A. Disable PortFast on the switch
B. Configure the voice VLAN on a private VLAN port
C. Modify the default QoS settings of the port
D. Enable the voice VLAN on the switch
E. Configure the voice VLAN on a normal-range VLAN
Answer: C D
Explanation
Before you enable voice VLAN, we recommend that you enable QoS on the switch by entering the mls qos global configuration command and configure the port trust state to trust by entering the mls qos trust cos interface configuration command -> By default, QoS is disabled on the switch and all ports are untrusted. These command modifies the default QoS settings.
The Port Fast feature is automatically enabled when voice VLAN is configured. When you disable voice VLAN, the Port Fast feature is not automatically disabled.
Question 51
Which result occurs when you configure the switchport mode dynamic auto command on the switch ports at both ends of a trunk link?
A. The trunk forms immediately because both switch ports are configured for permanent trunking mode
B. Either switch port can initiate the trunk
C. Both switch ports actively form the trunk
D. The trunk fails to form because both switch ports fail to initiate trunking
Answer: D
Explanation
switchport mode dynamic auto makes the interface able to convert the link to a trunk link. The interface becomes a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk or desirable mode. The default switchport mode for newer Cisco switch Ethernet interfaces is dynamic auto. Note that if two Cisco switches are left to the common default setting of auto, a trunk will never form.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2181837&seqNum=8
Note: We just need to remember that in “dynamic auto” mode, the interface does not try to negotiate a trunk. In “trunk”, “dynamic desirable” modes, the interface try to negotiates a trunk link.
Question 52
To which two categories of routing protocols does BGP belong? (Choose two)
A. link-state
B. distance-vector
C. path-vector
D. composite
E. exterior
Answer: C E
Explanation
BGP is an example of an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) which exchanges routing information between different autonomous systems.
BGP is a path vector protocol. Path vector protocol does not rely on the bandwidth of the links (like OSPF) or hop count (like RIP) or a group of parameters (like EIGRP). Path vector protocol relies on the number of autonomous systems it has to go through. In other words, it choose the path with least number of autonomous systems (shortest AS Path) to reach the destination, provided that the path is loop-free.
Question 53
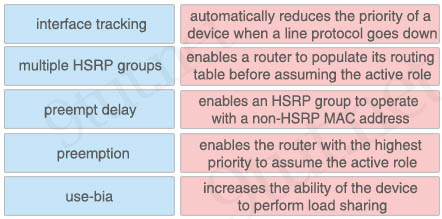
Drag and drop the HSRP feature from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Answer:
+ automatically reduces the priority of a device when a line protocol goes down: interface tracking
+ enables a router to populate its routing table before assuming the active role: preempt delay
+ enables an HSRP group to operate with a non-HSRP MAC address: use-bia
+ enables the router with the highest priority to assume the active role: preemption
+ increases the ability of the device to perform load sharing: multiple HSRP groups
Question 54
Which purpose of the network command in the BGP configuration of a router is true?
A. It advertises a valid network as local to the autonomous system of a router
B. It enables router advertisement in the BGP routing process on the router
C. It indicates whether a neighbor supports route refresh
D. It advertisers any route in BGP with no additional configuration
Answer: B
Question 55
Refer to the exhibit.
| #show ip eigrp events Ignored route, dup router: 2.2.2.2 |
Which problem is indicated by this error?
A. Two or more networks have been defined in the OSPF process
B. The same EIGRP process has already been defined on another router
C. Two or more devices on the network have the same router ID
D. Two or more interfaces have been assigned to the same network
Answer: C
Explanation
In Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(2) and later, Cisco records the duplicate router IDs in the EIGRP events log, which you can view with the show ip eigrp events command.
Question 56
In which configuration can a PPPoE client operate normally?
A. on a dialer interface configured with multilink PPP
B. on a CPE with more than 10 other clients
C. on an Ethernet connection between two endpoints
D. on a dialer interface configured for QoS queuing
Answer: A
Explanation
The following is an example of configuring Multilink PPP over a dialer interface link:
| Router(config)# interface dialer 1 Router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.100.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)# encapsulation ppp Router(config-if)# dialer pool 3 Router(config-if)# service-policy output policy1 Router(config-if)# service-policy input policy1 Router(config-if)# ppp authentication chap Router(config-if)# ppp chap hostname ISPCorp Router(config-if)# ppp chap password 7 Router(config-if)# ppp multilink Router(config-if)# ppp multilink fragment delay 20 Router(config-if)# ppp multilink interleave |
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios-xml/ios/qos_latjit/configuration/15-2mt/qos-mlppp-dl.html
According to this link: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/bbdsl/configuration/xe-3s/bba-pppoe-client.html
The PPPoE client does not support the following:
+ More than ten clients per customer premises equipment (CPE)-> This means a CPE can support up to 10 clients so answer B is not correct.
+ Coexistence of the PPPoE client and server on the same device
+ Quality of service (QoS) transmission with queueing on the dialer interface -> answer D is not correct
Answer C is a bit funny as PPPoE cannot operate on a connection. It can only operate on a host/device/router.
Question 57
Which two outcomes are effects of configuring the snmp-server host 10.1.1.1 traps version 3 auth md5 cisco command on router R1? (Choose two)
A. It configures R1 to accept SNMP traffic from the device at 10.1.1.1
B. It configures R1 to send SNMP traps to the device at 10.1.1.1
C. It sets the username cisco on the device at 10.1.1.1
D. It sets the R1 password to cisco
E. It configures R1 to send SNMP informs to the device at 10.1.1.1
Answer: B D
Explanation
In fact, the above command is not correct as we tested it with IOSv15.4:

The correct command should be ” snmp-server host 10.1.1.1 traps version 3 auth cisco”
The syntax of above command is shown below:
snmp-server host host-addr [informs | traps] [version {1 | 2c | 3 {auth | noauth | priv}}] community-string [udp–port port]
This command specify the recipient of an SNMP trap operation.
+ For host-addr, specify the name or Internet address of the host (the targeted recipient).
+ (Optional) Enter informs to send SNMP informs to the host.
+ (Optional) Enter traps (the default) to send SNMP traps to the host.
+ (Optional) Specify the SNMP version (1, 2c, or 3). Default is version 1. SNMPv1 does not support informs.
+ (Optional) For Version 3, select authentication level auth, noauth, or priv.
Note: The priv keyword is available only when the cryptographic software image is installed.
+ For community-string, when version 1 or version 2c is specified, enter the password-like community string sent with the notification operation. When version 3 is specified, enter the SNMPv3 username.
+ (Optional) For port, specify the UDP port of the notification host. Default is port 162.
Therefore with the above command, “md5” is in fact the SNMPv3 username:

Question 58
Which value is considered first when a stack elects the stack master switch for all stack members powered on within the 20 sec time frame?
A. priority of each switch
B. software feature set of each switch
C. startup time of each switch
D. MAC address of each switch
Answer: A
Explanation
Master Election
The stack master is elected based on one of these factors in the order listed:
1. The switch that is currently the stack master.
2. The switch with the highest stack member priority value.
3. The switch that has the configuration file.
4. The switch with the highest uptime.
5. The switch with the lowest MAC address.
If this is the first time this stack elects a master then it will elect the switch with the highest priority to be the master.
Question 59
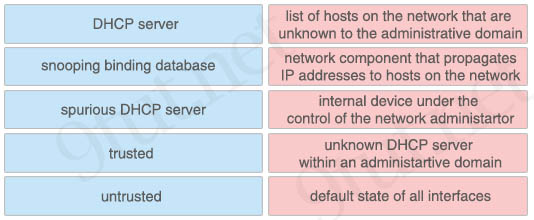
Drag and drop the DHCP snooping terms from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Answer:
+ DHCP server: network component that propagates IP addresses to hosts on the network
+ snooping binding database: list of hosts on the network that are unknown to the administrative domain
+ spurious DHCP server: unknown DHCP server within an administrative domain
+ trusted: internal device under the control of the network administrator
+ untrusted: default state of all interfaces
Question 60
Drag and drop the SDN components from the left onto the correct API types on the right.
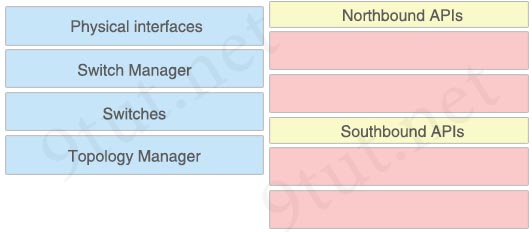
Answer:
Northbound APIs:
+ Switch Manager
+ Topology Manager
Southbound APIs:
+ Physical interfaces
+ Switches
Question 61
Drag and drop the networking features or functions from the left onto the planes on which they operate on the right.
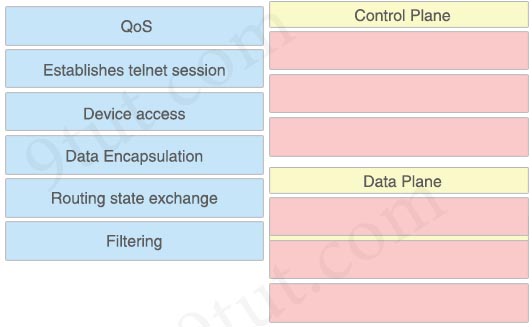
Answer:
Control Plane:
3. Routing state exchange
4. Establishes telnet session
5. Device access
Data Plane:
1. QoS
2. Filtering
6. Data Encapsulation
Explanation
The control plane: The control plane is the brain of the router. It consists of dynamic IP routing protocols (that is OSPF, IS-IS, BGP, and so on), the RIB, routing updates, in addition to other protocols such as PIM, IGMP, ICMP, ARP, BFD, LACP, and so on. In short, the control plane is responsible for maintaining sessions and exchanging protocol information with other router or network devices.
The data plane: The data plane is the forwarding plane, which is responsible for the switching of packets through the router (that is, process switching and CEF switching). In the data plane, there could be features that could affect packet forwarding such as quality of service (QoS) and access control lists (ACLs).
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2272154&seqNum=3
Question 62
Drag and drop about QoS.
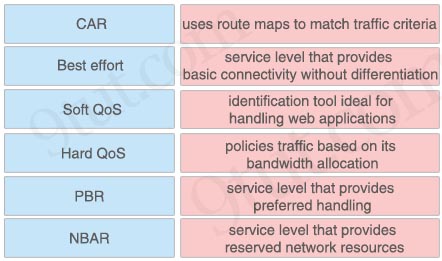
Answer:
+ CAR: policies traffic based on its bandwidth allocation
+ Best effort: service level that provides basic connectivity without differentiation
+ Soft QoS: service level that provides preferred handling
+ Hard QoS: service level that provides reserved network resources
+ PBR: uses route maps to match traffic criteria
+ NBAR: identification tool ideal for handling web applications
Note:
+ Committed Access Rate (CAR)
+ Network-based application recognition (NBAR)
+ Policy-based routing (PBR)
+ Soft QoS: also known as Differentiated Services (Diffserv), which ensures resources for applications based on available bandwidth
+ Hard QoS: Differentiated Service (DiffServ) is an appropriate example for this type of QoS service
Question 63
In an HSRP failover environment, which two tasks must you perform on the preferred active router so that it always assumes the active role when it comes up? (Choose two)
A. Configure the router with a higher priority than the other routers in the group
B. Configure the router with a higher MAC address than the other routers in the group
C. Configure preemption on the router
D. Configure the router with a higher IP address than the other routers in the group
E. Configure tracking on the router
Answer: A C
Explanation
If a HSRP router with highest priority is booted at the same time with other HSRP router in the same group then it will take the active role. But if it is rebooted without configuring preemption then it will lose the active role so we have to configure preemption in this case.
Question 64
Which two services can the ICMP Echo IP SLA provide? (Choose two)
A. network performance monitoring
B. inventory maintenance
C. asset depreciation reporting
D. hardware information exchange between devices
E. network device availability reporting
Answer: A E
Explanation
The ICMP Echo operation measures end-to-end response time between a Cisco router and any devices using IP. Response time is computed by measuring the time taken between sending an ICMP Echo request message to the destination and receiving an ICMP Echo reply.
With IP SLAs, routers and switches perform periodic measurements. Therefore ICMP Echo IP SLA can be used to monitor network performance and network device availability reporting
Using IP SLAs can provide these benefits:
+ Service-level agreement monitoring, measurement, and verification.
+ Network performance monitoring
– Measures the jitter, latency, or packet loss in the network.
– Provides continuous, reliable, and predictable measurements.
Question 65
Which interior routing protocol reduces the size of route tables by advertising default routes for all destinations outside of the default area?
A. OSPF
B. BGP
C. EIGRP
D. RIP
Answer: A
Explanation
This question wants to mention about the Stub/Totally Stubby area of OSPF.
In stub area, the routers do not accept routes belonging to external autonomous systems (AS). In order to reach the outside networks, the routers in the stub area use a default route which is injected into the area by the Area Border Router (ABR)
In totally stubby area, only intra-routes are allowed and the routers use default route to send any traffic outside the area.
Note: Although EIGRP also support stub routing but the router in this area will not advertise routes received from other EIGRP neighbors to the hub router. The stub routers do not receive queries from the hub router any more.
Question 66
Which state does a port with BPDU guard enabled enter when it receives a BPDU?
A. learning
B. err-disabled
C. forwarding
D. disabled
Answer: B
Explanation
BPDU Guard feature allows STP to shut an access port in the event of receiving a BPDU and put that port into err-disabled state.
Question 67
Which role is used by VLAN 1 by default?
A. to propagate VLAN information between switches
B. to pass management traffic
C. to initialize the STP protocol
D. to pass traffic designated for isolation from other traffic on the switch
Answer: B
Explanation
The default Ethernet VLAN is VLAN 1. It is a security best practice to configure all the ports on all switches to be associated with VLANs other than VLAN 1. All used ports are associated with VLANs distinct from VLAN 1.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2181837&seqNum=11
All control/management traffic (like CDP, VTP, DTP…) is sent on VLAN 1 and we should separate management and user data traffic. Another reason is by default, the native VLAN is also VLAN 1 which is untagged on trunk links so it may cause a security hole.
Question 68
Which two requirements must be met to allow two routers running EIGRP for IPv6 to become neighbors? (Choose two)
A. Both routers must be configured to use the MTU K value for metric calculations.
B. The peering interface on each router must be set to passive.
C. The EIGRP process must be in no shutdown mode on both routers.
D. The autonomous system numbers must match.
E. The routers must be operating on different subnets.
Answer: C D
Explanation
The following requirements must be met to allow EIGRPv4 and EIGRPv6 to establish a neighbor relationship:
| Requirement | EIGRPv4 | EIGRPv6 |
| Interface is in up/up state | Yes | Yes |
| Interface addresses are in the same subnet | Yes | No |
| The same ASN is used on router eigrp/ipv6 router eigrp commands | Yes | Yes |
| Hello and hold timers have to match | No | No |
| RIDs (router IDs) have to be unique | No | No |
| K-values (used in EIGRP metric calculation formula) have to match | Yes | Yes |
| EIGRP authentication must pass (optional) | Yes | Yes |
Question 69
Which two tasks use OSPFv3 hello packets? (Choose two)
A. Beginning neighbor discovery
B. Requesting topology changes
C. Sharing link-state databases
D. Acknowledging message receipt
E. Performing DR election
Answer: A E
Explanation
Hello packets are OSPF packet Type 1. These packets are multicast periodically to 224.0.0.5 multicast address on all interfaces (unicast on virtual-links) enabling dynamic discovery of neighbors and maintain neighbor relationships. On broadcast and NBMA networks, Hello packets are used to elect DR and BDR.
Question 70
Which two statements about LACP are true? (Choose two)
A. A port in active mode initiates an EtherChannel peering
B. A port in passive mode can receive LACP requests
C. A port in on mode attempts to negotiate an EtherChannel peering
D. A port in auto mode accepts EtherChannel requests without making requests of its own
E. A port in desirable mode initiates an EtherChannel peering
Answer: A B
Explanation
In LACP there are only two modes which are “active” and “passive”. “On” belongs to static mode.
Question 71
Which two features are supported only in named access lists? (Choose two)
A. identifying QoS traffic for marking
B. filtering traffic on VTY lines
C. limiting debug output
D. noncontiguous port filtering
E. deleting entries
Answer: D E
Explanation
The Named ACL Support for Noncontiguous Ports on an Access Control Entry feature allows you to specify noncontiguous ports in a single access control entry, which greatly reduces the number of entries required in an access control list when several entries have the same source address, destination address, and protocol, but differ only in the ports. For example:
Router(config)#ip access-list extended noncontiguousPorts
Router(config-ext-nacl)# permit tcp any eq telnet ftp any eq 23 45 34
Only with named ACL, we can easily remove an individual entry. For example:
R1# show access-list
Standard IP access list nat_traffic
10 permit 10.1.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255
20 permit 10.2.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255
30 permit 10.3.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255
Then to remove the second statement (the line “20 permit 10.2.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.255”) we just need to type “no 20”:
R1(config)#ip access-list standard nat_traffic
R1(config-std-nacl)#no 20
But for numbered ACL, we have to recreated the whole ACL when entries are moved.
Question 72
Which statement describes how the EIGRP feasible distance is calculated?
A. It is the best metric along a path that includes the metric to the neighbor advertising the path
B. It is a path with a reported distance less than the current best path
C. It is the sum of all K values in EIGRP process
D. It is the total metric advertised by the upstream neighbor
Answer: A
Explanation
Feasible distance (FD) is the sum of the the cost from the neighbor to the destination (AD) plus the cost between the local router and the next-hop router.
Maybe it’s a bit confused with these terms so below is an example to make it clear.
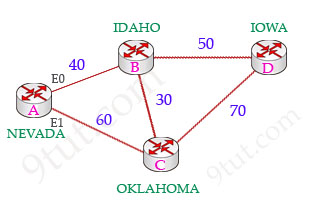
Suppose you are in NEVADA and want to go to IOWA. From NEVADA you need to specify the best path (smallest cost) to IOWA.
In this topology, suppose router A & B are exchanging their routing tables for the first time. Router B says “Hey, the best metric (cost) from me to IOWA is 50 and the metric from you to IOWA is 90” and advertises it to router A. Router A considers the first metric (50) as the Advertised distance. The second metric (90), which is from NEVADA to IOWA (through IDAHO), is called the Feasible distance.
All of these routes are placed in the topology table of router A:
| Route | Advertised distance | Feasible distance |
| NEVADA -> IDAHO -> IOWA | 50 | 90 |
| NEVADA -> OKLAHOMA -> IOWA | 70 | 130 |
Router A will select the route to IOWA via IDAHO as it has the lowest Feasible distance and put it into the routing table.
Question 73
Which type of routing protocol relies on the shortest path tree?
A. path-vector
B. hybrid routing
C. link-state
D. distance-vector
Answer: C
Question 74
Which two marking methods are supported with the IPv4 header? (Choose two)
A. DSCP
B. IPP
C. EXP
D. CoS
E. TID
Answer: A B
Explanation
QoS Packet Marking refers to changing a field within a packet either at Layer 2 (802.1Q/pCoS, MPLS EXP) or Layer 3 (IP Precedence, DSCP and/or IP ECN).
At Layer 3, packet marking can be accomplished using the ToS byte in an IPv4 header. Two predominant types of marking mechanisms leverage the ToS byte: IP Precedence (IPP) and Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP).
IP Precendence is an old approach and has been successively replaced by DSCP for marking IP packets. IP Precedence uses the 3 leftmost bits in the ToS byte.
Reference: CCIE Collaboration Quick Reference
Note: MPLS Experimental (EXP) is a Layer 2 marking technique for IP packet which is encapsulated in MPLS. We cannot mark the DSCP within the IP header as that would require first de-capsulating from MPLS). In this question, it only asks about IPv4 header which is Layer 3 marking.
Question 75
Which two statements about VLAN port assignment are true? (Choose two)
A. By default, all ports are assigned to VLAN 2
B. Ports are assigned to a dynamic VLAN based on the device IP address
C. It can be performed statically or dynamically
D. Static port assignments are based on a preset configuration on a dedicated server.
E. A port in access mode can be assigned to only one VLAN
Answer: C E
Explanation
By default all ports are assigned to VLAN 1, which is the default VLAN.
Ports are assigned to a dynamic VLAN based on its MAC address, not IP address.
The administrator can assign static port on any VLAN and it is not based on any configuration on a server. Only dynamic VLAN assignment requires the configuration from a dedicated server, called the VMPS (VLAN Member Policy Server).
When in access mode, a port can only be assigned to only one VLAN.
This is also a good reference:
VLAN Port Assignments
+ VLANs are assigned to individual switch ports.
+ Ports can be statically assigned to a single VLAN or dynamically assigned to a single VLAN.
+ All ports are assigned to VLAN 1 by default
+ Ports are active only if they are assigned to VLANs that exist on the switch.
+ Static port assignments are performed by the administrator and do not change unless modified by the administrator, whether the VLAN exists on the switch or not.
+ Dynamic VLANs are assigned to a port based on the MAC address of the device plugged into a port.
+ Dynamic VLAN configuration requires a VLAN Membership Policy Server (VMPS) client, server, and database to operate properly.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=29803&seqNum=2
Question 76
Which two statements identify differences between single-homed and dual-homed WAN topologies? (Choose two)
A. Dual-homed topologies provide greater redundancy than single-homed topologies
B. Only dual-homed connections require dynamic routing to the ISP
C. Single-homed topologies are more costly to an enterprise than dual-homed topologies
D. Only dual-homed connections are connected to the same ISP
E. Single-homed topologies are more appropriate for small-business networks than dual-homed topologies
Answer: A E
Explanation
Single-homed: single connection to only one ISP

In a dual-homed setup, the router in a company is still connected to the outside networks via only one ISP, but with two routers or two connections. When one of the dual-homed connection fails, traffic can still flow via other connection so it can tolerate the loss of a network link.
Question 77
Which two characteristics of extended access lists are true? (Choose two)
A. They can compare source traffic only against a permit or deny statement
B. They must be identified with a number between 100 and 199 or 2000 and 2699
C. They can be identified only with a number between 100 and 199
D. They can be configured to filter only UDP or TCP traffic
E. They can compare source and destination traffic against a permit or deny statement
Answer: B E
Question 78
When you configure VTP on a switch, which VTP mode is enabled by default?
A. transparent
B. server
C. off
D. client
Answer: B
Question 79
Which WAN technology is secure and encrypted by default?
A. VPN
B. VSAT
C. DSL
D. MPLS
Answer: A
Question 80
You attempt to execute the APIC-EM ACL path trace feature without specifying the protocol. How does the ACL path trace respond?
A. It runs normally and reports all possible ACE matches for the protocol field.
B. It runs normally and reports that traffic for all possible protocol matches is denied.
C. It fails to execute the path trace.
D. It runs normally and flags all possible ACE entries as invalid.
Answer: A
Explanation
The following rules effect the ACL path trace results:
+ Only matching access control entry (ACE) are reported.
+ If you leave out the protocol, source port, or destination port when defining a path trace, the results include ACE matches for all possible values for these fields.
+ If no matching ACEs exists in the ACL, the flow is reported to be implicitly denied.
Question 81
Which two statements about traffic shaping are true? (Choose two)
A. It can be applied in the outbound direction only.
B. Packets that exceed the configured threshold are remarked and sent.
C. Packets that exceed the configured threshold are held in a buffer.
D. It can be applied in the inbound and outbound directions.
E. Packets that exceed the configured threshold are dropped
Answer: A C
Explanation
The following diagram illustrates the key difference between traffic policing and traffic shaping. Traffic policing propagates bursts. When the traffic rate reaches the configured maximum rate (or committed information rate), excess traffic is dropped (or remarked). The result is an output rate that appears as a saw-tooth with crests and troughs. In contrast to policing, traffic shaping retains excess packets in a queue and then schedules the excess for later transmission over increments of time. The result of traffic shaping is a smoothed packet output rate.

Traffic shaping is applicable only on outbound interfaces as buffering and queuing happens only on outbound interfaces.
Question 82
Which two values are combined to generate the PVST+ bridge ID on the root switch? (Choose two)
A. the root path cost
B. the switch priority
C. the MAC address
D. the port ID
E. the interface number
Answer: B C
Explanation
The Bridge ID is composed of the bridge priority value (0-65535, 2 bytes) and the bridge MAC address (6 bytes).
Bridge ID = Bridge Priority + MAC Address
Question 83
By default, which two K values does EIGRP for IPv6 use to calculate the metric? (Choose two)
A. reliability
B. bandwidth
C. load
D. MTU
E. delay
Answer: B E
Explanation
First you should learn the formula to calculate the metric. It’s a bit complex conditional formula, I think 🙂
metric = [K1 * bandwidth + (K2 * bandwidth)/(256 – load) + K3 * delay] * [K5/(reliability + K4)] if K5 > 0
metric = [K1 * bandwidth + (K2 * bandwidth)/(256 – load) + K3 * delay] if K5 = 0
By default, K1 = 1, K2 = 0, K3 = 1, K4 = 0, K5 = 0 which means that the default values use only bandwidth & delay parameters while others are ignored. The metric formula is now reduced:
metric = bandwidth + delay
Question 84
What is the minimum level of SNMP that provides encryption?
A. SNMPv3 authPriv
B. SNMPv3 authNoPriv
C. SNMPv3 noAuthNoPriv
D. SNMPv2 noAuthNoPriv
Answer: A
Explanation
+ noAuthNoPriv – Security level that does not provide authentication or encryption.
+ authNoPriv – Security level that provides authentication but does not provide encryption.
+ authPriv – Security level that provides both authentication and encryption.
Question 85
Which two statements about interior gateway routing protocols are true? (Choose two)
A. They may use the Dijkstra algorithm.
B. They can be used to connect to another AS across the Internet as a virtual instance.
C. They may use the Bellman-Ford algorithm.
D. They cannot be used when two devices are connected through a firewall.
E. They can be used to connect to the Internet backbone.
Answer: A C
Explanation
Interior gateway routing protocols like OSPF (uses Dijkstra algorithm), RIP (uses Bellman-Ford algorithm) should be used within an organization or ISP.
Question 86
Which two characteristics of a distance-vector routing protocol are true? (Choose two)
A. It may use the Dijkstra algorithm.
B. It has a complete picture of the network.
C. It has a higher CPU requirement than link-state protocols.
D. It sends periodic updates.
E. It may use the Bellman-Ford algorithm.
Answer: D E
Question 87
Which two statements are benefits of stackable switches? (Choose two)
A. They can support dissimilar Cisco IOS features in a single stack.
B. They are less redundant than modular aggregation.
C. They cannot perform switch-to-router aggregation.
D. They can perform link aggregation.
E. They perform unified management from a single switch stack.
Answer: D E
Question 88
Refer to the exhibit.
| R1(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 1/1/1 R1(config-if)# no ip address R1(config-if)#pppoe enable R1(config-if)#pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1 R1(config-if)#exit |
Which effect of this configuration is true?
A. It configures PPP over Ethernet globally for the device.
B. It configures PPP over Ethernet in client mode.
C. It configures PPP over Multilink.
D. It configures PPP over Ethernet in server mode.
Answer: B
Explanation
The picture below shows all configuration needed for PPPoE. Notice that under PPPoE client physical interface Ethernet0/1 there is no IP address configured and it is linked to the Dialer pool 1 (with the dialer pool 1 command.)

Question 89
For which reason can OSPFv3 fail to start between two routers?
A. OSPFv3 is configured only under an interface.
B. The interface assigned to OSPFv3 is in NBMA mode with only one neighbor defined.
C. The router is configured with IPv6 addresses only and it is unable to find an OSPFv3 router ID.
D. IPv6 unicast routing is enabled.
Answer: C
Explanation
Although OSPFv3 deals solely with IPv6 addresses, it still uses 32-bit router IDs, which are expressed in dotted-decimal (IPv4) format. This router ID must be manually configured if we don’t have any IPv4 interfaces on our router. For example:
ipv6 router ospf 1
router-id 172.16.1.1
Question 90
Which statement about using the keepalive command on a tunnel interface is true?
A. It can be configured on either side of the tunnel or on both sides.
B. It can be configured only on the downstream side of the tunnel.
C. If it is configured on both sides of the tunnel, the values must match.
D. It can be configured only on the upstream side of the tunnel.
Answer: A
Explanation
GRE tunnels are designed to be completely stateless. This means that each tunnel endpoint does not keep any information about the state or availability of the remote tunnel endpoint. A consequence of this is that the local tunnel endpoint router does not have the ability to bring the line protocol of the GRE Tunnel interface down if the remote end of the tunnel is unreachable. Such scenarios would cause data packets that go through the GRE tunnel to be “black holed”. Keepalives on the GRE tunnel interface are used in order to solve this issue in the same way as keepalives are used on physical interfaces. With this feature, the tunnel interface dynamically shuts down if the keepalives fail for a certain period of time.
Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) keepalive packets may be sent from both sides of a tunnel or from just one side. If they are sent from both sides, the period and retry parameters can be different at each side of the link. If you configure keepalives on only one side of the tunnel, the tunnel interface on the sending side might perceive the tunnel interface on the receiving side to be down because the sending interface is not receiving keepalives. From the receiving side of the tunnel, the link appears normal because no keepalives were enabled on the second side of the link.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2sb/feature/guide/sb_gretk.html
Note: GRE tunnel keepalives are only supported on point-to-point GRE tunnels. Tunnel keepalives are configurable on multipoint GRE (mGRE) tunnels but have no effect.
Question 91
Which statement about STP root bridges is true?
A. Each VLAN must have a separate root bridge.
B. An individual switch can be the root bridge for only one VLAN.
C. The switch with the highest root ID is elected as the root bridge.
D. Dynamic root bridge assignment is most efficient.
Answer: A
Explanation
With STP, RSTP or PVST, each VLAN must have its own root bridge.
Question 92
Which statement about the default VLAN is true?
A. It is always the same as the native VLAN.
B. Its name is Default by default.
C. It can be removed without additional configuration.
D. It is always VLAN 1.
Answer: D
Question 93
In which two ways can you isolate the location of a connectivity issue between two devices on your network? (Choose two)
A. Test whether the next hop from the source can reach the destination and work toward the destination.
B. Send an extended ping from the destination to the source.
C. Execute a traceroute from the destination and work toward the source to locate the problematic hop.
D. Send an extended ping from the source to the destination.
E. Execute a traceroute from the source to the destination to locate the problematic hop.
Answer: C E
Explanation
To isolate the connectivity issue location we have to use traceroute to find out the exact location where the trace stops.
Question 94
Which configuration item is the default username for PPP local authentication?
A. the router MAC address
B. the router hostname
C. cisco
D. The router serial number
Answer: B
Explanation
By default for the authentication, CHAP uses the hostname of the router is used to identify itself. If the ppp chap hostname name command is configured, a router uses the name in place of the hostname to identify itself.
With PAP, we have to configure the command “ppp pap sent-username username password password” to match with the local username on the other side (configured with “username username password password” global configuration command)
Question 95
Which three features are supported when you use TACACS+ for device management? (Choose three)
A. It can restrict the commands that individual users are allowed to execute.
B. It can connect disparate networks.
C. It can create network access clients.
D. It can provide additional challenges beyond the username and password.
E. It supports UNIX server functionality.
F. It supports user notifications.
Answer: A D F
Explanation
During a session, if additional authorization checking is needed, the access server checks with a TACACS+ server to determine if the user is granted permission to use a particular command. This provides greater control over the commands that can be executed on the access server while decoupling from the authentication mechanism -> Answer A is correct.
The authentication facility provides the ability to conduct an arbitrary dialog with the user (for example, after a login and password are provided, to challenge a user with a number of questions, like home address, mother’s maiden name, service type, and social security number). In addition, the TACACS+ authentication service supports sending messages to user screens. For example, a message could notify users that their passwords must be changed because of the company’s password aging policy -> Answer F is correct.
Answer F seems to be correct too as “TACACS+ is a security application that provides centralized validation of users attempting to gain access to a router or network access server. TACACS+ services are maintained in a database on a TACACS+ daemon running, typically, on a UNIX or Windows NT workstation”
Question 96
Which WAN topology has the highest degree of reliability?
A. hub-and-spoke
B. full mesh
C. point-to-point
D. router-on-a-stick
Answer: B
Explanation
Full-mesh is a network topology in which there is a direct link between all pairs of nodes. Below is an example of full-mesh topology.
Question 97
Which command do you enter to determine the status of the SVI for VLAN 10?
A. show ip interface brief
B. show run interface vlan 10
C. show vtp status
D. show interface trunk
Answer: A
Explanation
The Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) can be checked using the same command as physical interfaces like “show ip interface brief”. For example we can see the SVIs of VLANs 10 & 20 here:
L3Switch#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/1 10.1.4.6 YES manual up up Vlan10 10.2.1.1 YES manual up up Vlan20 10.2.2.2 YES manual up up
Question 98
Which protocol is incompatible with CGMP leave processing?
A. GARP
B. VRRP
C. HSRPv1
D. HSRPv2
Answer: C
Explanation
HSRPv1 uses the multicast address 224.0.0.2 to send hello packets, which can conflict with Cisco Group Management Protocol (CGMP) leave processing. You cannot enable HSRPv1 and CGMP at the same time; they are mutually exclusive.
Question 99
After you configure a new IP SLA, you notice that it is failing to run or generate statistics. Which step do you take first to identify the problem?
A. Use the debug ip sla trace command on the device to troubleshoot.
B. Add the verify-data command to the IP SLA configuration.
C. Add procative threshold conditions to the IP SLA to facilitate troubleshooting.
D. Use the debug ip sla error command on the device to troubleshoot.
Answer: B
Explanation
The command “debug ip sla error” enables debugging output of Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) operation run-time errors
Note: The command “debug ip sla trace” traces the execution of a Cisco IOS IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) operation, use the debug ip sla trace command
+ If the IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) operation is not running and not generating statistics, add the verify-data command to the configuration (while configuring in IP SLA configuration mode) to enable data verification. When data verification is enabled, each operation response is checked for corruption. Use the verify-data command with caution during normal operations because it generates unnecessary overhead.
+ Use the debug ip sla trace and debug ip sla error commands to help troubleshoot issues with an IP SLAs operation.
Therefore we should add the “verify-data” command first before using the “debug ip sla error” or “debug ip sla trace” command.
Question 100
Which statement about GRE tunnels is true?
A. They pass clear-text traffic.
B. They are stateful.
C. They are unable to carry multicast traffic.
D. They use MD5 for encryption.
Answer: A
Explanation
GRE tunnels are completely stateless. This means that each tunnel endpoint does not keep any information about the state or availability of the remote tunnel endpoint. GRE tunnels can carry multicast traffic so they can be used to transport multicast traffic over networks that have no multicast support. GRE support IPSec for encryption.


thanks
I think the answer to “Drag and drop the steps in the process of establishing an OSPFv3 neighbor relationship from the left onto the correct sequence on the right” is a little bit incorrect, see from (https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/5_x/nx-os/unicast/configuration/guide/l3_cli_nxos/l3_ospfv3.pdf):
“OSPFv3 is an IETF link-state protocol (see “Overview” section on page 1-1). An OSPFv3 router sends
a special message, called a hello packet, out each OSPF-enabled interface to discover other OSPFv3
neighbor routers. Once a neighbor is discovered, the two routers compare information in the Hello packet
to determine if the routers have compatible configurations. The neighbor routers attempt to establish
adjacency, which means that the routers synchronize their link-state databases to ensure that they have
identical OSPFv3 routing information. Adjacent routers share link-state advertisements (LSAs) that
include information about the operational state of each link, the cost of the link, and any other neighbor
information. The routers then flood these received LSAs out every OSPF-enabled interface so that all
OSPFv3 routers eventually have identical link-state databases. When all OSPFv3 routers have identical
link-state databases, the network is converged (see the “Convergence” section on page 1-6). Each router
then uses Dijkstra’s Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to build its route table.”
So that the order must be the following:
1: An interface on each router is enabled for OSPFv3
2: The routers send hello messages
3: The routers attempt to identify a common configuration
4: The routers synchronise their databases
5: The routers calculate the SPF
6: The network is converged
Or 🙂
1: An interface on each router is enabled for OSPFv3
2: The routers send hello messages
3: The routers attempt to identify a common configuration
4: The routers synchronise their databases
5: The network is converged
6: The routers calculate the SPF
Can we get some verification on the OSPFv3 Drag and Drop?
The Cisco document shows “Each router
then uses Dijkstra’s Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to build its route table.” at then end of the explanation.
This seems correct:
1: An interface on each router is enabled for OSPFv3
2: The routers send hello messages
3: The routers attempt to identify a common configuration
4: The routers synchronise their databases
5: The network is converged
6: The routers calculate the SPF
Is there any reason why this is not the correct answer?
Another source: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2294214 doesn’t tell exactly what order is right but we can do another consequence)
Some Cisco questions are lottery)
Passed the ICND2 exam will ease today!!! All of the above questions were on the exam. Sims were very similar but a little different. As long as you know the concepts and practice here you will pass. This site is great to take off the anxiety before the test. Best of luck
Q14,
I am wondering the answer is correct.
PortFast:
Enabling the PortFast feature causes a switch or a trunk port to enter the STP forwarding-state immediately or upon a linkup event, thus bypassing the listening and learning states.
so the answer: enables a port to immediately transition to the forwarding state: should be PortFast, not RootGuard as above.
can anyway have more clarification please?
Q16:
the answers are not right
the correct answer should be:
configures the port to serve only one VLAN: access mode
provides virtual separation of broadcast domains: Access VLAN
Question 28
Which two statements about CHAP authentication are true? (Choose two)
A. The called router sends a challenge packet to the calling router
B. It is by definition a one-way authentication method
C. PPP authentication is performed after the CHAP process is complete
D. CHAP authentication can only be used in one direction
E. By default, the calling router authenticates the called router
F. It is by definition a two-way authentication method
May be (A, B), but not (A, E) because the answers are controversial and based on (https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wan/point-to-point-protocol-ppp/25647-understanding-ppp-chap.html#oneway) “CHAP is defined as a one-way authentication method”
Some answers seem wrong…
transition to forwarding state is > PORTFAST<
I’ll be taking the test tomorrow. I will update here after I have finished the test.
omg thank you!
how did your test go? did you see some of the things about? What command line sim question did you get?
@all: Thanks for your detection, we have just updated Q.14, Q.28.
Ill be taking the exam on Monday I will let you guys know
We appreciate your feedback Anton! Charlie has proved to be unreliable 🙁
Question 54, I saw somewhere else, the answer should be A and I believed A is the correct answer.
Which purpose of the network command in the BGP configuration of a router is true?
A. It advertises a valid network as local to the autonomous system of a router
testing on 29 th
Guys I took the exam today.. simulations were eigrp and ospf
also questions that came up SVI Questions, GRE questions, PPPOE Questions, PAPG/LACP, Policing and shaping, APIC PATH TRACE…..a lot that is covered on here! good luck!
Taking the test this afternoon. Will dump what I remember right after.
Wish me luck!
any details you remember would help a lot, thanks!
Boom!
Hit a 970! So, tons of SDN, Etherchannel/PAGP. The EIGRP(had the k value variance) and GRE (exactly the same as shown on 9tut) sims
2,6,7,8,44,45,46,53,74,78,80.
If anyone is interested in the dumps I used, lmk
Why question 6 has such answers? I thought it would be the other way around:
Configuration values may be different between devices:
+ hello timers
+ hold timers
+ router IDs
Configuration values must match between device:
+ authentication password
+ autonomous system number
+ shutdown command status
I would say what has to match is hello and hold timers as well as autonomous system number. Why is that not correct?
@Grimraven http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2264458&seqNum=2 under the topic Manipulating EIGRP Hello and Hold Timers
yes, I made a mistake because I thought of OSPF and this questions is about EIGRP.
@ItsaGundam! would studying just this release be enough for passing or should I study all the releases? What dump did you use? Testing on Saturday!!!!!!! :l
Has drag and drop question 7 been confirmed? It doesn’t make sense that the SPF algorithm would run before they even synchronized databases? What are they running SPF on with nothing exchanged?
So will I be good if I study and learn the material in Part 6 and Part 7 and all the links in the main page under ” For ICND2 candidates:”
No, youy still need to study a lot before coming to this website,l otherwise you will fail miserably. These questions guide you to what you do know and not know., you might get 10 questions in one exam form 9tut. the rest you must know and studied for. Stop looking for shortcuts
question 44. the answer is wrong is suppose to be R2 f0/0
Hi guys and 9Tut staff, I got my membership recently and was checking the “ICND2v3 – New Questions” from part 1 to 8 and noticed that parts from 1 to 4 and maybe 5 as well are quite old (from 2018).
I am taking ICND2 very soon and was wondering if these old questions are still valid?, is still worth it to invest time in those parts from 1 to 5 or have they been deprecated?
Thanks for your time and effort to put this amazing resource together.
Checking is to report that I passed ICND2 today with 921. Minimum passing score 811. Studied with Wendall Odom’s exam guide, Cisco learning acadamy resources, and checked out “New Questions Parts 6-8” of this website. 80% of the questions on my exam were covered here.