ICND1v3 – New Questions Part 2
Note: These new questions have not been classified into specific topics so please learn them separately.
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via these links:
+ Question 1 to 15
+ Question 16 to 30
+ Question 31 to 50
+ Question 51 to 70
+ Question 71 to 90
+ Question 91 to 110
+ Question 111 to 124
Question 1
Drag and drop the Ethernet types from the left onto the correct service descriptions on the right.
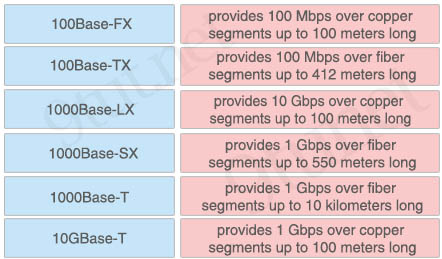
Answer:
+ provides 100 Mbps over copper segments up to 100 meters long: 100Base-TX
+ provides 100 Mbps over fiber segments up to 412 meters long: 100Base-FX
+ provides 10 Gbps over copper segments up to 100 meters long: 10GBase-T
+ provides 1 Gbps over fiber segments up to 550 meters long: 1000Base-SX
+ provides 1 Gbps over fiber segments up to 10 kilometers long: 1000Base-LX
+ provides 1 Gbps over copper segments up to 100 meters long: 1000Base-T
Explanation
First we need to understand the meaning behind each Ethernet type. Let’s take an example with 100Base-FX:
+ 100: represents frequency in MHz (Mega Hertz) for which this cable is made. The greater the MHz, the greater speeds the cable can handle. In this example it is 100MHz. The 100 MHz speed translates to 100Mbit per second.
+ Base (in Ethernet standards): refers to the baseband signalling, which uses the entire bandwidth of the cable to transmit a single signal. Therefore only one communication channel is available at any given time. It is contradict to broadband which shares the bandwidth of the cable.
+ TX/FX: The “T” refers to “Twisted Pair” (pairs that are twisted) physical medium that carries the signal so all “BASE-T…” types are copper.. The “FX” means it’s a two strand fiber-optic cable and supports speeds up to 100 Mbps. Maximum length is usually up to two kms.
100Base-TX (sometimes referred as “T” only) is the IEEE standard that defines the requirement for sending information at 100Mbps on unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling. It uses two of the four available pairs within the UTP cable. It is also called fast Ethernet. Maximum length of 100Base-TX cable is 100 meters.
100Base-FX is simply Fast Ethernet over fiber. The maximum length of any segment of fiber-optic cabling connecting a station (computer) to a hub is 412 meters.
+ SX refers to Short-wavelength laser. It is a fiber optic Gigabit Ethernet standard for operation over multi-mode fiber using a 770 to 860 nanometer, near infrared (NIR) light wavelength. The standard specifies a distance capability between 220 meters and 550 meters.
+ LX refers to Long-wavelength laser. 1000BASE-LX can run over both single mode fiber and multimode fiber with a distance of up to 10 km (for single mode fiber) and 3km (for multimode fiber).
+ ZX refers to extended-wavelength laser. 1000BASE-ZX can only run in single mode fiber. The maximum length can be up to 100km
-> The frequency (in MHz) can be used to eliminate wrong options easily. For the rest we have to remember the maximum distance to solve this question:
Maximum distance: T (TX) (100m) < FX (412m)< SX (220m to 550m) < LX (3km to 10km) < ZX (over 10km)
Question 2
Drag and drop the DHCP messages from the left into the correct sequence for a DHCP IP address request on the right.
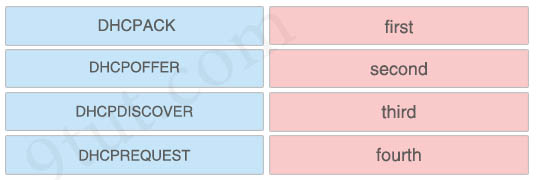
Answer:
+ first: DHCPDISCOVER
+ second: DHCPOFFER
+ third: DHCPREQUEST
+ fourth: DHCPACK
Explanation
Remember this order of DHCP messages: DORA (Discover -> Offer -> Request -> Ack). For more information of how DHCP messages are exchanged, please read our DHCP tutorial.
Question 3
Drag and drop the descriptions of static routing or dynamic routing from the left onto the correct categories on the right.
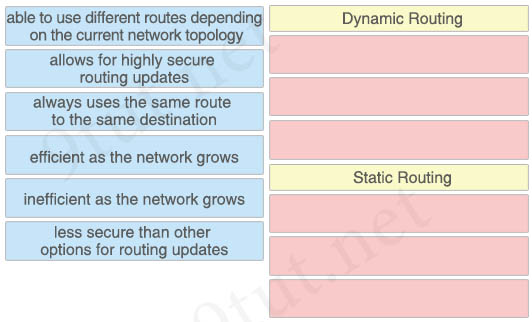
Answer:
Dynamic Routing:
+ able to use different routes depending on the current network topology
+ efficient as the network grows
+ less secure than other options for routing updates
Static Routing:
+ allows for highly secure routing updates
+ always uses the same route to the same destination
+ inefficient as the network grows
Question 4
You are configuring a default route on a Cisco router. Drag and drop the commands from the left into the correct sequence on the right. Not all commands are used.
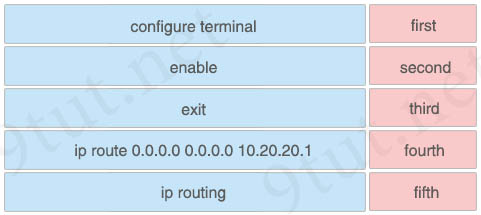
Answer:
+ first: enable
+ second: configure terminal
+ third: ip routing
+ fourth: ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.20.20.1
+ fifth: exit
Question 5
Drag and drop the address blocks from the left onto the correct address types on the right.

Answer:
+ global unicast: 2000::/3
+ link-local unicast: FE80::/10
+ multicast: FF00::/8
+ unique-local unicast: FC00::/8
Explanation
Below is the list of common kinds of IPv6 addresses:
| Loopback address | ::1 |
| Link-local address | FE80::/10 |
| Site-local address | FEC0::/10 |
| Global address | 2000::/3 |
| Multicast address | FF00::/8 |
Link-local addresses only used for communications within the local subnetwork (automatic address configuration, neighbor discovery, router discovery, and by many routing protocols). It is only valid on the current subnet. It is usually created dynamically using a link-local prefix of FE80::/10 and a 64-bit interface identifier (based on 48-bit MAC address).
Global (unicast) address is globally unicast address sent through the public Internet (equivalent to public IPv4 addresses).
Unique-local unicast (also known as Site-local address). They are analogous to IPv4’s private address classes.
Question 6
Drag and drop the show cdp commands from the left onto the output they generate on the right.

Answer:
+ show cdp:
Global CDP information:
Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds
Sending a holdtime value of 180 seconds
Sending CDPv2 advertisements is enabled
+ show cdp traffic:
CDP counters:
Total packets output: 19, Input: 16
Hdr syntax: 0, Chksum error: 0, Encaps failed: 0
No memory: 0, Invalid packet: 0, Fragmented: 0
CDP version 1 advertisements output: 0. Input: 0
CDP version 2 advertisements output: 19, Input: 16
+ show cdp neighbor detail:
Device ID: R2 Entry address(es): IP address: 192.168.1.2 Platform: Cisco 7206VXR, Capabilities: Router Interface: Ethernet1/1, Port ID (outgoing port): Ethernet1/1 Holdtime: 174 Version: Cisco IOS Software, 7200 Software (C7200-ADVTPSERVICESK9-M), Version 12.4(2)T, RELEASE SOFTWARE(fc1) Advertisement version: 2 Duplex: Half
+ show cdp neighbor ethernet1/1:
Capability Codes: R — Router, T - Trans Bridge, B — Source Route Bridge S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater Device ID Local Interface Holdtime Capability Platform Port ID R2 Eth 1/1 162 R 7206VXR Eth 1/1
Question 7
You are updating the IOS on a Cisco router. Drag and drop the tasks from the left into the correct sequence on the right.

Answer:
Step 1: Ensure that the router and the FTP server have connectivity to one another
Step 2: Copy the IOS image to the router
Step 3: Validate that the correct IOS image is stored in NVRAM
Step 4: Verify that the configuration register and boot variable are set correctly on the router
Step 5: Save the running configuration of the router
Step 6: Reload the router
Explanation
According to https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/routers/3800-series-integrated-services-routers/49044-sw-upgrade-proc-ram.html, the following steps should be performed to upgrade a Cisco IOS software image:
Step 1: Select a Cisco IOS Software Image
Step 2: Download the Cisco IOS Software Image to the TFTP Server
Step 3: Identify the File System to Copy the Image
Step 4: Prepare for the Upgrade
Step 5: Verify that the TFTP Server has IP Connectivity to the Router (equivalent to our Step 1)
Step 6: Copy IOS Image to the Router (equivalent to our Step 2)
Step 7: Verify the Cisco IOS Image in the File System (equivalent to our Step 3)
Step 8: Verify the Configuration Register (equivalent to our Step 4)
Step 9: Verify the Boot Variable (equivalent to our Step 4)
Step 10: Save the Configuration and Reload the Router (equivalent to our Step 5 & 6)
Step 11: Verify the Cisco IOS Upgrade (Verify that the router runs with the proper image)
Question 8
Drag and drop the components of a standard IPv4 access list entry from the left into the correct sequence on the right.

Answer:
+ component 1: access-list
+ component 2: 10
+ component 3: permit
+ component 4: 192.168.1.0
+ component 5: 0.0.0.255
+ component 6: log
Explanation
The full command is “access-list 10 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 log”. It allows packets with source IP addresses in the range of 192.168.1.0/24 and creates a log message to the device console. The first packet that the access list inspects triggers the access list to log a message at the device console. Subsequent packets are collected over 5-minute intervals before they are displayed or logged. Log messages include information about the access list number, the source IP address of packets, the number of packets from the same source that were permitted or denied in the previous 5-minute interval, and whether a packet was permitted or denied.
Question 9
Drag and drop the VTP terms from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
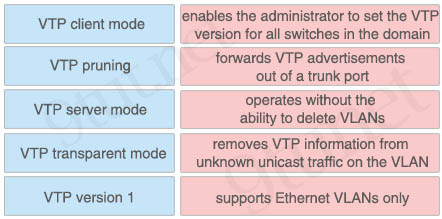
Answer:
+ enables the administrator to set the VTP version for all switches in the domain: VTP server mode
+ forwards VTP advertisements out of a trunk port: VTP transparent mode
+ operates without the ability to delete VLANs: VTP client mode
+ removes VTP information from unknown unicast traffic on the VLAN: VTP pruning
+ supports Ethernet VLANs only: VTP version 1
Explanation
VTPv1 & VTPv2 support VLANs 1 to 1000 only (which is called the Ethernet VLANs).
Question 10
A host is sending packets to a router. Drag and drop the steps in the packet-handling process from the left into the correct sequence on the right.

Answer:
+ Step 1: The packet is created
+ Step 2: A frame encapsulates the packet
+ Step 3: The destination IP address is checked
+ Step 4: The frame is transmitted
+ Step 5: The packet is extracted from the frame
+ Step 6: The packet is forwarded to the exit interface
Explanation
Step 1 to 4 describe how the packet is sent from the host: At the host side, data is encapsulated from Layer 7 to Layer 1 so at Layer 3 the packet is created and at Layer 2, a frame encapsulate the packet. The destination IP address is checked before transmitting this frame to the router.
In step 5, the frame arrived to the router and the router extracts the frame to get the packet inside. Then finally the packet is forwarded to the suitable exit interface. Many steps were omitted between step 5 & 6 so it is difficult to understand this question.
Question 11
Drag and drop the OSI model layers from the left onto the correct TCP/IP model layers on the right.
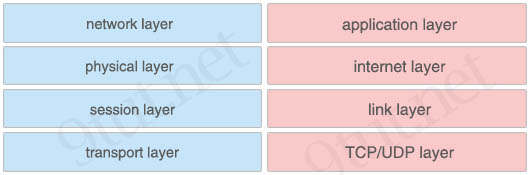
Answer:
+ application layer: session layer
+ internet layer: network layer
+ link layer: physical layer
+ TCP/UDP layer: transport layer
Explanation
The Internet Layer in TCP/IP Model is equivalent to the Network Layer of the OSI Model.
Question 12
Drag and drop the routing protocols from the left onto the default administrative distances on the right.
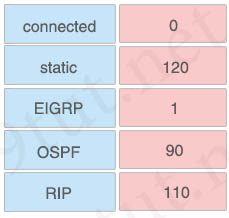
Answer:
+ 0: connected
+ 120: RIP
+ 1: static
+ 90: EIGRP
+ 110: OSPF
Question 13
Drag and drop the VLAN port membership modes from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
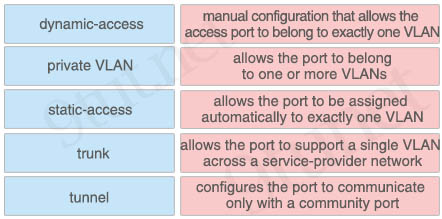
Answer:
+ manual configuration that allows the access port to belong to exactly one VLAN: static-access
+ allows the port to belong to one or more VLANs: trunk
+ allows the port to be assigned automatically to exactly one VLAN: dynamic-access
+ allows the port to support a single VLAN across a service-provider network: tunnel
+ configures the port to communicate only with a community port: private VLAN
Question 14
Drag and drop the IOS commands from a RIP router from the left onto the correct effects on the right.
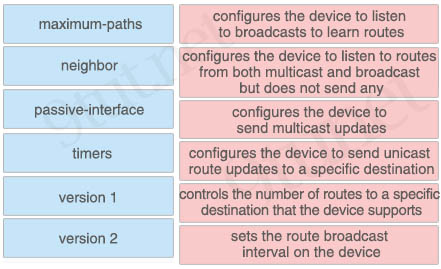
Answer:
+ configures the device to listen to broadcasts to learn routes: version 1
+ configures the device to listen to routes from both multicast and broadcast but does not send any: passive-interface
+ configures the device to send multicast updates: version 2
+ configures the device to send unicast route updates to a specific destination: neighbor
+ controls the number of routes to a specific destination that the device supports: maximum-paths
+ sets the route broadcast interval on the device: timers
Question 15
Drag and drop the DNS-lookup configuration commands from the left onto the correct effects on the right.

Answer:
+ adds an entry to the host table: ip host switch_1 192.168.0.1
+ completes the FQDN of the DNS server: ip domain-name
+ displays address-mapping information: show hosts
+ enables host-to-IP-address translation: ip domain-lookup
+ specifies the IP address of the DNS server: ip name-server
Explanation
The command “ip name-server <IP address>” specifies the address of one or more name servers.
The command “ip domain-name” defines a default domain name that is used to complete unqualified host names. For example, if we defines “ip domain-name 9tut.net” then a host3 queries to this router is known as host3.9tut.net.
The command “ip domain-lookup” enables DNS lookup feature (DNS-based host name-to-address translation). This command is enabled by default.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/domain-name-system-dns/24182-reversedns.html
The command “ip host” defines a static hostname-to-address mapping in the hostname cache. For example if we define “ip host sw1 192.168.1.1” then we can ping to Sw1 with the command “ping sw1” (or telnet, traceroute… to it with the “telnet sw1”), which is easier to remember than the “ping 192.168.1.1” command.
The following example shows how to configure the DNS server lookup feature:
Switch(config)#ip domain-name 9tut
Switch(config)#ip name-server 192.1.0.1
Switch(config)#ip domain-lookup //Note: this command is enabled by default
Note: A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is an unambiguous domain name that specifies the exact location in the Domain Name System’s tree hierarchy through to a top-level domain and finally to the root domain. Technically, a FQDN has a trailing dot. For example: router3.9tut.net
The “show hosts” command displays the cached DNS name servers and domain names. For example:
router# show hosts Default domain is 9tut.net Name/address lookup uses domain service Name servers are 255.255.255.255 Host Flags Age(hr) Type Address(es) host1.9tut.net (temp, OK) 1 IP 192.168.1.10 abc (perm, OK) 0 IP 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.3
Question 16
Drag and drop the logging types from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right. Not all logging types are used.
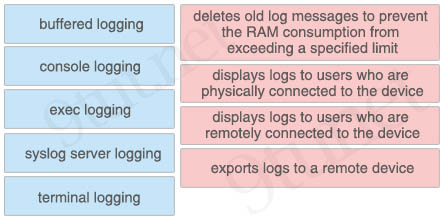
Answer:
+ deletes old log messages to prevent the RAM consumption from exceeding a specified limit: buffered logging
+ displays logs to users who are physically connected to the device: console logging
+ displays logs to users who are remotely connected to the device: terminal logging
+ exports logs to a remote device: syslog server logging
Explanation
Console logging: By default, the router sends all log messages to its console port. Hence only the users that are physically connected to the router console port can view these messages.
Terminal logging: It is similar to console logging, but it displays log messages to the router’s VTY lines instead. This is not enabled by default.
Buffered logging: This type of logging uses router’s RAM for storing log messages. Buffer has a fixed size to ensure that the log will not deplete valuable system memory. The router accomplishes this by deleting old messages from the buffer as new messages are added.
Syslog Server logging: The router can use syslog to forward log messages to external syslog servers for storage. This type of logging is not enabled by default.
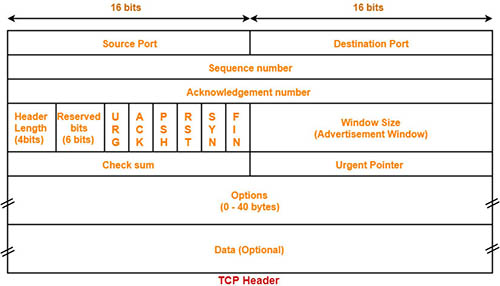
Question 17
Refer to the exhibit. Drag and drop the TCP header fields from the left into the correct positions on the right.
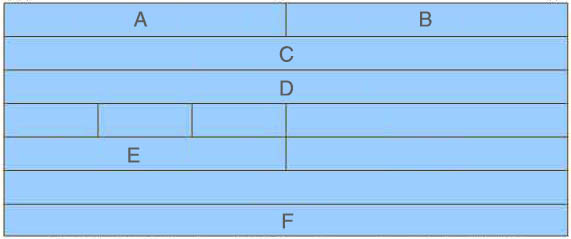
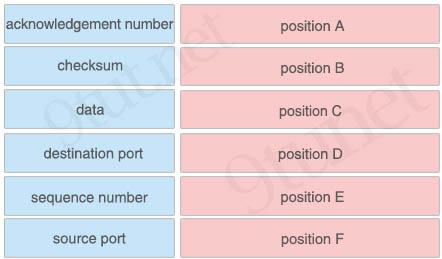
Answer:
+ position A: source port
+ position B: destination port
+ position C: sequence number
+ position D : acknowledgement number
+ position E: checksum
+ position F: data
Explanation
Question 18
Drag and drop the logging configuration commands from the left onto the logging locations they configure on the right.
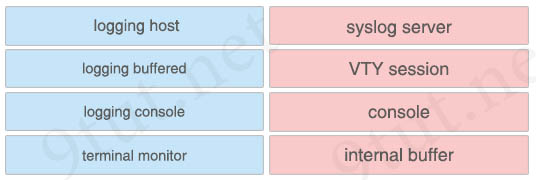
Answer:
+ syslog server: logging host
+ VTY session: terminal monitor
+ console: logging console
+ internal buffer: logging buffered
Explanation
Console logging: By default, the router sends all log messages to its console port. Hence only the users that are physically connected to the router console port can view these messages. If the console logging is disabled for some reasons, we can enable it again with the “logging console” command. By default, the console receives debugging messages and numerically lower levels. If we want to change the level, we can use the “logging console level” command.
The command “terminal monitor” helps logging messages appear on the your current terminal session.
Buffered logging: This type of logging uses router’s RAM for storing log messages. Buffer has a fixed size to ensure that the log will not deplete valuable system memory. The router accomplishes this by deleting old messages from the buffer as new messages are added.
Syslog Server (logging): The router can use syslog to forward log messages to external syslog servers for storage. This type of logging is not enabled by default.
Question 19
Drag and drop the DNS lookup commands from the left onto the correct effects on the right.
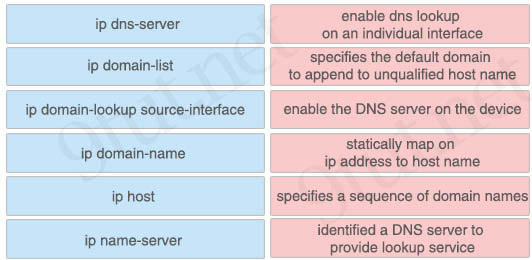
Answer:
+ enable the DNS server on the device: ip name-server
+ specifies a sequence of domain names: ip domain-list
+ enable dns lookup on an individual interface: ip domain lookup source-interface
+ specifies the default domain to append to unqualified host name: ip domain-name
+ statically map on ip address to host name: ip host
+ identified a DNS server to provide lookup service: ip dns-server
Explanation
Question 20
Drag and drop the DHCP client states from the left into the standard order in which the client passes through them on the right.
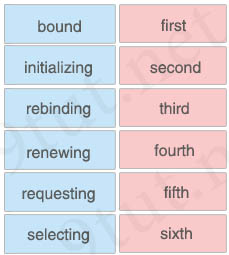
Answer:
initializing – first
selecting – second
requesting – third
bound (binding)– fourth
renewing – fifth
rebinding – sixth
Reference: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc958935.aspx
Question 21
Drag and drop the PDUs from the left onto the correct TCP/IP layers on the right.
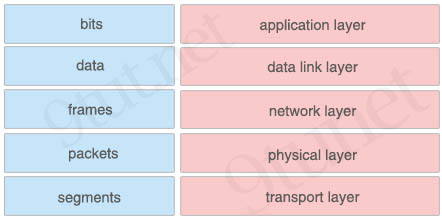
Answer:
+ application layer: data
+ data link layer: frames
+ network layer: packets
+ physical layer: bits
+ transport layer: segments
Question 22
Drag and drop the route source codes in a routing table from the left onto the correct meanings on the right.
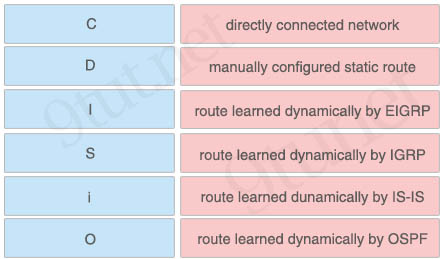
Answer:
+ directly connected network: C
+ manually configured static route: S
+ route learned dynamically by EIGRP: D
+ route learned dynamically by IGRP: I
+ route learned dunamically by IS-IS: i
+ route learned dynamically by OSPF: O
Explanation
The symbol of EIGRP routes is “D”, not “E” because “E” has been used for Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP), which is the BGP predecessor. But the support for EGP has been removed since Cisco IOS 12.2T.
Question 23
Drag and drop the IEEE standard Cable names from the left onto the correct cable types on the right.
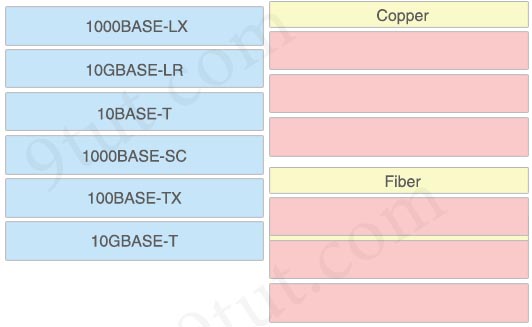
Answer:
Copper:
+ 10BASE-T
+ 100BASE-TX
+ 10GBASE-T
Fiber:
+ 10GBASE-LR
+ 1000BASE-LX
+ 1000BASE-SC
Explanation
The “T” letter symbolizes for “twisted pair cable” so all “BASE-T…” types are copper.
Question 24
Drag and drop the benefits of a Cisco wireless Lan controller from the left onto the correct examples on the right.
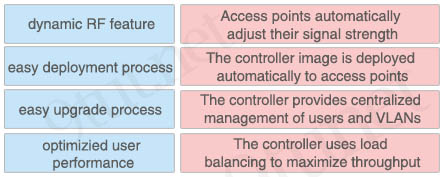
Answer:
+ Access points automatically adjust their signal strength: Dynamic RF Feature
+ The controller image is deployed automatically to access points: Easy upgrade process
+ The controller provides centralized management of users and VLANs: Easy Deployment Process
+ The controller uses load balancing to maximize throughput: Optimized user performance
Question 25
Drag and Drop the protocols from the left onto the correct IP traffic types on the right.
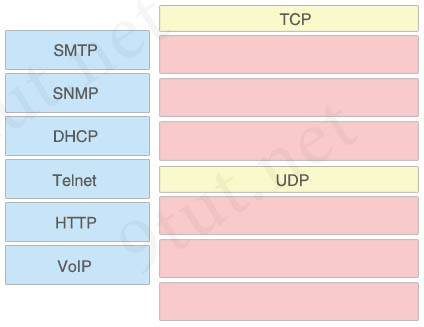
Answer:
TCP:
+ SMTP
+ Telnet
+ HTTP
UDP:
+ SNMP
+ DHCP
+ VoIP
Explanation
In this question we should remember that Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) runs on TCP port because email is very important.
Question 26
Drag and drop the IPv6 addresses from the left onto the correct types on the right
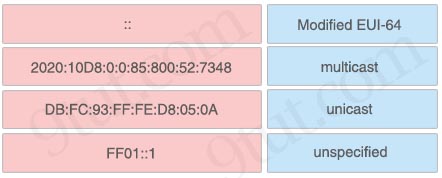
Answer:
+ Modified EUI-64: DB:FC:93:FF:FE:D8:05:0A
+ multicast: FF01::1
+ unicast: 2020:10D8:0:0:85:800:52:7348
+ unspecified: ::
Question 27
Drag and drop the values in a routing table from the left onto the correct meanings on the right
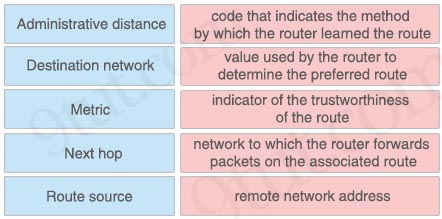
Answer:
+ Administrative distance: indicator of the trustworthiness of the route
+ Destination network: remote network address
+ Metric: value used by the router to determine the preferred route
+ Next hop: network to which the router forwards packets on the associated route
+ Route source: code that indicates the method by which the router learned the route
Question 28
Drag and drop the switching concepts from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
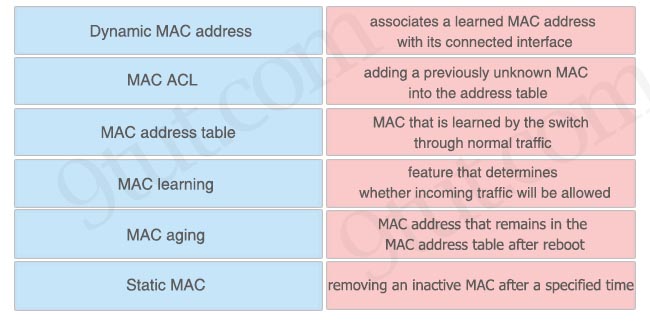
Answer:
+ Dynamic MAC address: MAC that is learned by the switch through normal traffic
+ MAC ACL: feature that determines whether incoming traffic will be allowed
+ MAC address table: associates a learned MAC address with its connected interface
+ MAC learning: adding a previously unknown MAC into the address table
+ MAC aging: removing an inactive MAC after a specified time
+ Static MAC: MAC address that remains in the MAC address table after reboot
Question 29
Refer to the exhibit. Router R4 is reachable from Router R3. Which two scenarios would prevent the subnet 172.16.2.0/24 from being added to the routing table on router R3? (Choose two)
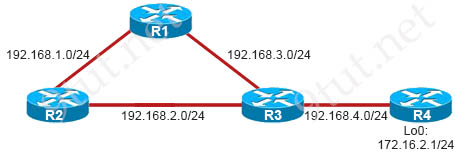
R3#show ip route Gateway of last resort is not set C 192.168.4.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/2 R 192.168.1.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.3.1, 00:00:09, Ethernet1/0 C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/1 C 192.168.3.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0 R3#ping 192.168.4.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.4.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 64/66/68
A. Router R4 is running RIPv1 instead of RIPv2.
B. Network updates are looping around routers R1, R2, and R3.
C. The subnet uses a loopback interface.
D. Routers R3 and R4 are running different versions of RIP.
E. The subnet uses a classless network.
F. Router R3 has split horizon enabled.
Answer: A D
Explanation
Remember that RIPv2 device can understand RIPv1 device but not vice versa so:
+ If R3 runs RIPv1 and R4 runs RIPv2 then R3 cannot understand R4 so it ignores all RIPv2 updates sent from R4.
+ If R3 runs RIPv2 and R4 runs RIPv1 then R4 can only advertise major network 172.16.0.0/24 so R3 can only learn this major network, not the subnet 172.16.2.0/24 (-> Answer A is correct)
-> Answer D is correct.
Question 30
Which address scheme is used to route traffic to the public Internet?
A. 2000::/3
B. 172.30.1.024
C. FC007
D. 192.168.10.024
Answer: A
Explanation
All IPv6 global address starts with 2000::/3 so an IPv6 address must belong to this range to route on the public Internet.
Question 31
Which IP address is the broadcast address for subnet 172.16.0.0/19?
A. 172.16.0.255
B. 172.16.31.255
C. 172.16.32.255
D. 172.31.255.255
Answer: B
Explanation
Increment: 32 (/19 is 1110 0000 at 3rd octet)
Network address: 172.16.0.0
Broadcast address: 172.16.31.255
Question 32
Refer to the exhibit.
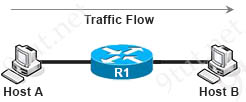
If host A is sending packets to host B, where does the Layer 2 frame rewrite occur?
A. on the router before it forwards the packet to host B
B. on host B when it receives the packet from the router
C. on the router when it receives the packet from host A
D. on host A before it sends the packet toward the router
Answer: A
Explanation
Before forwarding packet to Host B, router R1 needs to rewrite both the source & destination MAC address. The new source MAC would be the MAC address of the exiting interface of R1 and the new destination MAC address would be the MAC address of Host B.
Question 33
Which condition is most important to support the use of syslog messages for troubleshooting?
A. Messages are logged to a UNIX-based server.
B. The router has a large internal buffer space.
C. NTP is in use to ensure accurate timestamps.
D. Messages are logged to a Cisco UCS Server.
Answer: C
Explanation
We have to configure Network Time Protocol (NTP) so that each syslog message is recorded with the correct time which can help us to identify the problem more easily.
Question 34
Which value in a routing table entry represents the subnet mask?
A. prefix length
B. route source code
C. administrative distance
D. next-hop
Answer: A
Explanation
The prefix length in the routing table, for example: 192.168.1.0/24, helps us indicate the subnet mask (in this case /24 is equivalent to the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0).
Question 35
Which statement about port security is true?
A. It is not supported on private VLANs.
B. It can be configured on SPAN destination ports.
C. The default port security configuration allows for a maximum of 10 MAC addresses.
D. In sticky mode, the port retains dynamically-learned addresses during a link failure.
Answer: D
Explanation
The “sticky ” keyword (in the command switchport port-security mac-address sticky [MAC]) is used to make the MAC address appear in the running configuration so even if during a link failure, the port still retains the dynamically-learned addresses. But if we don’t save them (to the startup configuration) before rebooting, they will be lost.
Question 36
Which configuration register value do you enter on a device to bypass the startup configuration?
A. 0x2102
B. 0x2120
C. 0x2124
D. 0x2142
Answer: D
Explanation
By changing the configuration register to 0x2142, when that router reboots it will bypass the startup-config and no password is required.
Question 37
Which two DNS record types are currently supported? (Choose two)
A. NIL
B. A
C. MX
D. B
E. ACK
Answer: B C
Explanation
Commonly used record types:
+ A (Host address)
+ AAAA (IPv6 host address)
+ ALIAS (Auto resolved alias)
+ CNAME (Canonical name for an alias)
+ MX (Mail eXchange)
+ NS (Name Server)
+ PTR (Pointer)
+ SOA (Start Of Authority)
+ SRV (location of service)
+ TXT (Descriptive text)
Question 38
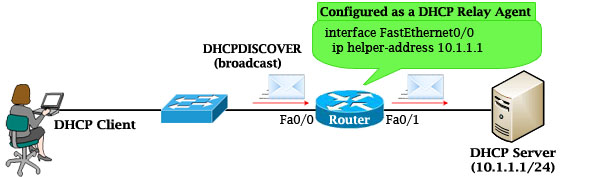
Which command can you enter to forward DHCP requests to a server on behalf of a client on a different network?
A. service dhcp
B. network 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0
C. ip helper-address address
D. ip dhcp-pool pool_name
Answer: C
Explanation
If the DHCP Server is not on the same subnet with the DHCP Client, we need to configure the router on the DHCP client side to act as a DHCP Relay Agent so that it can forward DHCP messages between the DHCP Client & DHCP Server. To make a router a DHCP Relay Agent, simply put the “ip helper-address <IP-address-of-DHCP-Server>” command under the interface that receives the DHCP messages from the DHCP Client.
Question 39
Which statement about device security is true?
A. A router can have a maximum of two passwords configured
B. The password you configure is encrypted in the running configuration by default
C. The enable password must be used before the enable secret password
D. If an encrypted password is lost, the NVRAM configuration must be ignored on boot
Answer: D
Explanation
NVRAM holds the router’s startup configuration file. Therefore if we forget the password of the device, we should ignored the NVRAM configuration on boot. We usually do this by changing the configuration register to 0x2142.
Question 40
Which option can be used in case a backup route is required in the routing table?
A. floating static route
B. No extra configuration is required.
C. next hop
D. route distribution
Answer: A
Explanation
Floating static routes are static routes that have an administrative distance greater than the administrative distance (AD) of another static route or dynamic routes. By default a static route has an AD of 1 then floating static route must have the AD greater than 1. Floating static route has a manually configured administrative distance greater than that of the primary route and therefore would not be in the routing table until the primary route fails.
Question 41
Which two features are supported with SLAAC? (Choose two)
A. Duplicate IPv6 addresses are detected.
B. The first 64 bits of a device IPv6 address can be calculated automatically from its MAC address.
C. IPv6 address have an infinite lifetime by default.
D. Router advertisements can track lifetime timers.
E. Globally-routed paths are preferred over equal-cost link-local paths.
Answer: A D
Explanation
IPv6 stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC) is the native IPv6 method used to provide end hosts with IPv6 address and default gateway information dynamically without requiring DHCPv6 address allocation.
Stateless Address Auto-Configuration (SLAAC) is configured as follows:
+ Host sends a router solicitation message.
+ Hosts waits for a Router Advertisement message.
+ Hosts take the first 64 bits of the IPv6 prefix from the Router Advertisement message and combines it with the 64 bit EUI-64 address (in the case of ethernet, this is created from the MAC Address) to create a global unicast message (-> Answer B is not correct). The host also uses the source IP address, in the IP header, of the Router Advertisement message, as its default gateway.
+ Duplicate Address Detection is performed by IPv6 clients in order to ensure that random addresses that are picked do not collide with other clients.
+ The choice of algorithm is up to the client and is often configurable.
The Router Lifetime field in the Router advertisement (RA) can track lifetime timers.
Question 42a
Which IPv4 address type is used to communicate with all hosts on a subnet?
A. broadcast
B. link-local
C. anycast
D. multicast
Answer: A
Question 42b
Which IPv4 address type can reach each node on a network?
A. unicast
B. anycast
C. broadcast
D. multicast
Answer: C
Question 43
Which VLAN ID is reserved?
A. 1
B. 1002
C. 1006
D. 4094
Answer: B
Explanation
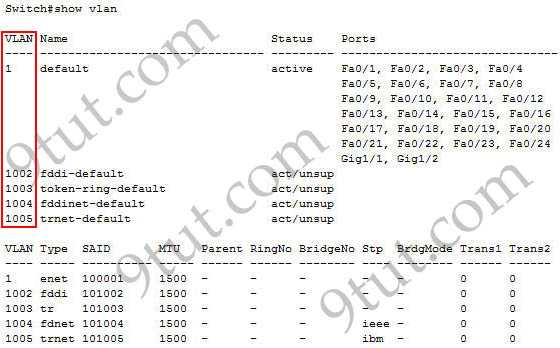
VLANs 1002-1005 are default VLANs for FDDI & Token Ring. They are reserved and cannot be deleted or used for Ethernet.
Question 44
An administrator is in the process of changing the configuration of a router. What command will allow the administrator to check the changes that have been made prior to saving the new configuration?
A. Router# show startup-config
B. Router(config)# show running-config
C. Router# show running-config
D. Router# show running-config changes
Answer: C
Question 45
Which step is needed to configure SSH on a switch?
A. Configuring an IP domain name.
B. Configuring RSTP.
C. Configuring an SNMP community string.
D. Configuring Telnet on a VTY line.
Answer: A
Explanation
There are four steps required to enable SSH support on a Cisco IOS router:
1. Configure the hostname command.
2. Configure the DNS domain.
3. Generate the SSH key to be used.
4. Enable SSH transport support for the virtual type terminal (vtys).
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security-vpn/secure-shell-ssh/4145-ssh.html
Question 46a
You attempt to ping a remote device by name from a PC, and the ping operation fails and returns the error message “Ping request could not find host.” You verify that the router DHCP pool is configured with a name server. What are two possible reasons for the problem? (Choose two)
A. The DNS server is not reachable.
B. The PC network interface card device driver is missing.
C. The host that must be resolved does not exist.
D. The subnet mask of the DHCP pool is incorrect.
E. The DHCP server cannot provide an address to the PC.
Answer: A C
Explanation
As we ping by name so a valid DNS server is required. Therefore if we cannot ping to the destination device then maybe either the DNS server or the remote device was down/unreachable.
Question 46b
Refer to the exhibit.
| % Unrecognized host or address, or protocol not running |
You ping a remote device by name from a router, and the ping operation returns this response. What are two reasons for this problem? (Choose two)
A. An ACL on the router blocked the ping.
B. A firewall blocked the ping.
C. The DNS server database does not include a record for the name.
D. The router is blacklisted by the DNS server.
E. Only one DNS server is configured on the router.
Answer: C D
Question 47
Which value does an IPv6 host use to create an EUI-64?
A. the MAC address
B. the OSPFv6 router ID
C. the IPv6 address
D. the IPv4 address
Answer: A
Explanation
Extended Unique Identifier (EUI) allows a host to assign itself a unique 64-Bit IPv6 interface identifier (EUI-64). This feature is a key benefit over IPv4 as it eliminates the need of manual configuration or DHCP as in the world of IPv4. The IPv6 EUI-64 format address is obtained through the 48-bit MAC address. The MAC address is first separated into two 24-bits, with one being OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier) and the other being NIC specific. The 16-bit 0xFFFE is then inserted between these two 24-bits for the 64-bit EUI address. IEEE has chosen FFFE as a reserved value which can only appear in EUI-64 generated from the an EUI-48 MAC address.
For example, suppose we have the MAC address of C601.420F.0007. It would be divided into two 24-bit parts, which are “C60142” (OUI) and “0F0007” (NIC). Then “FFFE” is inserted in the middle. Therefore we have the address: C601.42FF.FE0F.0007.
Then, according to the RFC 3513 we need to invert the Universal/Local bit (“U/L” bit) in the 7th position of the first octet. The “u” bit is set to 1 to indicate Universal, and it is set to zero (0) to indicate local scope.
Therefore with the subnet of 2001:DB8:0:1::/64, the full IPv6 address is 2001:DB8:0:1:C601:42FF:FE0F:7/64
Question 48
Which protocol does a Cisco IP phone use to identify the voice VLAN?
A. CDP
B. LDAP
C. SIP
D. COS
Answer: A
Explanation
Cisco IP phones use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to know which VLANs to use.
Note: Voice vlan is just an ordinary VLAN. But in access port configuration you can specify that voice VLAN is exactly for voice traffic.
Question 49
You ping a remote device by name from a router, and the router you are using immediately displays a new prompt. What are two possible reasons for the problem? (Choose two)
A. The IP address of the remote device is listed in multiple ip host statements in the router configuration.
B. The ACL on the router blocked the ping.
C. The DNS server configuration on the router is missing.
D. The DNS server is unreachable.
E. The no ip domain-lookup command is configured on the router.
Answer: C E
Question 50
Which three statements about a meshed topology are true? (Choose three)
A. Every core device is connected to a distribution device.
B. Each access switch must be connected to at least one upstream distribution device and at least one core device.
C. Each distribution device is connected to exactly one core device.
D. Each access switch must be connected to exactly one upstream distribution device.
E. Every upstream distribution device is connected to an access switch.
F. Each access switch must be connected to at least two upstream distribution devices.
Answer: A E F
Explanation
This question wants to mention about hierarchical and meshed topology. Such a topology is shown below:
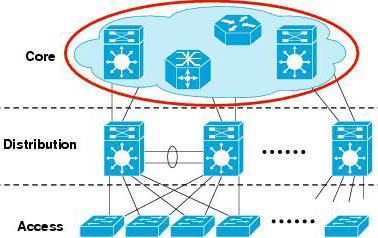
Note: Hierarchical network design has three layers: core, distribution, and access
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Campus/HA_campus_DG/hacampusdg.html
Question 51
Which two fields are included in an Ethernet header? (Choose two)
A. source MAC address
B. destination IP address
C. payload
D. Ether Type
E. source IP address
Answer: A D
Explanation
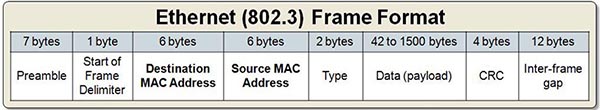
Below is the Ethernet frame format which includes source MAC address and (Ether) type:
Question 52
Refer to the exhibit.
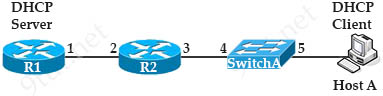
Which interface must be configured as the DHCP relay agent so that host A can receive an IP address from the DHCP server?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
Answer: C
Explanation
If the DHCP Server is not on the same subnet with the DHCP Client, we need to configure the router on the DHCP client side to act as a DHCP Relay Agent so that it can forward DHCP messages between the DHCP Client & DHCP Server. To make a router a DHCP Relay Agent, simply put the “ip helper-address <IP-address-of-DHCP-Server>” command under the interface that receives the DHCP messages from the DHCP Client.

Question 53
Which two network device types perform the translation of internal IP addresses to external IP addresses? (Choose two)
A. ACS
B. routers
C. bridges
D. WLCs
E. firewalls
Answer: B E
Question 54
Which two fields are used in TCP and UDP headers? (Choose two)
A. urgent pointer
B. ACK number
C. checksum
D. length
E. padding
Answer: C D
Explanation
The TCP and UDP headers are shown below:

As we can see, the UDP header is very simple with only 4 fields: source port, destination port, length and checksum. The two last fields also present in TCP headers. In which the length field is the size (in bytes) of the UDP header and the encapsulated data.
Question 55
Which two statements about access ports are true? (Choose two)
A. They can act as a host and a trunk port simultaneously
B. They forward all 802.1Q packets to trunk ports
C. An individual access port can transmit traffic for only one data VLAN
D. Each individual access port can support multiple data VLANs
E. They are assigned to VLAN 1 by default
Answer: C E
Question 56
You recently applied a common configuration to several PCs on different VLANs. The PCs are connected to the same switch with a router-on-a-stick, but users report that the PCs cannot ping one another. Which two are possible reasons for the problem? (Choose two)
A. The access ports on the PCs are misconfigured.
B. The native VLAN on the router is misconfigured.
C. The ip default-network command is misconfigured on the router.
D. The trunking protocol is configured incorrectly on the router subinterfaces.
E. The VLAN is configured incorrectly on the router subinterfaces.
Answer: A E
Question 57
Refer to the exhibit.
switch-A#show mac address-table
MAC Address Table
----------------------------------------
Vlan Mac Address Type Ports
---- ----------- ------- --------
1 0000.0000.0001 DYNAMIC Fa0/1
Total Mac Addresses for this criterion: 1
If switch-A receives a frame with destination MAC address 0000.0000.0001 on its Fa0/1 interface, how does it process the frame?
A. It holds the packet until MAC address timer expires and then drops the frame.
B. It forwards the frame back out of interface Fa0/1.
C. It floods the frame to all interfaces except Fa0/1.
D. It drops the frame immediately.
Answer: D
Explanation
In brief, the basic switching function at Layer 2 adheres to these rules for determining forwarding responsibility:
+ If the destination MAC address is found in the CAM table, the switch sends the frame out the port that is associated with that destination MAC address in the CAM table. This process is called forwarding.
+ If the associated port to send the frame out is the same port that the frame originally came in on, there is no need to send the frame back out that same port, and the frame is ignored. This process is called filtering.
+ If the destination MAC address is not in the CAM table (that is, unknown unicast), the switch sends the frame out all other ports that are in the same VLAN as the received frame. This is called flooding. It does not flood the frame out the same port on which the frame was received.
+ If the destination MAC address of the received frame is the broadcast address (FFFF.FFFF.FFFF), the frame is sent out all ports that are in the same VLAN as the received frame. This is also called flooding. The only exception is the frame is not sent out the same port on which the frame was received.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2348264
In the output, switch A learned that the device with MAC address of 0000.0000.0001 is attached to port Fa0/1. But the switch receives a frame with the same destination MAC address from port Fa0/1 so the switch will filter out (drop) this frame.
Question 58
Which two statements about prefixes in a routing table are true? (Choose two)
A. The router prefers longer prefixes over shorter prefixes.
B. The router prefers prefixes that have more bit positions for the host than for the network.
C. The router prefers the prefix that includes the most 1 bits in the subnet mask.
D. The router prefers shorter prefixes over longer prefixes.
E. The router prefers the prefix that includes the most 0 bits in the subnet mask.
Answer: A C
Explanation
Suppose there are three routes in our routing table:
router# show ip route .... D 192.168.32.0/26 [90/25789217] via 10.1.1.1 R 192.168.32.0/24 [120/4] via 10.1.1.2 O 192.168.32.0/19 [110/229840] via 10.1.1.3 ....
If a packet arrives on a router interface destined for 192.168.32.1, which route would the router choose? It depends on the prefix length, or the number of bits set in the subnet mask. Longer prefixes are always preferred over shorter ones when forwarding a packet.
In this case, a packet destined to 192.168.32.1 is directed toward 10.1.1.1, because 192.168.32.1 falls within the 192.168.32.0/26 network (192.168.32.0 to 192.168.32.63). It also falls within the other two routes available, but the 192.168.32.0/26 has the longest prefix within the routing table (26 bits verses 24 or 19 bits).
Likewise, if a packet destined for 192.168.32.100 arrives on one of the router’s interfaces, it’s forwarded to 10.1.1.2, because 192.168.32.100 doesn’t fall within 192.168.32.0/26 (192.168.32.0 through 192.168.32.63), but it does fall within the 192.168.32.0/24 destination (192.168.32.0 through 192.168.32.255). Again, it also falls into the range covered by 192.168.32.0/19, but 192.168.32.0/24 has a longer prefix length.
-> This is called “longest prefix match” rule so answer A is correct.
Answer C has the same meaning as “the most 1 bits in the subnet mask” means “longer prefix”
Question 59
Which two attributes of a packet change at every router along the path from source to destination? (Choose two)
A. destination IP address
B. source MAC address
C. packet MTU
D. source IP address
E. destination MAC address
Answer: B E
Explanation
When a packet is sent from a source to a destination, only the source & destination MAC addresses are changed on each segment while the source & destination IP addresses remain unchanged.
Question 60
Refer to the exhibit.

If Host A pings Host B, which statement about the ping is true?
A. The router looks up the destination IP network of the ping in its MAC address table
B. Host A encapsulates the packet within a frame before sending it
C. The ping packet includes both the destination MAC address and the source address
D. Host A sends the packet one byte at a time
Answer: B
Explanation
The router will check the destination IP network in its routing table -> Answer A is not correct.
The ping packet from host A will include: the source IP address of host A, the destination IP address of host B; the source MAC address of host A and the destination MAC address of the inbound interface of R1 -> Answer C is not correct.
When we make a ping from a Windows OS host, each ping packet is 32 bytes but if we ping from a Linux OS host, each ping packet is 64 bytes so it depends on the Operating System (OS) of the host. But each ping packet is surely larger than one byte -> Answer D is not correct.
Question 61
Which statement about port security on a trunk link is true?
A. It error-disables the port after 10 MAC addresses are statically configured
B. It is not supported
C. By default, it shuts down the port if it learns more than one MAC address
D. When it is enabled, it disables the native VLAN configuration
Answer: C
Explanation
Although some online Cisco documents say that “A secure port cannot be a trunk port” (like this document) but some say “Trunk port security extends port security to trunk ports” (like this document) so we decided to test on a Cisco switch version 15.1 and had this result:
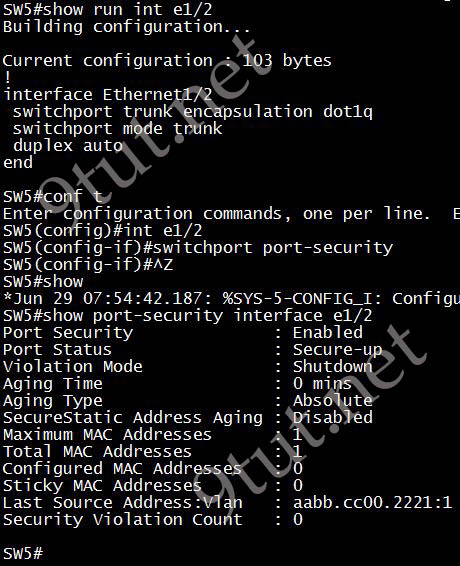
So we can configure port-security on a trunk port and the maximum MAC addresses allowed is 1 and the violation mode is “Shutdown” by default. Therefore it will shutdown the port if it learns more than one MAC address.
Question 62
Which component of an Ethernet frame supports error detection?
A. EtherType
B. frame check sequence
C. 802.1Q tag
D. preamble
Answer: B
Explanation
At the end of each frame there is a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. FCS can be analyzed to determine if errors have occurred. FCS uses cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithm to detect errors in the transmitted frames. Before sending data, the sending host generates a CRC based on the header and data of that frame. When this frame arrives, the receiving host uses the same algorithm to generate its own CRC and compare them. If they do not match then a CRC error will occur.

Question 63
Which two statements about administrative distance are true? (Choose two)
A. The metric is used to determine which administrative distance is selected from the routing table.
B. The metric is calculated independently of the administrative distance.
C. It identifies the routing protocol priority.
D. It identifies the metric used for path calculation.
E. The metric uses the administrative distance to calculate a path.
Answer: B C
Explanation
The administrative distance (AD) of a routing protocol is fixed while the metric of each routing protocol is calculated based on some parameters (for example in RIP it is the hop count, in OSPF it is the bandwidth…) -> Answer B is correct.
The lower the AD, the higher priority of the routing protocol. For example, EIGRP (AD of 90) is always preferred to OSPF (AD of 110).
Question 64
Which two IPv6 multicast groups are joined when an IPv6 address is configured on an interface? (Choose two)
A. FF02::2
B. 2002::5
C. FF80::6
D. FF80::5
E. FF02::1
Answer: A E
Explanation
Every device automatically joins the all nodes (FF02::1) and solicited-node (FF02::1:FFxx:xxxx) multicast groups. The all-node group is used to communicate with all interfaces on the local link, and the solicited-nodes multicast group is required for link-layer address resolution. Routers also join a third multicast group, the all-routers group (FF02::2).
Reference: IP Routing on Cisco IOS, IOS XE, and IOS XR: AN Essential Guide to Understanding and Implementing IP Routing Protocols
These addresses are equivalent to IPv4 well-known multicast addresses in the range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
Question 65
Which command do you enter to assign all untagged packets on a trunk to VLAN 999?
A. switchport trunk pruning vlan add 999
B. switchport trunk allowed vlan 999
C. switchport trunk native vlan 999
D. swtichport trunk allowed vlan add 999
Answer: C
Explanation
By default the native VLAN is 1 but we can assign a new native VLAN by the command “switchport trunk native vlan <vlan-id>”.
Question 66
Which two commands must you apply to a router to configure it as a router-on-a-stick? (Choose two)
A. spanning-tree portfast
B. encapsulation
C. vtp domain
D. vtp transparent
E. ip address
Answer: B E
Explanation
An example of how to configure a router-on-a-stick at router side is shown below:
R1(config)#int fa0/0
R1(config-if)#no ip address
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int fa0/0.10
R1(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10 //Configure dot1q encapsulation for VLAN 10 on sub-interface fa0/0.10
R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
R1(config-subif)#no shutdown
R1(config)#int fa0/0.20
R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
R1(config-subif)#no shutdown
Question 67
How does an access port configured for VLAN 10 handle an incoming packet with an 802.1q tag for VLAN 2?
A. It drops the packet.
B. It dynamically configures the port to accept traffic on VLAN 2.
C. It adds VLAN 2 to the VLAN database.
D. It forwards the packet to a port on VLAN 2.
E. It processes the packet and places it in a queue for future delivery.
Answer: A
Question 68
In which network topology does each network device have a direct physical connection to every other device?
A. point-to-multipoint
B. mesh
C. bus
D. star
Answer: B
Explanation
Full-mesh is a network topology in which there is a direct link between all pairs of nodes. Below is an example of full-mesh topology.
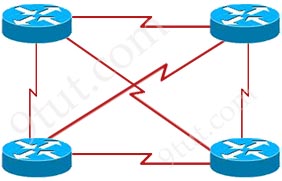
Question 69
Which two statements about IPv6 SLAAC are true? (Choose two)
A. The default gateway of the host is configured during the SLAAC process
B. It is incompatible with DHCP
C. The host uses the EUI-64 algorithm to calculate the first 64 bits of the destination IPv6 address from the MAC address
D. It has a built-in mechanism to identify duplicate IP addresses on the network
E. The host sends a router advertisement message to begin the SLAAC process
Answer: A D
Explanation
IPv6 stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC) is the native IPv6 method used to provide end hosts with IPv6 address and default gateway information dynamically without requiring DHCPv6 address allocation.
Stateless Address Auto-Configuration (SLAAC) is configured as follows:
+ Host sends a router solicitation message.
+ Hosts waits for a Router Advertisement message.
+ Hosts take the first 64 bits of the IPv6 prefix from the Router Advertisement message and combines it with the 64 bit EUI-64 address (in the case of ethernet, this is created from the MAC Address) to create a global unicast message (-> Answer B is not correct). The host also uses the source IP address, in the IP header, of the Router Advertisement message, as its default gateway.
+ Duplicate Address Detection is performed by IPv6 clients in order to ensure that random addresses that are picked do not collide with other clients.
+ The choice of algorithm is up to the client and is often configurable.
Question 70
In which two scenarios do you implement private IPv4 IP addresses? (Choose two)
A. on the webmail portal of an organization
B. on the connection that a mobile device uses for application updates
C. to connect network equipment between different IDFs
D. for the VPN solution that end users use to connect to the local network
E. on an application server that connects to a local database server
Answer: C E
Explanation
In general, private IPv4 addresses are suitable for applications/connections that do not need to go to the Internet.
The intermediate distribution frames (IDF) refers to the switches in the access layer which provide connection in a building so they don’t need to use public IPv4 address to go to the Internet -> Answer C is correct.
Question 71
Which two ACL types support IP Access List Entry Sequence Numbering? (Choose two)
A. named
B. reflexive
C. firewall
D. dynamic
E. standard
Answer: A E
Explanation
The IP Access List Entry Sequence Numbering feature allows you to apply sequence numbers to permit or deny statements as well as reorder, add, or remove such statements from a named IP access list. The IP Access List Entry Sequence Numbering feature makes revising IP access lists much easier. Prior to this feature, you could add access list entries to the end of an access list only; therefore, needing to add statements anywhere except at the end of a named IP access list required reconfiguring the entire access list.
For example, we can resequence a standard/extended access list like this:
Device(config)# ip access-list resequence MYACCESSLIST 100 15 //resequence the MYACCESSLIST, starting from 100 and increment 15
After this command the “MYACCESSLIST” ACL will be like this:
| R1#show access-list Standard IP access list MYACCESSLIST 100 permit ip host xxxx host xxxxx 115 permit ip host xxxx host xxxxx 130 permit ip host xxxx host xxxxx 145 permit ip host xxxx host xxxxx 160 permit ip host xxxx host xxxxx 175 permit ip host xxxx host xxxxx 190 permit ip host xxxx host xxxxx |
We can use The IP Access List Entry Sequence Numbering feature in standard, extended and named ACL.
Question 72
Which command can you enter in ROMmon to bypass the password in the router startup configuration?
A. confreg 0x2142
B. configure terminal
C. config-register 0x2102
D. reset
Answer: A
Question 73
For which reason is a DHCP client unable to reach a host in different subnet?
A. The client and its gateway router have been assigned different subnet masks.
B. The client has been configured with only one DNS server.
C. DNS lookup has been disabled on the gateway router.
D. The client is connected to a switch in the same VLAN as its gateway router.
Answer: A
Question 74
Which command or command sequence do you enter to install a default route into a router that is configured with the no ip routing command?
A. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
B. router rip ip default-gateway
C. ip default-network
D. ip default-gateway
Answer: D
Explanation
When using the “no ip routing” command, a router will function like a host so we cannot perform routing function on it. We can only use the “ip default-gateway <IP address>” command to assign a default gateway for it (same as the default gateway in a host).
Question 75
Refer to the exhibit.
| show ip route 192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks |
Router R1 produced this partial output running on a current IOS. Which two statements about R1 and its network environment are true? (Choose two)
A. R1 has a combination of local and connected routes totaling two subnets.
B. R1 has learned a maximum of four networks via routing protocols.
C. R1 has a maximum of two connected subnets including local route.
D. R1 has learned at least one network via routing protocols.
E. R1 has a network environment that supports a maximum of 16 hosts.
Answer: C D
Question 76
Under which circumstance should a network administrator implement only outgoing NAT towards an ISP?
A. when traffic that originates inside the network must be routed to internal hosts
B. when the network has few public IP addresses and many private IP addresses that require outside access
C. when the network must route UDP traffic
D. when traffic that originates outside the network must be routed to internal hosts
Answer: B
Question 77
Which two syslog configuration commands do you use to log warnings to the syslog server? (Choose two)
A. logging trap level informational
B. logging trap level alerts
C. logging trap level notice
D. logging trap level critical
E. logging trap level error
Answer: A C
Question 78
Which three values must you specify to resequence an IP access list? (Choose three)
A. access list name
B. increment
C. starting sequence number
D. interface
E. dynamic access list number
F. ending sequence number
Answer: A B C
Question 79
For which two reasons might you choose to configure dynamic routing instead of static routing on a router? (Choose two)
A. The router is part of a stub network.
B. The router needs access only to a single default route.
C. Dynamic routing requires less router configuration throughout the network than static routing.
D. The network is growing intermittently.
E. Dynamic routing updates are more secure than static routing updates.
Answer: C D
Question 80
All protocols on a network are using their default administrative distances with no redistribution. In which two different ways can you modify them so that OSPF and RIPv2 learned routes are preferred over EIGRP-learned routes? (Choose two)
A. Change the OSPF administrative distance to 5.
B. Change the RIP administrative distance to 70.
C. Change the EIGRP administrative distance to 70.
D. Change the RIP administrative distance to 100.
E. Change the EIGRP administrative distance to 100.
Answer: A B
Question 81
Which two characteristics of plenum cable are true? (Choose two)
A. It is more fire-resistant than nonplenum cable.
B. It can be installed above a drop-down ceiling without additional safety precautions.
C. It is less fire-resistant than nonplenum cable.
D. When it burns, it may release more toxins than nonplenum cable.
E. It requires additional safety precautions when installed above a drop-down ceiling.
Answer: A B
Question 82
Which statement about wireless access points is true?
A. They are Layer 2 devices that are used to extend a LAN to wireless clients.
B. They provide full duplex connectivity to host devices.
C. They are used as routers between LANs in a wireless network.
D. They are used to physically connect host devices to the wireless network.
Answer: A
Question 83
Which option is the default time zone used on Cisco devices?
A. CST
B. UTC
C. EST
D. GMT
E. PST
Answer: B
Question 84
Which circumstance causes a security violation on a switch port with port security enabled?
A. The maximum number of secure MAC addresses is reached on a secure port and an unidentified MAC address attempts an ingress connection.
B. A configured MAC address attempts an ingress connection on a different port in a different VLAN.
C. The minimum number of secure MAC addresses is configured on a secure port and an unidentified MAC address attempts an ingress connection.
D. A minimum number of secure MAC addresses has filled the dynamic table.
Answer: A
Question 85
You have configured two hosts that are connected to a single switch, but reside in different VLANs. Which statement about the configuration is true?
A. The two hosts are unable to communicate without a router.
B. The two hosts can communicate with ICMP.
C. The two hosts are unable to communicate without a trunk port.
D. The two hosts are unable to communicate without a hub.
Answer: A
Question 86
Which type of route is the most trusted?
A. BGP
B. OSPF
C. static
D. connected
Answer: D
Question 87
Which statement about the enable password is true?
A. The space character is not supported.
B. It is not stored in a secured format.
C. It can be up to 32 characters long.
D. It is stored in a secured format.
Answer: B
Question 88
For what reason do you use a standard access list?
A. to filter traffic from identified source addresses
B. to deny traffic to identified destination addresses
C. to load-balance traffic over different interfaces
D. to identify traffic to be label-switched through the network
E. to deny traffic to unidentified destination addresses
Answer: A
Question 89
How does a switch handle a frame in which it detects an error in the frame check sequence?
A. It updates the frame check sequence and forwards the frame to its destination.
B. It discards the damaged frame without further action.
C. It forwards the frame to its destination unchanged.
D. It discards the damaged frame and requests the sender to retransmit it.
Answer: B
Question 90
Which static route can be used to forward a packet that is destined to 192.168.1.23?
A. ip route 192.168.1.16 255.255.255.252 192.168.255.1
B. ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.240 192.168.255.1
C. ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.255.1
D. ip route 192.168.1.20 255.255.255.252 192.168.255.1
Answer: D
Question 91
If a router receives a route 192.168.1.0/24 from peers running OSPF and EIGRP, how does the router forward traffic destined to that network?
A. It uses the path with the lowest metric.
B. It always uses the path learned from OSPF because OSPF is a vendor-neutral protocol.
C. It load-balances traffic across both paths.
D. It always uses the path learned from EIGRP because EIGRP has a lower administrative distance.
Answer: D
Question 92
Which statement about a router on a stick is true?
A. It requires encapsulation to be configured on subinterfaces.
B. It requires encapsulation to be configured on the main interface.
C. The VLAN tag is randomly assigned as a frame exists the interface.
D. A single VLAN can traverse the link.
Answer: A
Question 93
Which IPv6 address does a device use for neighbor discovery?
A. the link-local address
B. the multicast address
C. the unique local address
D. the global unicast address
Answer: A
Question 94
How are MAC addresses removed from a MAC address table?
A. They are removed automatically if they remain inactive for the duration of the switch aging timer.
B. They are removed automatically on a FIFO basis when the address-table limit has been reached.
C. They must be manually cleared from the table.
D. They are removed automatically if they remain inactive for the duration of the global MAC address timer.
Answer: D
Question 95
Which two statements are true about the operation of a full-duplex Ethernet network? (Choose two)
A. There are no collisions in full-duplex mode.
B. A dedicated switch port is not required for each full-duplex node.
C. Ethernet hub ports are preconfigured for full-duplex mode.
D. The device network card and the switch port must be capable of operating in full-duplex mode.
E. In a full-duplex environment, the host network card must check for the availability of the network media before transmitting.
Answer: A D
Question 96
Which value represents a host route?
A. 192.168.1.0/30
B. 192.168.1.0/24
C. 192.168.1.2/31
D. 192.168.1.0/32
Answer: D
Question 97
Which Cisco IOS feature can dynamically assign IP addresses to hosts?
A. DHCP Relay
B. TFTP
C. DNS
D. DHCP
Answer: D
Question 98
Which two statements about the default configuration of a Cisco IOS router are true? (Choose two)
A. In privileged EXEC mode, the console times out after 10 minutes of inactivity.
B. The loopback 0 interface is enabled.
C. The first connected interface becomes the gateway of last resort.
D. The enable password password and enable secret password are both set to cisco.
E. The hostname of the device is displayed in lower-case letters only, even if you specify capital letters.
F. The default hostname is Router.
Answer: A F
Question 99
Which statement about a router-on-a-stick configuration is true?
A. It is most appropriate for use on large networks with both Layer2 and Layer3 switches.
B. It can perform 802.1q encapsulation.
C. It can act as a multilayer switch.
D. It can classify packets for QoS.
Answer: B
Question 100
Which information is missing from a default syslog message?
A. HOSTNAME
B. SEVERITY
C. MESSAGE
D. TIMESTAMP
Answer: A
Question 101
Which statement about the default Cisco Discovery Protocol configuration is true?
A. CDPv1 is disabled on FastEthernet interfaces.
B. CDPv2 advertisements are unicast.
C. CDPv1 is enabled on Frame Relay subinterfaces.
D. CDPv2 advertisements are broadcast.
Answer: D
Question 102
A router is deployed with the default factory settings. If a user on the router mistypes a command, which option is the result?
A. The router immediately returns an error message.
B. The router recognizes the mistake and discards the request.
C. The router autocorrects the mistyped command.
D. The router attempts to resolve the command to an IP address.
E. The router disables DNS lookup.
Answer: D
Explanation
When you mistype a command in privileged mode (Router#), the router thinks you’re trying to Telnet to a remote host so you have to wait with a message like this:
Translating “contin”…domain server (255.255.255.255)
This is because by default the command “ip domain-lookup” is enabled. It enables the Domain Name Server (DNS) lookup feature which performs a DNS lookup on what you entered. If you haven’t configured DNS on the router, the command prompt will hang until the DNS lookup fails. We can cancel the translation with Ctrl + Shift + 6. If we don’t have a real DNS server then we should turn this feature off with the “no ip domain-lookup” command.
Question 103
Which value does RIPv2 use to calculate its route metric?
A. delay
B. bandwidth
C. hop count
D. reliability
Answer: C
Explanation
RIP only uses hop count (the number of routers) to determine the best way to a remote network.
Question 104
Which value is calculated by the sender and receiver of a frame to determine whether the frame has been damaged in transit?
A. the runt value
B. the CRC value
C. the giant value
D. the collision value
Answer: B
Explanation
At the end of each frame there is a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. FCS can be analyzed to determine if errors have occurred. FCS uses cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithm to detect errors in the transmitted frames. Before sending data, the sending host generates a CRC based on the header and data of that frame. When this frame arrives, the receiving host uses the same algorithm to generate its own CRC and compare them. If they do not match then a CRC error will occur.

Note:
+ Runts are frames which do not meet the minimum frame size of 64 bytes. Runts are usually created by collisions.
+ Giants: frames that are larger than 1,518 bytes
Question 105
What is the default number of secure MAC addresses for an interface configured with port security?
A. 1
B. 255
C. 1042
D. 3072
Answer: A
Question 106
Which device mode must you use to recover a password on a Cisco IOS device?
A. privileged EXEC
B. global configuration
C. user EXEC
D. ROMmon
Answer: D
Explanation
To reset the password we can type “confreg 0x2142” under rommon mode to set the configuration register to 2142 in hexadecimal (the prefix 0x means hexadecimal (base 16)). With this setting when that router reboots, it bypasses the startup-config.
Question 107
Which difference between TCP and UDP is true?
A. Only TCP orders the packets that are transmitted.
B. Only UDP retransmits packets to ensure delivery.
C. Only TCP has eliminated error checking.
D. Only UDP requires recipients to acknowledge packet receipt.
Answer: A
Explanation
UDP header does have a checksum field which provides error detection for this protocol. But the difference (from TCP) is it does not request a retransmit when an error is found, it just simply discards that packet. In short, UDP has error detection while TCP has error recovery mechanism.
Question 108
Which command do you enter to configure a device as an authoritative time server?
A. ntp authenticate
B. ntp server 127.0.0.1
C. ntp source 127.0.0.1
D. ntp master 1
Answer: D
Explanation
An Authoritative NTP Server can distribute time even when it is not synchronized to an existing time server. To configure a Cisco device as an Authoritative NTP Server, use the ntp master [stratum] command.
Question 109
Which two configuration steps will prevent an unauthorized PC from accessing the corporate network? (Choose two)
A. set the port security aging time to 0
B. create the port as a protected port and statically assign the MAC address to the address table
C. configure the switch to discover new MAC addresses after a set time of inactivity
D. enable port security on the switch
E. create the port as an access port and statically assign the MAC address to the address table
Answer: D E
Question 110
Which description refers to administrative distance?
A. the advertised metric to reach a network
B. the cost of a link between two neighboring routers
C. the cost to reach a network that is administratively set
D. a measure of the trustworthiness of a routing information source
Answer: D
Question 111
Which command do you enter on a router running RIP so that it advertises a route on the same interface on which it received the route?
A. no auto-summary
B. no ip split-horizon
C. passive-interface default
D. ip rip v2-broadcast
Answer: B
Explanation
The split-horizon rule states that “a router never sends information about a route back in same direction which is original information came”. This rule is used in distance vector protocol (like RIP or EIGRP) to prevent Layer 3 routing loop. But we can disable the rule with the “no ip split-horizon” command.
Question 112
Which hashing algorithm does NTP use for its authentication keys?
A. MD5
B. AES-256
C. 3DES
D. SHA
Answer: A
Explanation
MD5 keys are used for authentication only, not encryption. The purpose of the keys is to ensure a client it is receiving NTP time stamps from ONLY the intended server.
Question 113
Multicast IP addresses can be grouped into which two address-range assignments? (Choose two)
A. registered
B. dynamic
C. GLOP
D. source-specific multicast
E. private
Answer: A B
Question 114
Which two statements about 802.1Q are true? (Choose two)
A. It is an open-standard trunking protocol
B. It is a Cisco-proprietary trunking protocol
C. It inserts a 4-byte identifying tag in the Ethernet frame after the source MAC address field.
D. It encapsulates the original data frame inside a trunking header.
E. It uses a 20-bit label to identify packets within a trunk.
Answer: A C
Explanation
IEEE 802.1Q uses an internal tagging mechanism which inserts a 4-byte tag field in the original Ethernet frame itself between the Source Address (SA) and Type/Length fields. Because the frame is altered, the trunking device recomputes the FCS on the modified frame.
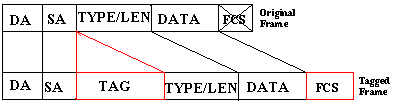
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/8021q/17056-741-4.html
Question 115
Which component is part of an Ethernet frame?
A. checksum
B. TTL
C. sequence number
D. frame check sequence
Answer: D
Explanation
An Ethernet frame structure is shown below:

There are no checksum, Time-to-live (TTL) or sequence number in an Ethernet frame.
At the end of each frame there is a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. FCS can be analyzed to determine if errors have occurred. FCS uses cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithm to detect errors in the transmitted frames. Before sending data, the sending host generates a CRC based on the header and data of that frame. When this frame arrives, the receiving host uses the same algorithm to generate its own CRC and compare them. If they do not match then a CRC error will occur.
Note: In fact in the Ethernet frame structure shown above, the CRC field should be written as FCS field.
Question 116
Which Cisco SDN controller supports existing enterprise network devices?
A. APIC-EM
B. OpenFlow
C. Open SDN
D. ACI
Answer: A
Question 117
Which command can you enter to configure an IPv6 floating static route?
A. router(config)#ipv6 route FE80:0202::/32 serial 0/1 1
B. router (config)#ipv6 route ::/0 serial 0/1
C. router(config)#ipv6 route static resolve default
D. router(config)#ipv6 route FE80.0202::/32serial 0/1 201
Answer: D
Explanation
IPv6 Floating static route is static route with a higher administrative distance than the dynamic routing protocol it is backing up.
Question 118
Which feature can validate address requests and filter out invalid messages?
A. IP Source Guard
B. port security
C. DHCP snooping
D. dynamic ARP inspection
Answer: C
Explanation
DHCP snooping can prevent DHCP spoofing attacks. DHCP snooping is a Cisco Catalyst feature that determines which switch ports can respond to DHCP requests. Ports are identified as trusted and untrusted.
Only ports that connect to an authorized DHCP server are trusted, and allowed to send all types of DHCP messages. All other ports on the switch are untrusted and can send only DHCP requests.
Question 119
Which subnet address is for the IP address 172.19.20.23/28?
A. 172.19.20.20
B. 172.19.20.0
C. 172.19.20.32
D. 172.19.20.15
E. 172.19.20.16
Answer: E
Explanation
Increment: 16 (/28 = 1111 0000 in fourth octet)
Network address: 172.19.20.16
Broadcast address: 172.19.20.31
Question 120
Which two statements are true for multicast MAC address directions? (Choose two)
A. 01:00:5E:AE:17:28
B. one to one
C. 01 00 43 AF5426B
D. 02 46 54BDCF6A8
E. one to many
Answer: A E
Question 121
How many host addresses are available on the network 192.168.1.0 subnet 255.255.255.240? (Choose two)
A. 6
B. 8
C. 14
D. 16
Answer: C
Explanation
240 = 1111 0000 in fourth octet so the formula of host addresses is: the number of host addresses = 2k – 2 (where k is the number of bit 0). In this case k = 4 so the number of host addresses = 24 – 2 = 14.
Question 122
Which two statements about fiber cable are true? (Choose two)
A. Single-mode fiber supports SC and LC connectors only.
B. Multimode cable supports speeds between 100 Mbps and 9.92 Gbps.
C. Single-mode cable is most appropriate for installations longer than 10 km.
D. Fiber cable is relatively inexpensive and supports a higher data rate than coaxial cable.
E. Mulitimode cable supports speeds between 100 Mbps and 100 Gpbs.
Answer: D E
Question 123
After you configure the ip dns spoofing command globally on a device, under which two conditions is DNS spoofing enabled on the device? (Choose two)
A. The ip dns spoofing command is disabled on the local interface
B. The ip host command is disabled
C. All configured IP name server addresses are removed
D. The DNS server queue limit is disabled
E. The no ip domain lookup command is configured
Answer: B C
Explanation
DNS spoofing is designed to allow a router to act as a proxy DNS server and “spoof” replies to any DNS queries using either the configured IP address in the ip dns spoofing ip-address command or the IP address of the incoming interface for the query. This feature is useful for devices where the interface toward the Internet service provider (ISP) is not up. Once the interface to the ISP is up, the router forwards DNS queries to the real DNS servers.This feature turns on DNS spoofing and is functional if any of the following conditions are true:
+ The no ip domain-lookup command is configured.
+ IP name server addresses are not configured.
+ There are no valid interfaces or routes for sending to the configured name server addresses
Question 124
Which statement about unique local IPv6 addresses is true?
A. Summarization is not supported.
B. They require all prefixes to be unique.
C. Their global IDs are assigned sequentially.
D. They are routable to the public Internet.
Answer: B
Explanation
IPv6 Unique Local Address is the approximate IPv6 counterpart of the IPv4 private address. It is not routable on the global Internet but it can be routable inside of a company’s multiple sites. A IPv6 Unique Local Address is an IPv6 address in the block FC00::/7.
Unique Local IPv6 addresses can be viewed as globally unique “private routable” IPv6 addresses, but only inside an organization -> Answer B seems to be correct.


Why question 4 ip routing?its wrong. Could you confirm these are question pearson vue Cisco?
THANK YOU FOR THE UPDATED QUESTIONS!!! I PASSES WITH A 919!!!
Hey Fancy, Same questions?
are those dumps still valid?
Any updates? Any repeated questions from above?
I had the question about switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
would you use the switchport nonegotiate command or not at the end ?
@oh yes
if you try to use command SW2(config-if)#switchport mode trunk you might get an error:
“Command rejected: An interface whose trunk encapsulation is “Auto” can not be configured to “trunk” mode.”
By default the switch will negotiate about the trunk encapsulation type. So you have to change enc. to dot1q (eventually ISL).
SW1(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
BTW. How was the exam? How many questions was repeated from 9tut?
doctore,
it was very difficult it looks like alot of stuff from icnd2 trickled down to incd1
alot of them were repeated i got a 782 i was almost there im taking again this friday the 16th
these are the commands i would use is this right ?
interface fa 0/1
switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
switchport mode trunk
switchport nonegotiate
on the interface would this be correct?
Also that if if you dont use nonegotiate command the the dtp frames will go through
i just dont remember the whole question to be sure
hey can somebody send me the latest dump please? jdsethkesler @ gmail.com
I took the test Today and passed 912/1000 had 6 drag and drop questions , 2 Sims
most of the ICND-1 questions exactly from 9tut.net questions and based on the same concepts
all from icnd1v3-new-questions-part-2 ….good luck everyone…many thanks to 9TUT.NET
congratulation Sheba and thanks for your comment. I am taking the exam on the 12th.
bardiagolkar
@
gmail
.
com
Thank you, exam is in two weeks.
Passed the ICND-1 yesterday. Thanks to 9TUT.NET Same questions from ICND1v3 New Questions Part-2. Off to ICND-2
@cablekrypto: Congrats! Did you see any questions from ICND1v3 New Questions Part-3 as I am learning on it?
Alan
Thanks, there was maybe 1 or 2 questions only, majority was from part 2.
@cablekrypto: Thank you very much for your information!
@cablekrypto: what about the simulations? are they the same as on 9tut?
I had 2 sims. One of them is the same as the configuration sim, the 2nd sim was about RIPv2. Similar to this simulation on the other 9tut website. https://www.9tut.com/ripv2-troubleshooting-sim#more-2853
I passed the ICND1 exam, with 910 final result. All 9tut questions are valid, especially V2. There were 5 Drag & Drop and 2 Labs. One lab is about Switch configuration. Two switches connected eath other, and 2 PC in each switch, the challenger was for creat VLANS 700 and 800, named the vlans and add to respective switches interface.
Hi, Thanks 9tut.net, I passed the ICDN1 exam, with 942, the 60% of questions especially of “ICND1v3 – New Questions Part 2” and the questions are similars questions and I found 10 new questions (Drag of Wireless and Wireless Protocols)
#43 correct answer should be D. 4094
reserved vlans:
0, 4095
1006-1024
1025-4094
Q75
Answer is A and C?
For example, if an IP address of 192.168.1.1/24 is set for the router interface,
the following entry should be created in the routing table.
L 192.168.1.1/32 …
C 192.168.1.0/24…
This is “2 Subnets, 2 masks”,
So [A . combination of local and connected routes totaling two subnets. ] is Collect.
Learning from the routing protocol cannot be judged from this output result, so D is incorrect.
Just passed ICND 1 with a 900. Thank you 9tut.net !!!
Did not pass got 747, needed to focus on sims more next time. Some questions were 9tut. In all fairness I did not use 9tut until a couple days before exam. I was told if you fail 2 sims, you won’t pass anyways.
Hi, i think u miss out another encapsulation dot1q config for the 2nd vlan in the explanation of Question 66.
Hey, someone can explaine me the answer of the question number 90 ?
Can you send me the latest dumps for 100-105 ICND1 to: yopiicnd1 @ gmail.com
much help
Yopi, Below is the explanation about the question 90:
Question 90
Which static route can be used to forward a packet that is destined to 192.168.1.23?
A. ip route 192.168.1.16 255.255.255.252 192.168.255.1
B. ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.240 192.168.255.1
C. ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.255.1
D. ip route 192.168.1.20 255.255.255.252 192.168.255.1
Let’s say the IP address 192.168.1.23 belongs to a specific device, for example PCA. Therefore, this address IP belongs to 192.168.1.20 subnet or network. In this subnet, the first usable IP address will be 192.168.1.21, and 192.168.1.23 will be the third usable IP address. So if I would like to add statically the network 192.168.1.20 where PCA belongs to (192.168.1.23), in my routing table, the command will be:
ip route 192.168.1.20 (target network to add in the routing table) 255.255.255.252 192.168.255.1 (can be next hop IP).
I hope it’s help.
someone please explain about Q-96 why the answer is D?
Can you send me the latest dumps for 100-105 ICND1 to : {email not allowed}
Can you send me the latest dumps for 100-105 ICND1 to : zaraq.zaman at gmaildotcom
Hey everyone,
Could anyone please send me the latest INCD 1 & 2 Dumps. That would be greatly appreciated.
Email: kelvin.mullings(@)gmail.com
Just pass the ICND1 with 896 today!!
Super excited and ready to tackle ICND2 on 1/28//2020.
Ppl, everything you need is on 9tut…facts!!
Big thanks 9tut!!
Grind till I Die!!!
Pass ICND1 with 896 today!
Thanks 9tut for the assist!!
Admin,
Is there a reason, why there is only CCNA test material and no CCNP?
passed my icnd1 exam today I got 930 most of the exam came from 9tut 2 simu and 5 drag and drop questions
Passed ICND1 with a 953. I had about 50% questions from this site. The lab sims were the same concept, but they broke different elements so you need to know your fundamentals.
I had two lab sims, probably 5-6 drag and drop. Probably only one subnetting question. A couple IPv6 questions I was not familiar with.
Question 21 references the OSI Model
Q90. Wouldn’t the answer be “A,” because the the host address 192.168.1.23 falls in between the 192.168.1.16 subnet? 192.168.1.23 is a broadcast address of 192.168.1.20 subnet. Correct me if I’m wrong, but use your binary chart.
@ Urkel
the increment is 4 ==> the networks are
.0
.4
.8
.12
.16
.20
.24
…
so 192.168.1.23 belong to the network 192.168.1.20
@Albra
192.168.1.20(network add)-192.168.1.23(broadcast)
Never use a network or broadcast address for a host. .0-.3 has four available IP’s, but only two addresses are available for hosts(.1 and .2).
*@Albra sry sub those numbers in my last post for .20-.3 and .21 and .22 and it makes more sense. For example 24 would be the next network address and .27 would be the next broadscast