ICND1 – NAT/PAT
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about NAT/PAT, please read my Network Address Translation NAT Tutorial.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]What happens when computers on a private network attempt to connect to the Internet through a Cisco router running PAT?
A. The router uses the same IP address but a different TCP source port number for each connection.
B. An IP address is assigned based on the priority of the computer requesting the connection.
C. The router selects an address from a pool of one-to-one address mappings held in the lookup table.
D. The router assigns a unique IP address from a pool of legally registered addresses for the duration of the connection.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Port Address Translation (PAT) can support thousands of users connect to the Internet using only one real global IP address. With PAT, each computer will be assigned a separate port number so that the router can identify which computer should receive the return traffic.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]In the configuration of NAT, what does the keyword overload signify?
A. When bandwidth is insufficient, some hosts will not be allowed to access network translation.
B. The pool of IP addresses has been exhausted.
C. Multiple internal hosts will use one IP address to access external network resources.
D. If the number of available IP addresses is exceeded, excess traffic will use the specified address pool.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The keyword “overload” specifies we are using NAT Overload (PAT) in which multiple internal hosts will use only one IP address to access external network resources.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]When configuring NAT, the Internet interface is considered to be what?
A. local
B. inside
C. global
D. outside
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
On the interface connecting to the Internet of the router we have to use the command “ip nat outside” for NAT to work. It identifies that interface as the outside interface.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NAT type is used to translate a single inside address to a single outside address?
A. dynamic NAT
B. NAT overload
C. PAT
D. static NAT
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
There are two types of NAT translation: dynamic and static.
Static NAT: Designed to allow one-to-one mapping between local and global addresses. This flavor requires you to have one real Internet IP address for every host on your network
Dynamic NAT: Designed to map an unregistered IP address to a registered IP address from a pool of registered IP addresses. You don’t have to statically configure your router to map an inside to an outside address as in static NAT, but you do have to have enough real IP addresses for everyone who wants to send packets through the Internet. With dynamic NAT, you can configure the NAT router with more IP addresses in the inside local address list than in the inside global address pool. When being defined in the inside global address pool, the router allocates registered public IP addresses from the pool until all are allocated. If all the public IP addresses are already allocated, the router discards the packet that requires a public IP address.
In this question we only want to translate a single inside address to a single outside address so static NAT should be used.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about the inside interface configuration in a NAT deployment is true?
A. It is defined globally
B. It identifies the location of source addresses for outgoing packets to be translated using access or route maps.
C. It must be configured if static NAT is used
D. It identifies the public IP address that traffic will use to reach the internet.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
When we specify a NAT “inside” interface (via the “ip nat inside” command under interface mode), we are specifying the source IP addresses. Later in the “ip nat” command under global configuration mode, we will specify the access or route map for these source addresses.
For example the command:
Router(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool PoolforNAT
after the keyword “source” we need to specify one of the three keywords:
+ list: specify access list describing local addresses (but this command does not require an “inside” interface to be configured)
+ route-map: specify route-map
+ static: specify static local -> global mapping
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Under which circumstance should a network administrator implement one-way NAT?
A. when the network must route UDP traffic
B. when traffic that originates outside the network must be routed to internal hosts
C. when traffic that originates inside the network must be routed to internal hosts
D. when the network has few public IP addresses and many private IP addresses require outside access
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]How many addresses will be available for dynamic NAT translation when a router is configured with the following commands?
Router(config)#ip nat pool TAME 209.165.201.23 209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 9 pool TAME
A. 7
B. 8
C. 9
D. 10
E. 24
F. 32
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]What does the “Inside Global” address represent in the configuration of NAT?
A. the summarized address for all of the internal subnetted addresses
B. the MAC address of the router used by inside hosts to connect to the Internet
C. a globally unique, private IP address assigned to a host on the inside network
D. a registered address that represents an inside host to an outside network
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the graphic:
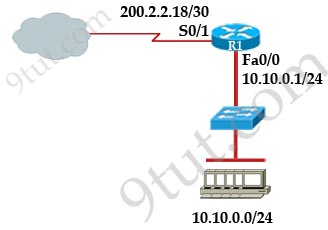
A company wants to use NAT in the network shown. Which commands will apply the NAT configuration to the proper interfaces? (Choose two)
A.
R1 (config)# interface serial0/1
R1 (config-if)# ip nat inside
B.
R1 (config)# interface serial0/1
R1 (config-if)# ip nat outside
C.
R1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R1 (config-if)# ip nat inside
D.
R1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R1 (config-if)# ip nat outside
E.
R1(config)# interface serial0/1
R1 (config-if)# ip nat outside source pool 200.2.2.18 255.255.255.252
F.
R1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R1 (config-if)# ip nat inside source 10.10.0.0 255.255.255.0
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
After configuring all the requirements for NAT, we need to apply them to “source interface” and “outgoing” interface by going to the appropriate interfaces and type the “ip nat inside” and “ip nat outside” commands.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which form of NAT maps multiple private IP addresses to a single registered IP address by using different ports?
A. static NAT
B. dynamic NAT
C. overloading
D. overlapping
E. port loading
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement describes the effect of the overload keyword in the ip nat inside source list 90 interface ethernet 0/0 overload command?
A. Addresses that match address list inside are translated to the IP address of the Ethernet 0/0 interface.
B. Hosts that match access inside are translated to an address in the Ethernet 0/0 network.
C. Hosts on the Ethernet 0/0 LAN are translated to the address pool in access list 90.
D. Addresses that match access list 90 are translated through PAT to the IP address of the Ethernet 0/0 interface
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The command ip nat inside source list 90 interface ethernet 0/0 overload means:
+ “ip nat inside”: “I want to NAT from inside to outside”
+ “list 90” means “the source IP addresses to NAT are included in Access-list 90”
+ “interface ethernet 0/0” means “NAT out of this interface”
+ “overload” means “use PAT for the IP translation”
Question 12
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NAT command can be applied to an interface?
A. ip nat inside
B. ip nat inside test access-list-number pool pool-name
C. ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.0 10.10.10.50
D. ip nat pool test 10.10.10.0 10.10.10.50 255.255.255.0
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The “ip nat inside” command can be applied to an interface to indicate this interface is the source NAT.
Question 13
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command displays the number of times that an individual router translated an inside address to an outside address?
A. show ip protocol 0
B. show ip nat translation
C. show counters
D. show ip route
E. show ip nat statistics
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The outputs of the two commands “show ip nat statistics” and “show ip nat translation” are shown below:
Router#show ip nat statistics Total active translations: 2 (0 static, 2 dynamic; 2 extended) Peak translations: 3, occurred 5d04h ago Outside interfaces: Serial1/0 Inside interfaces: Ethernet0/1 Hits: 34531 Misses: 0 CEF Translated packets: 34526, CEF Punted packets: 0 Expired translations: 11 Dynamic mappings: -- Inside Source [Id: 1] access-list nat_traffic interface Serial1/0 refcount 2 Total doors: 0 Appl doors: 0 Normal doors: 0 Queued Packets: 0
Router#show ip nat translation Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp 201.15.3.5:628 10.1.1.7:628 201.15.3.17:628 201.15.3.17:628 icmp 201.15.3.5:629 10.1.1.7:629 201.15.3.6:629 201.15.3.6:629 icmp 201.15.3.5:610 10.1.1.8:610 201.15.3.17:610 201.15.3.17:610 icmp 201.15.3.5:611 10.1.1.8:611 201.15.3.6:611 201.15.3.6:611 icmp 201.15.3.5:727 10.1.1.17:727 201.15.3.17:727 201.15.3.17:727 icmp 201.15.3.5:728 10.1.1.17:728 201.15.3.6:728 201.15.3.6:728 icmp 201.15.3.5:633 10.1.1.21:633 201.15.3.17:633 201.15.3.17:633 icmp 201.15.3.5:634 10.1.1.21:634 201.15.3.6:634 201.15.3.6:634 icmp 201.15.3.5:480 10.2.2.1:480 201.15.3.17:480 201.15.3.17:480 icmp 201.15.3.5:481 10.2.2.1:481 201.15.3.6:481 201.15.3.6:481 icmp 201.15.3.5:840 10.10.123.2:840 201.15.3.17:840 201.15.3.17:840 icmp 201.15.3.5:841 10.10.123.2:841 201.15.3.6:841 201.15.3.6:841 icmp 201.15.3.5:578 10.10.123.3:578 201.15.3.17:578 201.15.3.17:578 icmp 201.15.3.5:579 10.10.123.3:579 201.15.3.6:579 201.15.3.6:579 icmp 201.15.3.5:595 192.168.1.1:595 201.15.3.17:595 201.15.3.17:595 icmp 201.15.3.5:596 192.168.1.1:596 201.15.3.6:596 201.15.3.6:596
From that we can see the correct answer should be “show ip nat statistics”.
Question 14
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NAT term is defined as a group of addresses available for NAT use?
A. one-way nat
B. static nat
C. dynamic nat
D. nat pool
Answer: D[/am4show]


Anyone,
I plan on taking exam next week. What other sims/labs did you get besides the OSPF 6 router?
Thanks in Advance!
ccent someday how did the exam go?
haven’t taken it yet. This coming Thursday.
I think the link to the tutorial is broken.
Passed CCENT Friday, did okay on questions, Sims ate up time.
Know your SHOW commands!
Passed my ICND1 last Friday 28th 🙂
– Lot of subnetting
– OSPF (neighborships)
– NAT & PAT
You don’t need to configure, but you do need to troubleshoot
SHOW commands are a must.
Thanks 9tut and good luck to the rest of you 9tutters
@9tut_Rulez
Do I need to learn STP, Vlan, VTP Configuration, Acl1 and Acl2??
Fez
I meant for ICND 1 100-101 exam what topics should be learned. Do I need to know stp, vlan, vpt, NAT and pat configuration?
icnd2 kicks off with vlan trunking, stp, and vpt. there are multiple choice questions on the icnd1 regarding pat config and acls.
Thanks derp
Passed my 100-101 exam today and question2,3 were there.. all the best
Took test today, all 3 were there.
Got 986/1000 Marks, {5/16/2014} 50 Questions, Ospf Sim, Security simlet, and Router and switch Simlet Was also there…..All questions From 9tut. and Examcollections…..Now Heading For Icnd2 And Blogging…..
For Any Help.
Manohar Tn
Website: http://www.techlinko.com
G+ : https://plus.google.com/u/0/+ManoharTN9/
These are the only NAT PAT questions seen on ICND1 exam?
Not understanding question 1. It is assumed that a private network is using private ip addresses, which are not routable through the internet, therefore the router can keep the same address, though the second part of that answer seems correct.
Maybe D?
sorry i was high. I get it now
Took exam yesterday, all these questions were on it. Thanks 9tut
Hi, taking an exam in a week, if anyone can share with dumps I would be grateful! Cheers
Questions 1-2-3 were in exam on 20/11/2014, more than 45 questions were from 9tut !
q1, 2 and 3 in icnd1 exam
Just passed with 92%.
Around 20 plus questions from Tut9!
Just passed at 01 April 2015 with 100 % score. question 1,2 and 3 were there!
I’m with you, Oshi, private address won’t get routed thru the Internet. Unless by saying PAT, they are saying you are using NAT/PAT overload, in which cause the private address does get change to a valid registered address. My answer for that question would be E, it doesn’t get on the net. Not with a private address in the socket.
Reading over again, and I can see why A would be right. Nothing it’s said that the computer actually get onto the Internet, it just says what the router would do. Once the router sends the packet to the net, the next hop will drop the packet.
My understanding of that question Gns3 is that the IP address it is referring to is the routers public IP address. That is paired with a port number and the two together map to the private IP address of your PC.
However seeing as I am only studying I could be completely wrong 🙂
Q 1,2,3 in exam
hi
can any good samaritan send me the latest dumps please to gmboya12@yahoo.com
@all: We had to move all the questions and answers out of 9tut. We can only keep the explanation. You can download the questions and answers at: https://mega.co.nz/#!oIdESYbD!yyu33vygrfKPy4rcmcbV6qW2fxINNoTokuDM3CjA_og
how many sims are the in the ICND1 exam?
I have a couple of questions I need answered how do I upload them here to this site?
anyone tell me –
I seen a question on the test about the Internet facing ….
is it Global, outside… Inside, or something else.
It was the very first question on the exam. I am not sure as it was a very generic question.
I believe it was talking about the interface that was facing the Internet – Which is ip nat outside
or what is the outside network called when facing the Internet – Which is Global ?
If anyone knows the exact question or what I am talking about – please advise.
Hi everyone,
Please need latest dumps IT11STUDENT11 AT GMAIL POINT COM
Question 1 and 2 was on the exam
When configuring NAT, the Internet interface is considered to be what?
A. local
B. inside
C. global
D. outside
Answer: D
Explanation
On the interface connecting to the Internet of the router we have to use the command “ip nat outside”
for NAT to work. It identifies that interface as the outside interface.
How is this possible when learning about nat they give you definition about
________
| NAT |
Inside Local | Router | Inside Global Outside Local/Global
|_______|
@ 8 february 2017:
answer D is the only correct one. The question specifies “When configuring NAT” so this is relevant only to the configuration.
Furthermore it says “the Internet interface” the word interface specifies the NAT-interface configuration: there are only two possibilities:
1) ip nat inside : specifies the interface connected to the network that is needing translation (local)
and
2) ip nat outside : specifies the interface connected to the network outside; usually the internet/ISP
Hopefully this help
NAT Configuration
1 : Static Nat :
(config): ip nat static “ local inside ip address “ “ Global outside ip address “
(config): interface interface type port numbere
(config-if):ip address ip address subnet mask
(config-if):ip nat { inside | outside }
2 : Dynamic Nat :
(config): ip nat pool pool-name , pool range Netmask { netmask | prefix length }
(config): access-list access list name Permit source { source-wildcard }
(config): ip nat inside source list access-list-number pool pool name
(config): interface interface type port numbere
(config-if):ip address ip address subnet mask
(config-if):ip nat { inside | outside }
3 : PAT (Dynamic ) :
(config): ip nat pool pool-name , pool range Netmask { netmask | prefix length }
(config): access-list access list name Permit source { source-wildcard }
(config): ip nat inside source list access-list-number pool pool name overload
(config): interface interface type port numbere
(config-if):ip address ip address subnet mask
(config-if):ip nat { inside | outside }
4: PAT (single address ) :
(config): ip nat static “ local inside ip address “ “ Global outside ip address “
(config): ip nat inside source list access-list-number interface interface type overload
(config): interface interface type port numbere
(config-if):ip address ip address subnet mask
(config-if):ip nat { inside | outside }
5: port forwarding
P.F is the act of forwarding traffic addressed to a specific network port from one network node to another . this technic allows an external user to reach a port on private ipv4 address from the outside , through a NAT-enable router .
Typically , peer to peer file-sharing programs and operations , such as web servicing and FTP , require that router ports be forwarded or open to allow this applications to work .
**CONFIGURATION**
Configuration is similar to PAT single address configuration .
(config): ip nat inside source { static tcp |udp local-ip local port global-ip global port }
[ extendable ]
Note : Extendable option is applied automatically . The extendable keyword allows the user to configure several ambiguous static translations , where ambiguous translations are translations with the same local or global address . it allows the router to extend the translation to more than one port if necessary .
Example :
R (config): ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.2 80 203.155.6.11 8080
Local-ip : 192.168.1.2 local-port : 80
Global-ip : 203.155.6.11 global-port : 8080
** NAT Verifying **
1 : show ip nat statistic
Displays information about the total number of active translations , nat configurations parameters , the number of addresses in the pool and how many of addresses have been allocated .
2: show ip nat translation
Display the details of the two previous NAT assignments . The command displays all static translations have been configured and any dynamic translations that have been created by traffic
3: Debug ip nat
Displays operation of the NAT feature by displaying information about every packet that is translated by the router.
4 : Show running-config
Displays total information about ACL , NAT , …
** NAT Troubleshooting main steps **
1: show ip nat translations
2 : show ip nat statistic
3 : show success-list
just put additional research about One-Way NAT
link: https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/63452
to put simple,
One-Way NAT =PAT.
Only the inside host can init the NAT, not the other way.
Can someone explain q6, why b? when do we use one-way NAT for?
Confirming the 353q dumps are valid.
I JUST PASSED ICND1!!! Thank you 9tut.I killed that exam!!
Just passed ICND1 with 894. Most of the question are here. Had two simulators, DHCP and Securiity, both are here, but the configuration is slightly different, so are answers. Very simple question about RFC related to depletion of IPv4 – is it 1518 or 1519? Still don’t know what Cisco wants. Different sources provide different answers. 1519, 1519 and 1520 all deal with depletion of IPv4.
Please i need some one to send me the questions for these answers so my e-mail address
{email not allowed}
Thanks
WINTER IS COMING
I see only the answers , where the questions
How many addresses will be available for dynamic NAT translation when a router is configured with the following commands?
Router(config)#ip nat pool TAME 209.165.201.23 209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 9 pool TAME
Why answer is 8?
Abdul, you need to buy a premium membership to see the questions.
ilyuwacopypaste
209.165.201.23 -> First inside global address
209.165.201.30 -> Last inside global address
So the difference is 8
Any latest dumps ?