Here you will find answers to WAN Questions
Question 1
As a network technician, you must know the various layers of the OSI model. At which layers of the OSI Model do Wide Area Networks operate in? (Choose two)
A. Physical Layer
B. Datalink Layer
C. Network Layer
D. Session Layer
E. Transport Layer
F. Presentation Layer
G. Application Layer
Answer: A B
Explanation
Frame Relay is a high-performance WAN protocol that operates at the physical and data link layers of the OSI reference model.
Question 2
Network equipment supporting the use of flow control mechanisms has been recently installed in the network. What is the purpose of flow control in a data network?
A. It ensures that data is retransmitted if an acknowledgment is not received.
B. It reassembles segments in the correct order on the destination device.
C. It provides a mechanism for the receiver to control the transmission speed.
D. It regulates the size of each datagram segment.
E. All of the above are functions of flow control
Answer: C
Explanation
Flow control is the process that control the rates at which data is transferred between two endpoints, enabling a receiving device to signal congestion to a sending device, which allows for the sending device to temporarily halt transmission, alleviating congestion at the receiving device.
Question 3
You are a network administrator working in the communication company. One day, you find that the encapsulation has been altered by someone on a synchronous serial line and this new configuration is not the optimal one. So you attempt to return the encapsulation to the default. Which measure will you take to reach this goal?
A. Issue the shutdown then no shutdown commands to reset the encapsulation on the interface.
B. Reboot the router and allow it to reload the configuration.
C. Configure the interface for HDLC encapsulation.
D. Change the encapsulation to ARPA.
Answer: C
Explanation
We can’t use the “shutdown” & “no shutdown” commands to reset the encapsulation because it doesn’t affect the encapsulation type -> A is not correct.
Reboot the router and reload the configuration can solve this problem but other configuration will be erased too -> not a good choice.
The question asks “attempt to return the encapsulation to the default” and the default encapsulation on a Cisco router is HDLC so we can configure the interface for HDLC encapsulation -> C is the correct.
D is not correct as ARPA is not the default WAN encapsulation of a Cisco router. ARPA is the standard Ethernet version 2.0 encapsulation.
Question 4
During your interview for a network administrator job, your interviewer gives you some statements to judge. The following options are all related to the configuration of a serial link on a Cisco router. You should point out which one is the correct. What is your answer?
A. The clock rate command is a requirement for DCE interfaces.
B. If the clock rate command is configured, then the bandwidth command is required.
C. If the bandwidth command is configured, then the clock rate command is required.
D. Cisco routers are DCE devices.
Answer: A
Explanation
The purpose of DCE equipment is to provide clocking and switching services in a network. Clock rate doesn’t have a default value so we have to configure it manually (while bandwidth does have a default value). Cisco routers can be configured as DTE or DCE devices.
Question 5
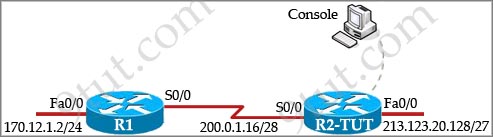
As a network technician, you should know how to gain information from the exhibit. According to the command output displayed in the following exhibit, please point out the correct description about interface Serial 0/0/0.
Exhibit
Router#show running-config
Building configuration
Current configuration :59 bytes
<output omitted>
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
!
|
A. The configuration is incomplete, which will cause the interface status to be “Serial0/0/0 is down, line protocol is down”
B. The interface is using Cisco HDLC for layer 2 encapsulation.
C. The configuration is incomplete, which will cause the interface status to be “Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is down”.
D. A ping to the remote address 209.165.200.226 will be successful.
Answer: B
Explanation
The configuration is correct and the “no shutdown” command was used (because we don’t see a “shutdown” line in the output) so we can see at least “Serial0/0/0 is up” -> A is not correct.
Although the configuration is correct but we don’t know if this interface is connected with another router or not. If it is connected with another interface (on another router) and that interface is up, we will see the “Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up”. Otherwise we will see “Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is down” -> we can’t guarantee answer C is correct.
Answer D is the same with C because we don’t know if the remote interface 209.165.200.226 exists (and turned up) or not.
For WAN interface (serial interface), the default layer 2 encapsulation is HDLC -> B is correct.
Question 6
Router2#show interface serial 0/0
Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is down
Hardware is PowerQUICC Serial
Internet address is 172.16.10.1/30
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 64 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, rely 255/255 load 1/255
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set, keepalive set (10 sec)
<output omitted> |
You work as a network administrator. You study the exhibits carefully. The corporate office and branch office have been attached through two non-Cisco routers over a highly reliable WAN connection over a year. A new Cisco router has been installed to replace the hardware at the branch location. Since the installation, IP communication cannot be verified across the link.
Given the output on router R1, what could be a logical first step to take to resolve this problem?
A. Ensure an exact match between the bandwidth setting on Router1 and Router2
B. Change the encapsulation on Router1 to PPP.
C. Change the bandwidth setting on Router1 to match the actual line speed
D. Verify successful DCE communication between the two sites.
E. Verify Layer1 communication on the Router1 Serial0/0 interface
Answer: B
Explanation
HDLC is a Cisco proprietary protocol so we can’t use it when connecting to a non-Cisco router. PPP is the standard protocol that is widely supported and used by many ISPs.
Question 7
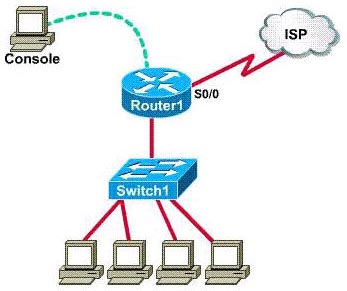
From the choices shown above, which port can be used for a WAN T1 connection?
A. Console
B. Serial 0
C. AUI
D. BRI
E. None of the other alternatives apply
Answer: B
Explanation
The console port is intended for local administrative access from an ASCII terminal or a computer using a terminal emulator.
Serial ports support WAN T1 connection.
Attachment Unit Interface (AUI) ports are designed to connect to an external transceiver for conversion to a specific media type (such as twisted pair, coax, or fiber). AUI can transfer only 1 bit at a time.
BRI ports are used for ISDN services (mostly voice).
Question 8
A WAN connection is shown below:
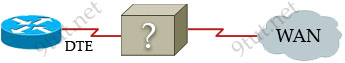
Based on this diagram, which two devices can be used to complete the connection between the WAN router at the customer site and the service provider? (Choose two)
A. CSU/DSU
B. modem
C. WAN switch
D. ATM switch
E. Frame Relay switch
F. ISDN TA
Answer: A B
Explanation
A modem or CSU/DSU can provide clock rate so it can be used for the topology above.
The Channel Service Unit (CSU) can echo loopback signals from the phone company for testing purposes.
The Data Service Unit (DSU) manages line control, and converts input and output between RS-232C, RS-449, or V.35 frames from the LAN and the time-division multiplexed (TDM) DSX frames on the T-1 line. The DSU provides a modem-like interface between the computer as Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and the CSU.