ICND1 – Syslog Questions
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Syslog – what does not belong?
A. host name
B. severity
C. timestamp
D. message
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Syslog – what does not belong?
A. host name
B. severity
C. timestamp
D. message
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements describe the operation of the CSMA/CD access method? (Choose two)
A. In a CSMA/CD collision domain, multiple stations can successfully transmit data simultaneously.
B. In a CSMA/CD collision domain, stations must wait until the media is not in use before transmitting.
C. The use of hubs to enlarge the size of collision domains is one way to improve the operation of the CSMA/CD access method.
D. After a collision, the station that detected the collision has first priority to resend the lost data.
E. After a collision, all stations run a random backoff algorithm. When the backoff delay period has expired, all stations have equal priority to transmit data.
F. After a collision, all stations involved run an identical backoff algorithm and then synchronize with each other prior to transmitting data.
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Explanation
CSMA/CD stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection. In an Ethernet LAN, before transmitting, a computer first listens to the network media. If the media is idle, the computer sends its data. If the media is not idle (another station is talking), the computer must wait for some time.
When a station transmits, the signal is referred to as a carrier. Carrier Sense means that before a station can send data onto an Ethernet wire, it have to listen to see if another “carrier” (of another station) is present. If another station is talking, this station will wait until there is no carrier present.
Multiple Access means that stations can access the network at any time. It is opposed to Token-Ring network where a station must have the “token” so that it can send data.
Although Carrier Sense help two stations not send data at the same time but sometimes two stations still send data at the same time! This is because two stations listen for network traffic, hear none, and transmit simultaneously -> a collision occurs and both stations must retransmit at some later time. Collision Detection is the ability of the media to detect collisions to know that they must retransmit.
Basically, the CSMA/CD algorithm can be summarized as follows:
+ A device that wants to send a frame must wait until the LAN is silent (no one is “talking”)
+ If a collision still occurs, the devices that caused the collision wait a random amount of time and then try to send data again.
Note: A switch separates each station into its own collision domain. It means that station can send data without worrying its data is collided with the data of other stations. It is as opposed to a hub which can cause collision between stations connected to it.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]On a live network, which commands will verify the operational status of router interfaces? (Choose two)
A. Router#show interfaces
B. Router#show ip protocols
C. Router#debug interface
D. Router#show ip interface brief
E. Router#show start
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
Only two commands “show interfaces” and “show ip interface brief” reveal the status of router interfaces (up/up, for example).
The outputs of two commands are shown below:
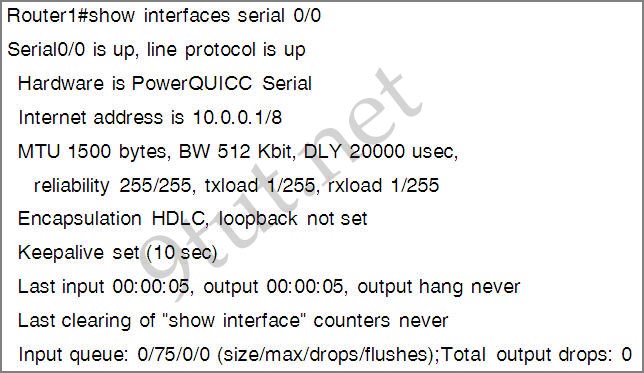
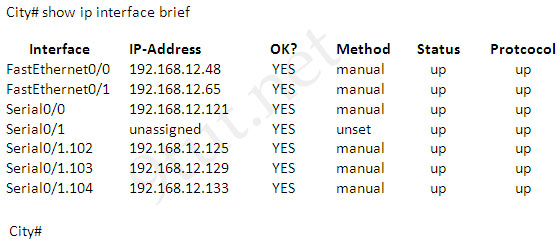
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What must occur before a workstation can exchange HTTP packets with a web server?
A. A UDP connection must be established between the workstation and its default gateway.
B. A UDP connection must be established between the workstation and the web server.
C. A TCP connection must be established between the workstation and its default gateway.
D. A TCP connection must be established between the workstation and the web server.
E. An ICMP connection must be established between the workstation and its default gateway.
F. An ICMP connection must be established between the workstation and the web sewer.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
HTTP is based on TCP connection so a TCP connection must be established first between the workstation and the web server.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. If the hubs in the graphic were replaced by switches, what would be virtually eliminated?
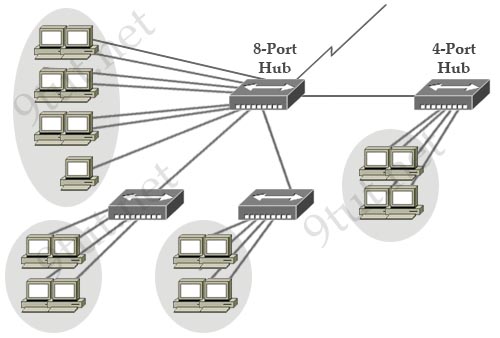
A. broadcast domains
B. repeater domains
C. Ethernet collisions
D. signal amplification
E. Ethernet broadcasts
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Hubs do not separate collision domains so if hub is used in the topology above, we will have only 1 collision domain. Switches do separate collision domains so if hubs are replaced by switches, we would have 22 collision domains (19 collision domains for hosts and 3 collision domains among three switches. Please notice that the WAN (serial) connection is not counted as a collision (or broadcast) domain.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]If a host experiences intermittent issues that relate to congestion within a network while remaining connected, what could cause congestion on this LAN?
A. half-duplex operation
B. broadcast storms
C. network segmentation
D. multicasting
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
A broadcast storm can cause congestion within a network. For more information about broadcast storm please read my STP tutorial.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator is testing connectivity from the branch router to the newly installed application server. What is the most likely reason for the first ping having a success rate of only 60 percent?
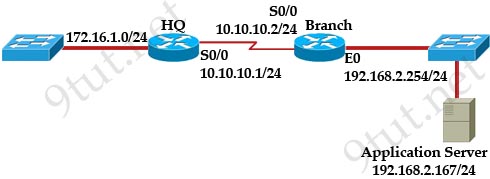
|
Branch# ping 192.168.2.167 Branch# ping 192.168.2.167 |
A. The network is likely to be congested, with the result that packets are being intermittently dropped.
B. The branch router had to resolve the application server MAC address.
C. There is a short delay while NAT translates the server IP address.
D. A routing table lookup delayed forwarding on the first two ping packets.
E. The branch router LAN interface should be upgraded to FastEthernet.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
Before a host can send ICMP (ping) packets to another device, it needs to learn the MAC address of the destination device so it first sends out an ARP Request. In fact, the first ping packet is dropped because the router cannot create a complete packet without learning the destination MAC address.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]An administrator is in the process of changing the configuration of a router. What command will allow the administrator to check the changes that have been made prior to saving the new configuration?
A. Router# show startup-config
B. Router# show current-config
C. Router# show running-config
D. Router# show memory
E. Router# show flash
F. Router# show processes
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The “show running-config” command displays active configuration in memory.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]What does a host on an Ethernet network do when it is creating a frame and it does not have the destination address?
A. drops the frame
B. sends out a Layer 3 broadcast message
C. sends a message to the router requesting the address
D. sends out an ARP request with the destination IP address
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which IOS command is used to initiate a login into a VTY port on a remote router?
A. router# login
B. router# telnet
C. router# trace
D. router# ping
E. router(config)# line vty 0 5
F. router(config-line)# login
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements are true about the operation of a full-duplex Ethernet network? (Choose three)
A. There are no collisions in full-duplex mode.
B. A dedicated switch port is required for each full-duplex node.
C. Ethernet hub ports are preconfigured for full-duplex mode.
D. In a full-duplex environment, the host network card must check for the availability of the network media before transmitting.
E. The host network card and the switch port must be capable of operating in full-duplex mode.
Answer: A B E[/am4show]
Explanation
Full-duplex communication allows both sending and receiving of data simultaneously. Switches provide full-duplex communication capability. Half-duplex communication only allows data transmission in only one direction at a time (either sending or receiving).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two options will help to solve the problem of a network that is suffering a broadcast storm? (Choose two)
A. a bridge
B. a router
C. a hub
D. a Layer 3 switch
E. an access point
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
Only a router or a Layer 3 switch can mitigate a broadcast storm because they separate broadcast domains -> B and D are correct.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network has been planned as shown. Which three statements accurately describe the areas and devices in the network plan? (Choose three)
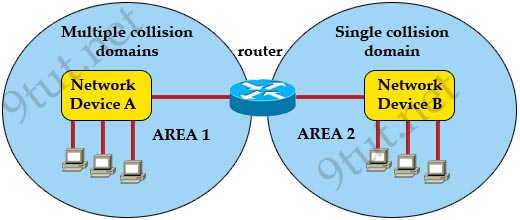
A. Network Device A is a switch.
B. Network Device B is a switch.
C. Network Device A is a hub.
D. Network Device B is a hub.
E. Area 1 contains a Layer 2 device.
F. Area 2 contains a Layer 2 device.
Answer: A D E[/am4show]
Explanation
AREA 1 has “multiple collision domains” so Network Device A must be a device operating in Layer 2 or above (a router or switch) -> A & E are correct.
AREA 2 only has “single collision domain” so Network Device B must be a device operating in Layer 1 (a hub or repeater) -> D is correct.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. If the resume command is entered after the sequence that is shown in the exhibit, which router prompt will be displayed?
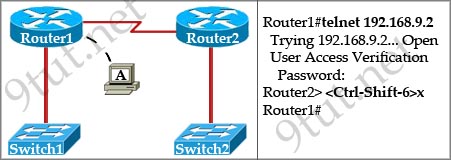
A. Router1>
B. Router1#
C. Router2>
D. Router2#
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The “Ctrl-Shift-6” and “x” is used to suspend the telnet session. In this case, the telnet session from Router1 to Router2 will be suspended.
If we enter the keyword “resume”, Router1 will try to resume the telnet session to Router2 (you will see the line [Resuming connection 1 to 192.168.9.2 … ]) and we will get back the Router2> prompt.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. All devices attached to the network are shown. How many collision domains are present in this network?
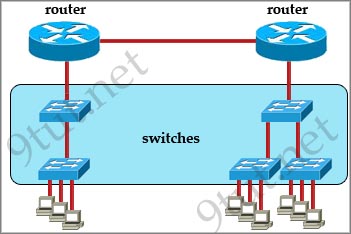
A. 2
B. 3
C. 6
D. 9
E. 15
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
In the topology above only routers and switches are used so for each link we have one collision domains. In the picture below each pink ellipse represents for one collision domain.
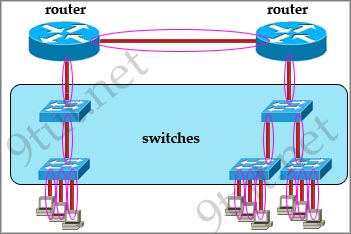
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which network topology allows all traffic to flow through a central hub?
A. bus
B. star
C. mesh
D. ring
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
Star topology is the most popular topology for the network which allows all traffic to flow through a central device.
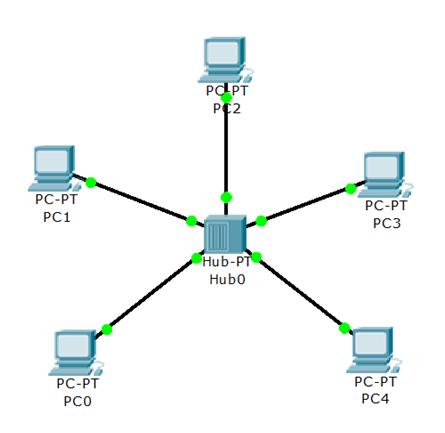
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]On which type of device is every port in the same collision domain?
A. a router
B. a Layer 2 switch
C. a hub
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature allows a device to use a switch port that is configured for half-duplex to access the network?
A. CSMA/CD
B. IGMP
C. port security
D. split horizon
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is the LAN access method used in Ethernet. When a device wants to gain access to the network, it checks to see if the network is free. If the network is not free, the device waits a random amount of time before retrying. If the network is free and two devices access the line at exactly the same time, their signals collide. When the collision is detected, they both back off and wait a random amount of time before retrying.
CSMA/CD is used with devices operating in half-duplex mode only. CSMA/CD helps devices connecting to half-duplex switch ports operate correctly.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which MTU size can cause a baby giant error?
A. 1500
B. 9216
C. 1600
D. 1518
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Ethernet frame size refers to the whole Ethernet frame, including the header and the trailer while MTU size refers only to Ethernet payload. Baby giant frames refer to Ethernet frame size up to 1600 bytes, and jumbo frame refers to Ethernet frame size up to 9216 bytes (according to this link: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-4000-series-switches/29805-175.html)
For example, standard Ethernet frame MTU is 1500 bytes. This does not include the Ethernet header and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) trailer, which is 18 bytes in length, to make the total Ethernet frame size of 1518.
So according to strict definition, MTU size of 1600 cannot be classified as baby giant frames as the whole Ethernet frames will surely larger than 1600 -> Answer C is not correct.
Answer D is a better choice as the MTU is 1518, so the whole Ethernet frame would be 1536 (1518 + 18 Ethernet header and CRC trailer). This satisfies the requirement of baby giant frames “Baby giant frames refer to Ethernet frame size up to 1600 bytes”.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What happens when the cable is too long?
A. Baby Giant
B. Late collision
C. Duplex mismatch
D. No connection
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]To what type of port would a cable with a DB-60 connector attach?
A. Serial port
B. Console port
C. Ethernet port
D. Fibre optic port
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
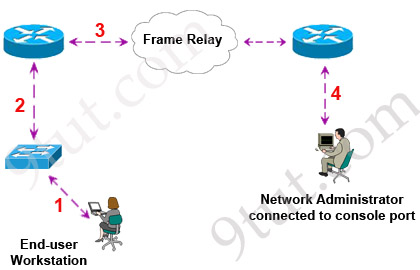
What kind of cable should be used to make each connection that is identified by the numbers shown?
A.
1 – Ethernet straight-through cable
2 – Ethernet crossover cable
3 – Serial cable
4 – Ethernet straight-through cable
B.
1 – Ethernet rollover cable
2 – Ethernet crossover cable
3 – Serial cable
4 – Null modem cable
C.
1 – Ethernet straight-through cable
2 – Ethernet crossover cable
3 – Serial cable
4 – Rollover cable
D.
1 – Ethernet crossover cable
2 – Ethernet straight-through cable
3 – Fiber Optic cable
4 – Rollover cable
E.
1 – Ethernet straight-through cable
2 – Ethernet straight-through cable
3 – Serial cable
4 – Rollover cable
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
To remember which type of cable you should use, follow these tips:
– To connect two serial interfaces of 2 routers we use serial cable
– To specify when we use crossover cable or straight-through cable, we should remember:
Group 1: Router, Host, Server
Group 2: Hub, Switch
One device in group 1 + One device in group 2: use straight-through cable
Two devices in the same group: use crossover cable
For example: we use straight-through cable to connect switch to router, switch to host, hub to host, hub to server… and we use crossover cable to connect switch to switch, switch to hub, router to router, host to host… )
Notice in this question, connecting to the Frame Relay means connecting to another router. Also we must use serial cable (or Fiber Optic cable) because the distance to the Frame Relay is far so we can’t use Ethernet cables.
Rollover cable can be used to connect a computer terminal to a network router’s console port. This is often used when we turn on the router for the first time.
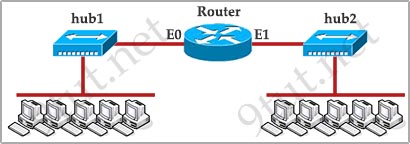
Question 12
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. How many collision domains are shown?
A. one
B. two
C. three
D. four
E. six
F. twelve
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 13
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Pierre has just installed the mail server and Switch2. For security reasons UDP packets are not permitted outbound on the Fa0/1 router interface. Pierre is now at his workstation testing the new installation and is not able to establish SMTP communication to the mail server.
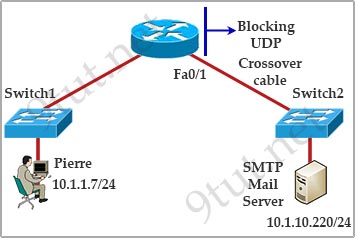
What is the most likely cause for lack of communication between Pierre’s workstation and the mail server?
A. The crossover cable should be a straight-through cable.
B. UDP is blocked coming out of the Fa0/1 interface on the router.
C. The server should be directly connected to the router.
D. The IP addresses are all on the same network. No router is required.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 14
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibits labeled A through E. All devices are to be connected over Ethernet. Which three device-to-device configurations are likely to require the use of a crossover connection? (Choose three.)
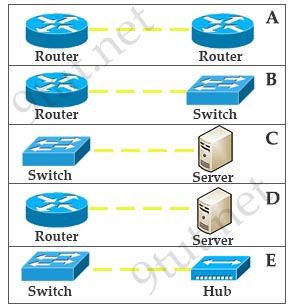
A. exhibit A
B. exhibit B
C. exhibit C
D. exhibit D
E. exhibit E
Answer: A D E[/am4show]
Question 15
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. All devices attached to the network are shown. Which number of collision domains are present in this network?

A. 9
B. 3
C. 6
D. 2
E. 15
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
Both switch and router separate collision domains. In other words, each port of the switch and router creates one collision domain so we have 15 collision domains in this topology.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about OSI Model, please read my OSI Model Tutorial.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which OSI layer header contains the address of a destination host that is on another network?
A. application
B. session
C. transport
D. network
E. data link
F. physical
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]At which layer of the OSI model does the protocol that provides the information that is displayed by the show cdp neighbors command operate?
A. application
B. transport
C. network
D. physical
E. data link
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
CDP runs at Layer 2 (Data Link) of the OSI model -> E is correct.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two common TCP applications? (Choose two)
A. TFTP
B. SMTP
C. SNMP
D. FTP
E. DNS
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It’s a set of communication guidelines that allow software to transmit email over the Internet while File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over TCP-based network.
Note: Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) uses UDP as the transport protocol for passing data between managers and agents. SNMP uses UDP to help reduce the impact on your network’s performance. Although SNMP can be configured to run on TCP but we should only do it in special situations. SNMP uses the UDP port 161 for sending and receiving requests, and port 162 for receiving traps from managed devices.
DNS work on both the TCP and UDP protocols. DNS uses TCP for zone exchanges between servers and UDP when a client is trying to
resolve a hostname to an IP address. Therefore in most cases we say “DNS uses UDP”.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two characteristics describe the access layer of the hierarchical network design model? (Choose two)
A. layer 3 support
B. port security
C. redundant components
D. VLANs
E. PoE
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
The primary function of an access-layer is to provide network access to the end user.
The hardware and software attributes of the access layer that support high availability include security services for additional security against unauthorized access to the network through the use of tools such as 802.1x, port security, DHCP snooping, Dynamic ARP Inspection, and IP Source Guard.
Question 5
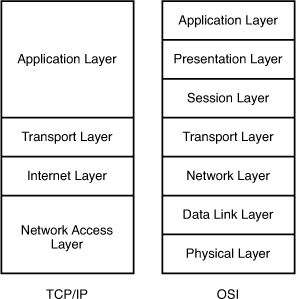
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which layer of the TCP/IP stack combines the OSI model physical and data link layers?
A. Internet layer
B. transport layer
C. application layer
D. network access layer
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The picture below compares the two TCP/IP and OSI models:
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which layer of the OSI model controls the reliability of communications between network devices using flow control, sequencing and acknowledgments?
A. Physical
B. Data-link
C. Transport
D. Network
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) has all the features mentioned above and TCP resides in Transport Layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model.
Flow control: A methodology used to ensure that receiving units are not overwhelmed with data from sending devices when buffers at a receiving unit are full, a message is transmitted to the sending unit to temporarily halt trans-missions until all the data in the receiving buffer has been processed and the buffer is again ready for action.
Sequencing: is used to number segments before sending so they can be put back together again in the correct order at the receiving side.
Acknowledgment: When the receiver gets the data, it sends a response telling the sender that the data have been safely arrived.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which network device functions only at Layer 1 of the OSI model?
A.  bridge
bridge
B. ![]() hub
hub
C.  NIC
NIC
D. ![]() router
router
E. ![]() switch
switch
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
In CCNA, the popular devices operate in Layer 1 are hub and repeater.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]A network administrator cannot connect to a remote router by using SSH. Part of the show interfaces command is shown.
| router#show interfaces Serial0/1/0 is up, line protocol is down |
At which OSI layer should the administrator begin troubleshooting?
A. physical
B. data link
C. network
D. transport
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]On which OSI layer does a VLAN operate?
A. Layer 1
B. Layer 2
C. Layer 3
D. Layer 4
Answer: B[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of the following are types of flow control? (Choose three)
A. buffering
B. cut-through
C. windowing
D. congestion avoidance
E. load balancing
Answer: A C D[/am4show]
Explanation
Three types of flow control are buffering, windowing & congestion avoidance:
+ Buffering: If a device receives packets too quickly for it to handle then it can store them in a memory section called a buffer and proceed them later.
+ Windowing: a window is the quantity of data segments that the transmitting device is allowed to send without receiving an acknowledgment for them. For example:
With the window size of 1, the sending device sends 1 segment and the receiving device must reply with 1 ACK before the sending device can send the next segment. This “waiting” takes some time.
By increasing the window size to 3, the sending device will send up to 3 segments before waiting an ACK -> helps reduce the waiting time.
+ Congestion avoidance: lower-priority traffic can be discarded when the network is overloaded -> minimize delays.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]A receiving host has failed to receive all of the segments that it should acknowledge. What can the host do to improve the reliability of this communication session?
A. decrease the window size
B. use a different source port for the session
C. decrease the sequence number
D. obtain a new IP address from the DHCP server
E. start a new session using UDP
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What must occur before a workstation can exchange HTTP packets with a web server?
A. A UDP connection must be established between the workstation and its default gateway.
B. A UDP connection must be established between the workstation and the web server.
C. A TCP connection must be established between the workstation and its default gateway.
D. A TCP connection must be established between the workstation and the web server.
E. An ICMP connection must be established between the workstation and its default gateway.
F. An ICMP connection must be established between the workstation and the web sewer.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
HTTP is based on TCP connection so a TCP connection must be established first between the workstation and the web server.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]How does TCP differ from UDP? (Choose two)
A. TCP provides best effort delivery.
B. TCP provides synchronized communication.
C. TCP segments are essentially datagrams.
D. TCP provides sequence numbering of packets.
E. TCP uses broadcast delivery.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
Before two computers can communicate over TCP, they must synchronize their initial sequence numbers (ISN) -> B is correct.
TCP uses a sequence number to identify each byte of data. The sequence number identifies the order of the bytes sent from each computer so that the data can be reconstructed in order, regardless of any fragmentation, disordering, or packet loss that may occur during transmission -> D is correct.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the purpose of flow control?
A. To ensure data is retransmitted if an acknowledgement is not received.
B. To reassemble segments in the correct order at the destination device.
C. To provide a means for the receiver to govern the amount of data sent by the sender.
D. To regulate the size of each segment.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network technician has added host A to the network. Host A cannot communicate on the network. A ping that is issued on the host to address 127.0.0.1 fails. What is the problem?
A. The router is not forwarding the ping packets to network 127.0.0.0.
B. The remote host at 127.0.0.1 is unreachable.
C. The default gateway is incorrect.
D. The IP address of host A is incorrect.
E. The TCP/IP protocols are not loaded.
Answer: E[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]A switch has 48 ports and 4 VLANs. How many collision and broadcast domains exist on the switch?
A. 4, 48
B. 48, 4
C. 48, 1
D. 1, 48
E. 4, 1
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
Each port on a switch is a collision domain while each VLAN is a broadcast domain because broadcast is only forwarded within that VLAN so we have 48 collision domains and 4 broadcast domains on this switch (if all ports are used).
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]A switch receives a frame on one of its ports. There is no entry in the MAC address table for the destination MAC address. What will the switch do with the frame?
A. drop the frame
B. forward it out of all ports except the one that received it
C. forward it out of all ports
D. store it until it learns the correct port
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which address type does a switch use to make selective forwarding decisions?
A. source IP address
B. destination IP address
C. source and destination IP address
D. source MAC address
E. destination MAC address
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
When a switch receives a frame, it first checks for the destination MAC address and tries to find a matching entry in its MAC address table. If found, the switch then forwards that frame on the corresponding port associated with that MAC address. If no entry is found, the switch will flood that frame out of all (active) ports except the port that sent it.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two characteristics apply to Layer 2 switches? (Choose two)
A. increases the number of collision domains
B. decreases the number of collision domains
C. implements VLAN
D decreases the number of broadcast domains
E. uses the IP address to make decisions for forwarding data packets
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the purpose of assigning an IP address to a switch?
A. provides local hosts with a default gateway address
B. allows remote management of the switch
C. allows the switch to respond to ARP requests between two hosts
D. ensures that hosts on the same LAN can communicate with each other
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]How does a switch differ from a hub?
A. A switch does not induce any latency into the frame transfer time.
B. A switch tracks MAC addresses of directly-connected devices.
C. A switch operates at a lower, more efficient layer of the OSI model.
D. A switch decreases the number of broadcast domains.
E. A switch decreases the number of collision domains.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
A hub is not as “intelligent” as a switch because a hub does not try to remember anything passing to it. It just floods out all the ports (except the one that sent it) when it receives a frame.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The ports that are shown are the only active ports on the switch. The MAC address table is shown in its entirety. The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives at the switch. What two operations will the switch perform when it receives this frame? (Choose two)
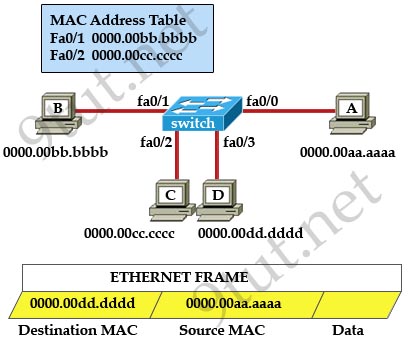
A. The MAC address of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be added to the MAC address table.
B. The MAC address of 0000.00dd.dddd will be added to the MAC address table.
C. The frame will be forwarded out port fa0/3 only.
D. The frame will be forwarded out fa0/1, fa0/2, and fa0/3.
E. The frame will be forwarded out all the active ports.
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
When a switch receives a frame, it first checks for the destination MAC address and tries to find a matching entry in its MAC address table. If found, the switch then forwards that frame on the corresponding port associated with that MAC address. If no entry is found, the switch will flood that frame out of all active ports except the port that sent it. In this case, the destination MAC address 0000.00dd.dddd has not been in the MAC address table so the switch will flood the frame out all of its ports except fa0/0 (the port that it received the frame) -> D is correct.
Also, the switch learns that the MAC address 0000.00aa.aaaa is received on fa0/0 -> the switch adds 0000.00aa.aaaa and its corresponding port fa0/0 to the MAC address table -> A is correct.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The MAC address table is shown in its entirety. The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives at the switch. What two operations will the switch perform when it receives this frame? (Choose two)
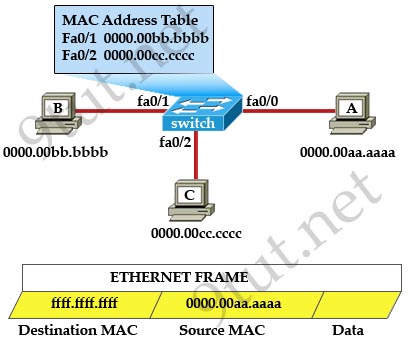
A. The switch will not forward a frame with this destination MAC address.
B. The MAC address of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be added to the MAC Address Table.
C. The MAC address of ffff.ffff.ffff will be added to the MAC address table.
D. The frame will be forwarded out all active switch ports except for port fa0/0.
E. The frame will be forwarded out fa0/0 and fa0/1 only.
F. The frame will be forwarded out all the ports on the switch.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
The destination MAC address is ffff.ffff.ffff so this is a broadcast frame so the switch will forward the frame out all active switch ports except for port fa0/0.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit is showing the topology and the MAC address table. Host A sends a data frame to host D. What will the switch do when it receives the frame from host A?
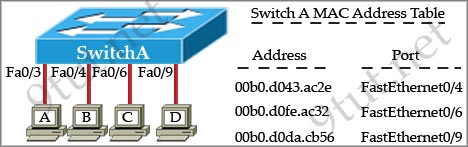
A. The switch will add the source address and port to the MAC address table and forward the frame to host D.
B. The switch will discard the frame and send an error message back to host A.
C. The switch will flood the frame out of all ports except for port Fa0/3.
D. The switch will add the destination address of the frame to the MAC address table and forward the frame to host D.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
In this case the destination MAC address has been learned so the switch just forwards the frame to the corresponding port. It also learn that the source MAC address of host A has not been existed in the MAC address table so it will add it (and port fa0/3) to its MAC address table.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the topology and switching table shown in the graphic. Host B sends a frame to Host C. What will the switch do with the frame?
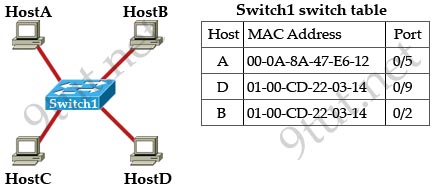
A. drop the frame
B. send the frame out all ports except port 0/2
C. return the frame to Host B
D. send an ARP request for Host C
E. send an ICMP Host Unreachable message to Host B
F. record the destination MAC address in the switching table and send the frame directly to Host C
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. SwitchA receives the frame with the addressing shown in the exhibit. According to the command output also shown in the exhibit, how will SwitchA handle this frame?
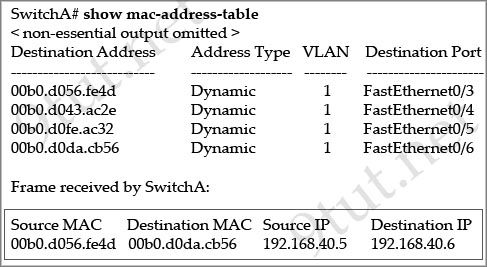
A. It will drop the frame.
B. It will forward the frame out port Fa0/6 only.
C. It will forward the frame out port Fa0/3 only.
D. It will flood the frame out all ports.
E. It will flood the frame out all ports except Fa0/3.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 12
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. An administrator replaced the 10/100 Mb NIC in a desktop PC with a 1 Gb NIC and now the PC will not connect to the network. The administrator began troubleshooting on the switch. Using the switch output shown, what is the cause of the problem?
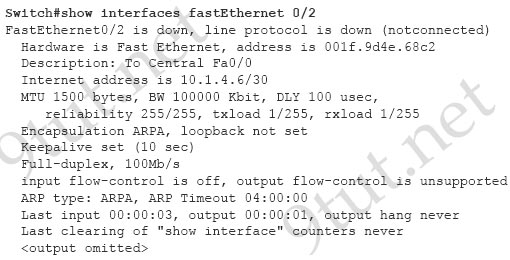
A. Speed is set to 100Mb/s.
B. Input flow control is off.
C. Encapsulation is set to ARPA.
D. The port is administratively down.
E. The counters have never been cleared.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 13
[am4show have=’p2;’]The system LED is amber on a Cisco Catalyst 2950 series switch. What does this indicate?
A. The system is not powered up.
B. The system is powered up and operational.
C. The system is malfunctioning.
D. The system is forwarding traffic.
E. The system is sensing excessive collisions.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The system LED shows whether the system is receiving power and functioning properly. Below lists the LED colors and meanings:
| Color | System Status |
| Off | System is not powered up. |
| Green | System is operating normally. |
| Amber | System is receiving power but is not functioning properly. |
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2950/hardware/installation/guide/hgovrev.html)
Question 14
[am4show have=’p2;’]SW-C has just been added to the network shown in the graphic
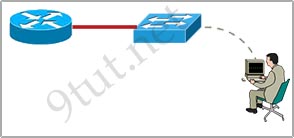
What is the purpose of assigning a default gateway to this switch?
A. allows connectivity to Router B from the switch prompt
B. allows console port connectivity to the switch from Host A
C. allows connectivity to remote network devices from Host B
D. allows the switch to pass traffic between Host A and Host B
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit is showing the topology and the MAC address table. Host A sends a data frame to host D. What will the switch do when it receives the frame from host A?

A. The switch will add the source address and port to the MAC address table and forward the frame to host D.
B. The switch will discard the frame and send an error message back to host A.
C. The switch will flood the frame out of all ports except for port Fa0/3.
D. The switch will add the destination address of the frame to the MAC address table and forward the frame to host D.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
In this case the destination MAC address has been learned so the switch just forwards the frame to the corresponding port. It also learn that the source MAC address of host A has not been existed in the MAC address table so it will add it (and port fa0/3) to its MAC address table.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about unicast frame forwarding on a switch is true?
A. The TCAM table stores destination MAC addresses
B. If the destination MAC address is unknown, the frame is flooded to every port that is configured in the same VLAN except on the port that it was received on.
C. The CAM table is used to determine whether traffic is permitted or denied on a switch
D. The source address is used to determine the switch port to which a frame is forwarded
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Two hosts are attached to a switch with the default configuration. Which statement about the configuration is true?
A. IP routing must be enabled to allow the two hosts to communicate.
B. The two hosts are in the same broadcast domain.
C. The switch must be configured with a VLAN to allow the two hosts to communicate.
D. Port security prevents the hosts from connecting to the switch.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
All ports on a Layer 2 switch are in the same broadcast domain. Only router ports separate broadcast domains.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Configuration of which option is required on a Cisco switch for the Cisco IP phone to work?
A. PortFast on the interface
B. the interface as an access port to allow the voice VLAN ID
C. a voice VLAN ID in interface and global configuration mode
D. Cisco Discovery Protocol in global configuration mode
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
When you connect an IP phone to a switch using a trunk link, it can cause high CPU utilization in the switches. As all the VLANs for a particular interface are trunked to the phone, it increases the number of STP instances the switch has to manage. This increases the CPU utilization. Trunking also causes unnecessary broadcast / multicast / unknown unicast traffic to hit the phone link.
In order to avoid this, remove the trunk configuration and keep the voice and access VLAN configured along with Quality of Service (QoS). Technically, it is still a trunk, but it is called a Multi-VLAN Access Port (MVAP). Because voice and data traffic can travel through the same port, you should specify a different VLAN for each type of traffic. You can configure a switch port to forward voice and data traffic on different VLANs. Configure IP phone ports with a voice VLAN configuration. This configuration creates a pseudo trunk, but does not require you to manually prune the unnecessary VLANs.
The voice VLAN feature enables access ports to carry IP voice traffic from an IP phone. You can configure a voice VLAN with the “switchport voice vlan …” command under interface mode. The full configuration is shown below:
| Switch(config)#interface fastethernet0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 Switch(config-if)#switchport voice vlan 20 |
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which address type does a switch use to make selective forwarding decisions?
A. source IP address
B. destination IP address
C. source and destination IP address
D. source MAC address
E. destination MAC address
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
When a switch receives a frame, it first checks for the destination MAC address and tries to find a matching entry in its MAC address table. If found, the switch then forwards that frame on the corresponding port associated with that MAC address. If no entry is found, the switch will flood that frame out of all (active) ports except the port that sent it.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]After the power-on self test (POST), the system LED of a Cisco 2950 switch turns amber. What is the status of the switch?
A. The switch has a problem with the internal power supply and needs an external power supply to be attached.
B. The switch has experienced an internal problem but data can still be forwarded at a slower rate.
C. The POST was successful.
D. POST failed and there is a problem that prevents the operating system of the switch from being loaded.
E. The switch passed POST, but all the switch ports are busy
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The system LED shows whether the system is receiving power and functioning properly. Below lists the LED colors and meanings:
| Color | System Status |
| Off | System is not powered up. |
| Green | System is operating normally. |
| Amber | System is receiving power but is not functioning properly. |
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2950/hardware/installation/guide/hgovrev.html)
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option is a invalid hostname for a switch?
A. 5witch-Cisco
B. Switch-Cisco!
C. 5witchCisc0
D. SwitchCisc0
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The “!” is an invalid letter for a hostname. The name is alphanumeric so it can begin with a number.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The ports that are shown are the only active ports on the switch. The MAC address table is shown in its entirety. The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives at the switch. What two operations will the switch perform when it receives this frame? (Choose two)

A. The MAC address of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be added to the MAC address table.
B. The MAC address of 0000.00dd.dddd will be added to the MAC address table.
C. The frame will be forwarded out port fa0/3 only.
D. The frame will be forwarded out fa0/1, fa0/2, and fa0/3.
E. The frame will be forwarded out all the active ports.
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
When a switch receives a frame, it first checks for the destination MAC address and tries to find a matching entry in its MAC address table. If found, the switch then forwards that frame on the corresponding port associated with that MAC address. If no entry is found, the switch will flood that frame out of all active ports except the port that sent it. In this case, the destination MAC address 0000.00dd.dddd has not been in the MAC address table so the switch will flood the frame out all of its ports except fa0/0 (the port that it received the frame) -> D is correct.
Also, the switch learns that the MAC address 0000.00aa.aaaa is received on fa0/0 -> the switch adds 0000.00aa.aaaa and its corresponding port fa0/0 to the MAC address table -> A is correct.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which table displays the MAC addresses that are learned on a switch?
A. FIB
B. ARP
C. TCAM
D. CAM
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
In short, TCAM (Ternary Content Addressable Memory) is used for faster IP look up while ARP table is Layer3 address to Layer2 address resolution so they are not correct.
The Content Addressable Memory (CAM) table on a switch keeps track of MAC addresses and on what port they appear, along with some other stuff like age. When a device that’s plugged into a particular port sends a frame to the switch, the switch makes note of the source MAC and the port and checks the CAM table. Notice that the CAM table is built on the source MAC addresses (while the destination MAC addresses are ignored).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]If a host experiences intermittent issues that relate to congestion within a network while remaining connected, what could cause congestion on this LAN?
A. half-duplex operation
B. broadcast storms
C. network segmentation
D. multicasting
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
A broadcast storm can cause congestion within a network. For more information about broadcast storm please read my STP tutorial.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two characteristics describe the access layer of the hierarchical network design model? (Choose two)
A. layer 3 support
B. port security
C. redundant components
D. VLANs
E. PoE
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
The primary function of an access-layer is to provide network access to the end user.
The hardware and software attributes of the access layer that support high availability include security services for additional security against unauthorized access to the network through the use of tools such as 802.1x, port security, DHCP snooping, Dynamic ARP Inspection, and IP Source Guard.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes the effect of this configuration?
| Router#configure terminal Router(config)#vlan 10 Router(config-vlan)#do show vlan |
A. The VLAN 10 VTP configuration is displayed.
B. VLAN 10 spanning-tree output is displayed.
C. The VLAN 10 configuration is saved when the router exits VLAN configuration mode.
D. VLAN 10 is added to the VLAN database.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
With the configuration above, when we type “do show vlan” we would not see VLAN 10 in the VLAN database because it has not been created yet. VLAN 10 is only created when we exits VLAN configuration mode (with “exit” command).
Note: We are sure the answer of Q.1 is C although Packet Tracer may give different answer. We believe the author of this question wants to test us in this case. We also tested this with switch v15.2 and the answer is C.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about native VLAN traffic is true?
A. Cisco Discovery Protocol traffic travels on the native VLAN by default
B. Traffic on the native VLAN is tagged with 1 by default
C. Control plane traffic is blocked on the native VLAN.
D. The native VLAN is typically disabled for security reasons
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Traffic on the native VLAN is untagged -> Answer B is not correct.
Control plane traffic (like CDP, VTP, STP…) runs on VLAN 1 by default. They are not blocked on the native VLAN -> Answer C is not correct.
If the answer says “the native VLAN should be set so that no real traffic running on it for security reasons” then it is correct but the native VLAN is not typically disabled -> Answer D is not correct.
CDP runs on VLAN 1 by default and the native VLAN is also VLAN 1 by default so answer A is the best choice here.
Question 3
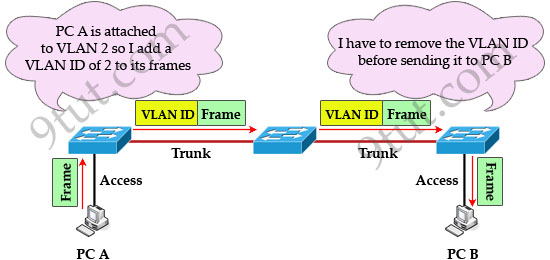
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which method does a connected trunk port use to tag VLAN traffic?
A. IEEE 802.1w
B. IEEE 802.1D
C. IEEE 802.1Q
D. IEEE 802.1p
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
IEEE 802.1Q is the networking standard that supports virtual LANs (VLANs) on an Ethernet network. When a frame enters the VLAN-aware portion of the network (a trunk link, for example), a VLAN ID tag is added to represent the VLAN membership of that frame. The picture below shows how VLAN tag is added and removed while going through the network.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which function enables an administrator to route multiple VLANs on a router?
A. IEEE 802.1X
B. HSRP
C. port channel
D. router on a stick
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two VLANs are reserved for system use only? (Choose two)
A. 1
B. 4095
C. 4096
D. 0
E. 1001
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
The VLANs 0 and 4095 are reserved by the IEEE 802.1Q standard and you cannot create, delete, or modify them so they are the correct answers.
Note:
+ VLAN 0 and 4095 are reserved for system use only. You cannot see or use these VLANs.
+ VLAN 1 and VLANs 1002-1005 are default VLANs. Default VLANs are created automatically and cannot be configured or deleted by users.
+ VLAN 2 to 1001 are normal VLANs. You can create, use and delete them.
+ VLAN 1002 to 1005 are normal VLANs too but Cisco reserved for FDDI an Token Ring. You cannot delete these VLANs.
+ VLAN 1006 to 4094 are extended VLANs (for Ethernet VLANs only)
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_4t/12_4t15/ht_xvlan.html and http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12-2SX/configuration/guide/book/vlans.html
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which network configuration can you use to segregate traffic for two different department in our organization?
A. VTP
B. STP
C. VLAN
D. Etherchannel
Answer: C[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about a router on a stick is true?
A. Its date plane router traffic for a single VLAN over two or more switches.
B. It uses multiple subinterfaces of a single interface to encapsulate traffic for different VLANs on the same subnet.
C. It requires the native VLAN to be disabled.
D. It uses multiple subinterfaces of a single interface to encapsulate traffic for different VLANs.
Answer: D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Based on the network shown in the graphic
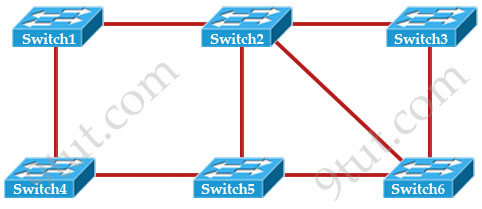
Which option contains both the potential networking problem and the protocol or setting that should be used to prevent the problem?
A. routing loops, hold down timers
B. Switching loops, split horizon
C. routing loops, split horizon
D. Switching loops, VTP
E. routing loops, STP
F. Switching loops, STP
Answer: F[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]By default, how many MAC addresses are permitted to be learned on a switch port with port security enabled?
A. 8
B. 2
C. 1
D. 0
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
By default, port security limits the MAC address that can connect to a switch port to one. If the maximum number of MAC addresses is reached, when another MAC address attempting to access the port a security violation occurs.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option is the default switch port port-security violation mode?
A. shutdown
B. protect
C. shutdown vlan
D. restrict
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Shutdown is the default switch port port-security violation mode. When in this mode, the switch will automatically force the switchport into an error disabled (err-disable) state when a violation occurs. While in this state, the switchport forwards no traffic. The switchport can be brought out of this error disabled state by issuing the errdisable recovery cause CLI command or by disabling and re-enabling the switchport.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the purpose of the switchport command?
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1
Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address 0018.DE8B.4BF8
A. It ensures that only the device with the MAC address 0018.DE8B.4BF8 will be able to connect to the port that is being configured.
B. It informs the switch that traffic destined for MAC address 0018.DE8B.4BF8 should only be sent to the port that is being configured.
C. It will act like an access list and the port will filter packets that have a source or destination MAC of 0018.DE8B.4BF8.
D. The switch will shut down the port of any traffic with source MAC address of 0018.DE8B.4BF8.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement is a Cisco best practice for switch port security?
A. Vacant switch ports must be shut down.
B. Empty ports must be enabled in VLAN 1.
C. VLAN 1 must be configured as the native VLAN.
D. Err-disabled ports must be configured to automatically re-enable.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]An administrator connects devices to a switch and wants dynamically learned MAC addresses and add them to the running config. What accomplishes this?
A. Enable port security and use the keyword sticky
B. Set the switchport mode to trunk and save the running configuration
C. Use the switchport protected command to have the MAC addresses added to the configuration
D. Use the no switchport port-security command to allow MAC addresses to be added to the configuration
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two of these functions do routers perform on packets? (Choose two)
A. examine the Layer 2 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
B. update the Layer 2 headers of outbound packets with the MAC addresses of the next hops
C. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
D. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the complete paths along which the packets will be routed to their ultimate destinations
E. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to valid next hops
F. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to their ultimate destinations
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
When packets travel through many routers, the source and destination IP addresses do not change but the source and destination MAC do change.
Question 2
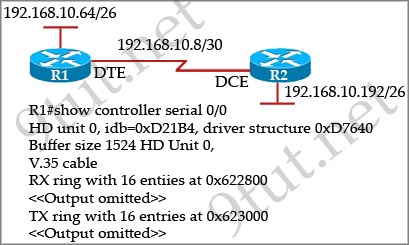
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. An administrator cannot connect from R1 to R2. To troubleshoot this problem, the administrator has entered the command shown in the exhibit. Based on the output shown, what could be the problem?
A. The serial interface is configured for half duplex.
B. The serial interface does not have a cable attached.
C. The serial interface has the wrong type of cable attached.
D. The serial interface is configured for the wrong frame size.
E. The serial interface has a full buffer.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The output above is unclear. Normally when we use this command we can see the type of serial connection on this interface, for example “V.35 DCE cable. Below is an example of the same command as above:
|
RouterA#show controllers serial 0 |
Or
|
RouterB#show controllers serial 0 |
but in this case we only get “V.35 cable”. So in fact we are not sure about the answer C. But the output above also does not have any information to confirm other answers are correct or not.
Just for your information, the V.35 male and V.35 female cable are shown below:


Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What two things does a router do when it forwards a packet? (Choose two)
A. switches the packet to the appropriate outgoing interfaces
B. computes the destination host address
C. determines the next hop on the path
D. updates the destination IP address
E. forwards ARP requests
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 4
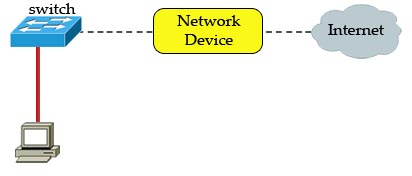
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network device needs to be installed in the place of the icon labeled Network Device to accommodate a leased line attachment to the Internet. Which network device and interface configuration meets the minimum requirements for this installation?
A. a router with two Ethernet interfaces
B. a switch with two Ethernet interfaces
C. a router with one Ethernet and one serial interface
D. a switch with one Ethernet and one serial interface
E. a router with one Ethernet and one modem interface
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two commands will display the current IP address and basic Layer 1 and 2 status of an interface? (Choose two)
A. Router#show version
B. Router#show ip interface
C. router#show protocols
D. router#show controllers
E. Router#show running-config
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
The outputs of “show protocols” and “show ip interface” are shown below:
| Global values: Internet Protocol routing is enabled Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 10.1.1.1/30 Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 209.65.200.225/30 Serial0/2 is up, line protocol is down Serial0/3 is up, line protocol is down NVI0 is up, line protocol is up Interface is unnumbered. Using address of NVI0 (0.0.0.0) Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 10.1.10.1/32 Loopback1 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 10.1.2.1/27 Loopback6 is up, line protocol is up |
| Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is down Internet address is 10.1.1.1/30 Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255 Address determined by non-volatile memory MTU is 1500 bytes Helper address is not set Directed broadcast forwarding is disabled Multicast reserved groups joined: 224.0.0.5 Outgoing access list is not set Inbound access list is not set Proxy ARP is enabled Local Proxy ARP is disabled Security level is default Split horizon is disabled ICMP redirects are always sent ICMP unreachables are always sent ICMP mask replies are never sent IP fast switching is enabled IP fast switching on the same interface is enabled IP Flow switching is disabled IP CEF switching is disabled IP Feature Fast switching turbo vector IP multicast fast switching is enabled IP multicast distributed fast switching is disabled IP route-cache flags are Fast Router Discovery is disabled IP output packet accounting is disabled IP access violation accounting is disabled TCP/IP header compression is disabled RTP/IP header compression is disabled Policy routing is disabled Network address translation is enabled, interface in domain inside BGP Policy Mapping is disabled WCCP Redirect outbound is disabled WCCP Redirect inbound is disabled WCCP Redirect exclude is disabled |
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. If the resume command is entered after the sequence that is shown in the exhibit, which router prompt will be displayed?

A. Router1>
B. Router1#
C. Router2>
D. Router2#
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The “Ctrl-Shift-6” and “x” is used to suspend the telnet session. In this case, the telnet session from Router1 to Router2 will be suspended.
If we enter the keyword “resume”, Router1 will try to resume the telnet session to Router2 (you will see the line [Resuming connection 1 to 192.168.9.2 … ]) and we will get back the Router2> prompt.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]When a router makes a routing decision for a packet that is received from one network and destined to another, which portion of the packet does if replace?
A. Layer 2 frame header and trailer
B. Layer 3 IP address
C. Layer 5 session
D. Layer 4 protocol
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The Layer 2 information (source and destination MAC) would be changed when passing through each router. The Layer 3 information (source and destination IP addresses) remains unchanged.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two of these functions do routers perform on packets? (Choose two)
A. examine the Layer 2 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
B. update the Layer 2 headers of outbound packets with the MAC addresses of the next hops
C. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the next hops for the packets
D. examine the Layer 3 headers of inbound packets and use that information to determine the complete paths along which the packets will be routed to their ultimate destinations
E. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to valid next hops
F. update the Layer 3 headers of outbound packets so that the packets are properly directed to their ultimate destinations
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
When packets travel through many routers, the source and destination IP addresses do not change but the source and destination MAC do change.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]How do you bypass password on Cisco device?
A. Change the configuration register to 0x2142
B. Reset the device
C. Unplug and plug the power
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Change the configuration register to 0x2142. With this setting when that router reboots, it bypasses the startup-config and no password is required.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which router command can be used to determine the status of Serial 0/0?
A. show ip route
B. show interfaces
C. show s0/0 status
D. debug s0/0
E. show run
F. show version
Answer: B[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
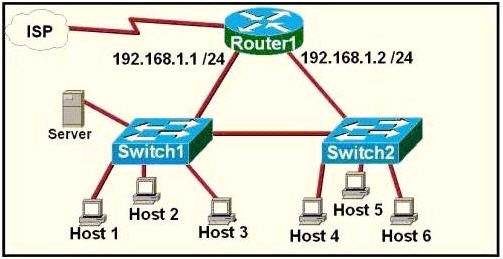
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is asked to design a small network with redundancy. The exhibit represents this design, with all hosts configured in the same VLAN. What conclusions can be made about this design?
A. The design will function as intended
B. Spanning-tree will need to be used.
C. The router will not accept the addressing scheme.
D. The connection between switches should be a trunk.
E. The router interfaces must be encapsulated with the 802.1Q protocol.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Each interface on a router must be in a different network. If two interfaces are in the same network, the router will not accept it and show error when the administrator assigns it.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Why did the device return this message?
| Router#show ru % Ambiguous command: “show ru” Router# |
A. The command requires additional options or parameters
B. There is no show command that starts with ru.
C. The command is being executed from the wrong router mode.
D. There is more than one show command that starts with the letters ru.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which commands display information about the Cisco IOS software version currently running on a router? (Choose three)
A. show running-config
B. show stacks
C. show version
D. show flash
E. show protocols
F. show IOS
Answer: A C D[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]After the shutdown command has been issued on the serial 0/0 interface, what will be displayed when the show interface serial 0/0 command is issued by the administrator?
A. Serial0/0 is administratively down, line protocol is down
B. Serial0/0 is down, line protocol is down
C. Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is down
D. Serial0/0 is administratively down, line protocol is administratively down
E. Serial0/0 is up, line protocol is up
F. Serial0/0 is down, line protocol is up
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 5
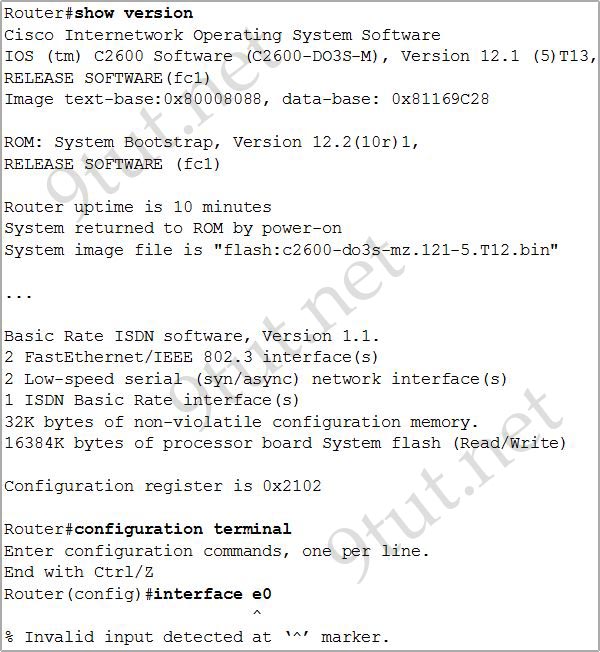
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the output of the three router commands shown in the exhibit. A new technician has been told to add a new LAN to the company router. Why has the technician received the error message that is shown following the last command?
A. The interface was already configured.
B. The interface type does not exist on this router platform.
C. The IOS software loaded on the router is outdated.
D. The router does not support LAN interfaces that use Ethernet.
E. The command was entered from the wrong prompt.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output of the “show version” command, we learn that there are only 2 FastEthernet interfaces (2 FastEthernet/IEEE 802.3 interfaces) and this router does not have any Ethernet interface so an error will occur when we enter the “interface e0” command.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true of the interface configuration? (Choose two)
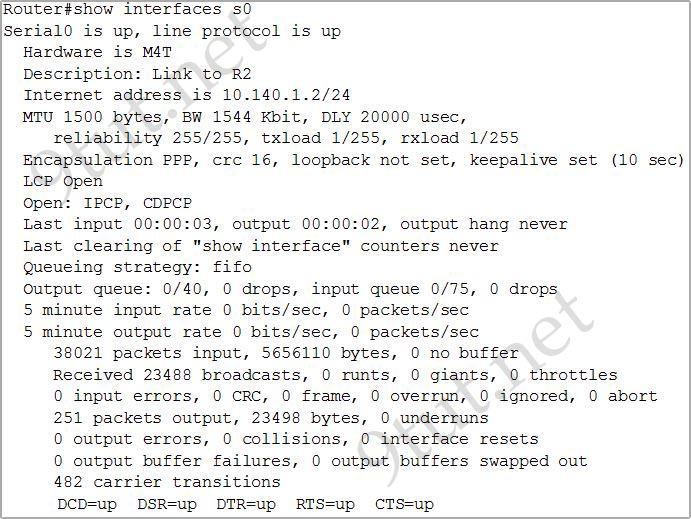
A. The encapsulation in use on this interface is PPP.
B. The default serial line encapsulation is in use on this interface.
C. The address mask of this interface is 255.255.255.0.
D. This interface is connected to a LAN.
E. The interface is not ready to forward packets.
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What does the address 192.168.2.167 represent?
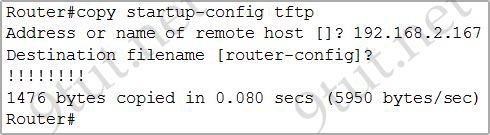
A. the TFTP server from which the file startup-config is being transferred
B. the router from which the file startup-config is being transferred
C. the TFTP server from which the file router-confg is being transferred
D. the TFTP server to which the file router-confg is being transferred
E. the router to which the file router-confg is being transferred
F. the router to which the file startup-config is being transferred
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which Ethernet interface command is present when you boot a new Cisco router for the first time?
A. speed 100
B. shutdown
C. ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
D. duplex half
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement describes the effect of the copy run start command on a router in enable mode?
A. The running configuration of the router is saved to NVRAM and used during the boot process.
B. The router reboots and loads the last saved running configuration.
C. A copy of the running configuration of the router is sent by FTP to a designated server.
D. A new running configuration is loaded from flash memory to the router.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]What does exec-timeout 30 mean?
A. the user inactivity timer is 30 seconds
B. the user inactivity timer is 30 minutes
C. the user inactivity timer is 30 hours
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The “exec-timeout” command is used to configure the inactive session timeout on the console port or the virtual terminal. The syntax of this command is:
exec-timeout minutes [seconds]
Therefore we need to use the “exec-timeout 30” command to set the user inactivity timer to 30 minutes. To set the user inactivity timer to 30 seconds we use the “exec-timeout 0 30”.
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]How many primary IPv4 addresses can be assigned on router interface?
A. One
B. Two
C. More than one
D. More than two
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
On each router interface we can only assign one primary IPv4 address (but we can assign many IPv6 addresses).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of the following statements are TRUE regarding Cisco access lists? (Choose two)
A. In an inbound access list, packets are filtered as they enter an interface.
B. In an inbound access list, packets are filtered before they exit an interface.
C. Extended access lists are used to filter protocol-specific packets.
D. You must specify a deny statement at the end of each access list to filter unwanted traffic.
E. When a line is added to an existing access list, it is inserted at the beginning of the access list.
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature automatically disables CEF when it is enabled?
A. RIB
B. ACL logging
C. multicast
D. IP redirects
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
ACL Logging means to use the “log” or “log-input” parameters at the end of the ACL statements. For example: “access-list 100 deny icmp any any echo reply log-input”. In either situation, remember that using either of these two parameters disables CEF switching, which seriously impacts the performance of the router.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. If CDP is enabled on all devices and interfaces, which devices will appear in the output of a show cdp neighbors command issued from R2?
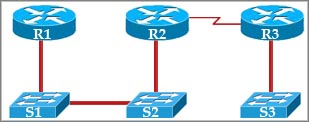
A. R2 and R3
B. R1 and R3
C. R3 and S2
D. R1, S1, S2, and R3
E. R1, S1, S2, R3, and S3
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
CDP runs at Layer 2 so it can recognize a switch (if that switch also runs CDP).
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]On a Cisco switch, which protocol determines if an attached VoIP phone is from Cisco or from another vendor?
A. RTP
B. TCP
C. CDP
D. UDP
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a proprietary protocol of Cisco so if you can see the VoIP phone via the “show cdp neighbors” command on a Cisco switch then that phone is from Cisco.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]At which layer of the OSI model does the protocol that provides the information that is displayed by the show cdp neighbors command operate?
A. application
B. transport
C. network
D. physical
E. data link
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
CDP runs at Layer 2 (Data Link) of the OSI model -> E is correct.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. For security reasons, information about RTA, including platform and IP addresses, should not be accessible from the Internet. This information should, however, be accessible to devices on the internal networks of RTA. Which command or series of commands will accomplish these objectives?
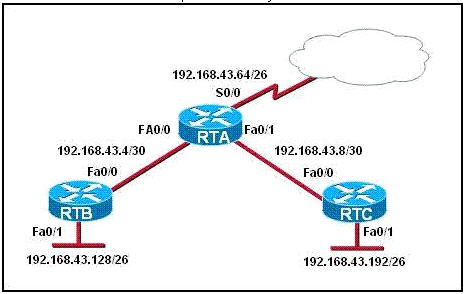
A – RTA(config)#no cdp run
B – RTA(config)#no cdp enable
C – RTA(config)#interface s0/0
RTA(config-if)#no cdp run
D – RTA(config)#interface s0/0
RTA(config-if)#no cdp enable
Answer: D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which protocol uses a connection-oriented service to deliver files between end systems?
A. TFTP
B. DNS
C. FTP
D. SNMP
E. RIP
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over TCP-based network, such as the Internet.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]On a Cisco switch, which protocol determines if an attached VoIP phone is from Cisco or from another vendor?
A. RTP
B. TCP
C. CDP
D. UDP
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a proprietary protocol of Cisco so if you can see the VoIP phone via the “show cdp neighbors” command on a Cisco switch then that phone is from Cisco.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which transport layer protocol provides best-effort delivery service with no acknowledgment receipt required?
A. HTTP
B. IP
C. TCP
D. Telnet
E. UDP
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) provides a connectionless datagram service that offers best-effort delivery, which means that UDP does not guarantee delivery or verify sequencing for any datagrams. UDP is typically used by programs that transmit small amounts of data at one time or have real-time requirements (voice, for example).
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statements accurately describe CDP? (Choose three)
A. CDP is an IEEE standard protocol.
B. CDP is a Cisco proprietary protocol.
C. CDP is a datalink layer protocol.
D. CDP is a network layer protocol.
E. CDP can discover directly connected neighboring Cisco devices.
F. CDP can discover Cisco devices that are not directly connected.
Answer: B C E[/am4show]
Explanation
CDP is a device discovery protocol that runs over Layer 2. We can view the CDP information with the show cdp neighbors command (thus the provided information is at layer 2), notice this command only shows information about directly connected devices. The output of the show cdp neighbors command is shown below:
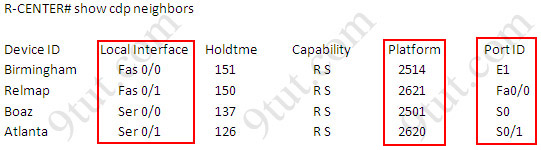
There are 3 columns you must pay attention to:
* Local interface: type & ID of the local interface on which CDP information of the neighbor were received.
* Device platform: the neighboring device model.
* Port ID: the connected interface of the neighbor.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]A workstation has just resolved a browser URL to the IP address of a server. What protocol will the workstation now use to determine the destination MAC address to be placed into frames directed toward the server?
A. HTTP
B. DNS
C. DHCP
D. RARP
E. ARP
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
After resolving a browser URL to an IP address (via DNS server), the workstation must learn the MAC address of the server so that it can create a complete packet (a complete packet requires destination MAC and IP address, source MAC and IP address). Therefore the workstation must use ARP to find out the MAC address from the IP address.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]How does TCP differ from UDP? (Choose two)
A. TCP provides best effort delivery.
B. TCP provides synchronized communication.
C. TCP segments are essentially datagrams.
D. TCP provides sequence numbering of packets.
E. TCP uses broadcast delivery.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
Before two computers can communicate over TCP, they must synchronize their initial sequence numbers (ISN) -> B is correct.
TCP uses a sequence number to identify each byte of data. The sequence number identifies the order of the bytes sent from each computer so that the data can be reconstructed in order, regardless of any fragmentation, disordering, or packet loss that may occur during transmission -> D is correct.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The two routers have had their startup configurations cleared and have been restarted. At a minimum, what must the administrator do to enable CDP to exchange information between R1 and R2?
![]()
A. Configure the router with the cdp enable command.
B. Enter no shutdown commands on the R1 and R2 fa0/1 interfaces.
C. Configure IP addressing and no shutdown commands on both the R1 and R2 fa0/1 interfaces.
D. Configure IP addressing and no shutdown commands on either of the R1 or R2 fa0/1 interfaces.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
By default CDP is enabled on Cisco routers -> A is not correct.
CDP runs at Layer 2 in the OSI model and it does not need an IP address to run -> C & D are not correct.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statements are true regarding ICMP packets? (Choose two)
A. They acknowledge receipt of TCP segments.
B. They guarantee datagram delivery
C. TRACERT uses ICMP packets.
D. They are encapsulated within IP datagrams.
E. They are encapsulated within UDP datagrams
Answer: C D[/am4show]
Explanation
Tracert (or traceroute) is used to trace the path between the sender and the destination host. Traceroute works by sending packets with gradually increasing Time-to-Live (TTL) value, starting with TTL value = 1. The first router receives the packet, decrements the TTL value and drops the packet because it then has TTL value zero. The router sends an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source. The next set of packets are given a TTL value of 2, so the first router forwards the packets, but the second router drops them and replies with ICMP Time Exceeded. Proceeding in this way, traceroute uses the returned ICMP Time Exceeded messages to build a list of routers that packets traverse, until the destination is reached and returns an ICMP Echo Reply message -> C is correct.
ICMP is encapsulated in an IP packet. In particular, the ICMP message is encapsulated in the IP payload part of an IP datagram -> D is correct.
Note: The TRACERT command on Windows Operating System uses ICMP while MAC OS X and Linux TRACEROUTE use UDP.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]The network administrator is using a Windows PC application that is called putty.exe for remote communication to a switch for network troubleshooting. Which two protocols could be used during this communication? (Choose two)
A. SNMP
B. HTTP
C. Telnet
D. RMON
E. SSH
Answer: C E[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which protocol verifies connectivity between two switches that are configured with IP addresses in the same network?
A. ICMP
B. STP
C. VTP
D. HSRP
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which RFC was created to alleviate the depletion of IPv4 public addresses?
A. RFC 4193
B. RFC 1519
C. RFC 1518
D. RFC 1918
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The RFC 1518 is Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR), which is created to save the IPv4 addresses because we can now assign IP addresses classless. Therefore, instead of assigning the whole block of a class B or C address, now smaller blocks of a class can be assigned. For example, instead of assigning a whole block of 200.1.45.0/24, a smaller block, like 200.1.45.0/27 or 200.1.45.32/27, can be assigned.
The RFC 1918 is Address Allocation for Private Internets, which reserves IP addresses for private and internal use. These addresses can be used for networks that do not need to connect to the Internet.
Therefore the RFC 1918 is the best choice to “alleviate the depletion of IPv4 public addresses”.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which destination IP address can a host use to send one message to multiple devices across different subnets?
A. 172.20.1.0
B. 127.0.0.1
C. 192.168.0.119
D. 239.255.0.1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
In order to send traffic to multiple devices (not all) across different subnets we need to use multicast addresses, which are in the range 224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255 -> D is correct.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which technology allows a large number of private IP addresses to be represented by a smaller number of public IP addresses?
A. NAT
B. NTP
C. RFC 1631
D. RFC 1918
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which IP address is a private address?
A. 12.0.0.1
B. 168.172.19.39
C. 172.20.14.36
D. 172.33.194.30
E. 192.169.42.34
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of the following IP addresses are valid Class B host addresses if a default Class B mask is in use? (Choose two)
A. 10.6.8.35
B. 133.6.5.4
C. 192.168.5.9
D. 127.0.0.1
E. 190.6.5.4
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]From where does a small network get its IP network address?
A. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
B. Internet Architecture Board (IAB)
C. Internet Service Provider (ISP)
D. Internet Domain Name Registry (IDNR)
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three network addresses are reserved for private network use? (Choose three)
A. 10.0.0.0
B. 172.15.0.0
C. 172.31.0.0
D. 192.162.24.0
E. 192.168.255.0
F. 224.192.0.0
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about Subnetting, please read my Subnetting Made Easy tutorial.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the subnet address for the IP address 172.19.20.23/28?
A. 172.19.20.0
B. 172.19.20.15
C. 172.19.20.16
D. 172.19.20.20
E. 172.19.20.32
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
From the /28 we can find all information we need:
Increment: 16 (/28 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000)
Network address: 172.19.20.16 (because 16 < 23)
Broadcast address: 172.16.20.31 (because 31 = 16 + 16 – 1)
In fact we don’t need to find out the broadcast address because the question only asks about subnet address (network address).
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the network address for the host with IP address 192.168.23.61/28?
A. 192.168.23.0
B. 192.168.23.32
C. 192.168.23.48
D. 192.168.23.56
E. 192.168.23.60
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
From the /28 we can find all information we need:
Increment: 16 (/28 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000)
Network address: 192.168.23.48 (because 48 = 16 * 3 and 48 < 61)
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Given an IP address of 192.168.1.42 255.255.255.248, what is the subnet address?
A. 192.168.1.8/29
B. 192.168.1.32/27
C. 192.168.1.40/29
D. 192.168.1.16/28
E. 192.168.1.48/29
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
From the subnet mask of 255.255.255.248 we learn:
Increment: 8 (248 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11111000)
Network address: 192.168.1.40 (because 40 = 8 * 5 and 40 < 42)
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which IP addresses are valid for hosts belonging to the 10.1.160.0/20 subnet? (Choose three)
A. 10.1.168.0
B. 10.1.176.1
C. 10.1.174.255
D. 10.1.160.255
E. 10.1.160.0
F. 10.1.175.255
Answer: A C D[/am4show]
Explanation
From the /20 we can find all information we need:
Increment: 16 (/20 = 11111111.11111111.11110000.00000000). This is applied for the 3rd octet.
Network address: 10.1.160.0 (because 160 = 16 * 10 and 160 = 160 -> the IP address above is also the network address.
Broadcast address: 10.1.175.255 (because 175 = 160 + 16 – 1)
Therefore only 10.1.168.0, 10.1.174.255 and 10.1.160.255 are in this range. Please notice 10.1.174.255 is not a broadcast address and can be assigned to host.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which one of the following IP addresses is the last valid host in the subnet using mask 255.255.255.224?
A. 192.168.2.63
B. 192.168.2.62
C. 192.168.2.61
D. 192.168.2.60
E. 192.168.2.32
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
Increment: 32 (224 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11100000)
Network address: x.x.x.(0;32;64;96;128;160;192;224)
Broadcast address: x.x.x.(31;63;95;127;159;191;223)
-> Last valid host (reduced broadcast addresses by 1): x.x.x.(30;62;94;126;158;190;222) -> Only B is correct.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]An administrator is working with the 192.168.4.0 network, which has been subnetted with a /26 mask. Which two addresses can be assigned to hosts within the same subnet? (Choose two)
A. 192.168.4.61
B. 192.168.4.63
C. 192.168.4.67
D. 192.168.4.125
E. 192.168.4.128
F. 192.168.4.132
Answer: C D[/am4show]
Explanation
Increment: 64 (/26 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000)
The IP 192.168.4.0 belongs to class C. The default subnet mask of class C is /24 and it has been subnetted with a /26 mask so we have 2(26-24) = 22 = 4 sub-networks:
1st subnet: 192.168.4.0 (to 192.168.4.63)
2nd subnet: 192.168.4.64 (to 192.168.4.127)
3rd subnet: 192.168.4.128 (to 192.168.4.191)
4th subnet: 192.168.4.192 (to 192.168.4.225)
In all the answers above, only answer C and D are in the same subnet.
Therefore only IPs in this range can be assigned to hosts.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]An administrator must assign static IP addresses to the servers in a network. For network 192.168.20.24/29, the router is assigned the first usable host address while the sales server is given the last usable host address. Which of the following should be entered into the IP properties box for the sales server?
A. IP address: 192.168.20.14
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Default Gateway. 192.168.20.9
B. IP address: 192.168.20.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.1
C. IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.25
D. IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
Default Gateway: 192.168.20.17
E. IP address: 192.168.20.30
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240
Default Gateway. 192.168.20.25
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
With network 192.168.20.24/29 we have:
Increment: 8 (/29 = 255.255.255.248 = 11111000 for the last octet)
Network address: 192.168.20.24 (because 24 = 8 * 3)
Broadcast address: 192.168.20.31 (because 31 = 24 + 8 – 1)
Therefore the first usable IP address is 192.168.20.25 (assigned to the router) and the last usable IP address is 192.168.20.30 (assigned to the sales server). The IP address of the router is also the default gateway of the sales server.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Given a Class C IP address subnetted with a /30 subnet mask, how many valid host IP addresses are available on each of the subnets?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
E. 252
F. 254
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The number of valid host IP addresses depends on the number of bits 0 left in the subnet mask. With a /30 subnet mask, only two bits 0 left (/30 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11111100) so the number of valid host IP addresses is 22 – 2 = 2. Also please notice that the /30 subnet mask is a popular subnet mask used in the connection between two routers because we only need two IP addresses. The /30 subnet mask help save IP addresses for other connections. An example of the use of /30 subnet mask is shown below:

Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements describe the IP address 10.16.3.65/23? (Choose two)
A. The subnet address is 10.16.3.0 255.255.254.0.
B. The lowest host address in the subnet is 10.16.2.1 255.255.254.0.
C. The last valid host address in the subnet is 10.16.2.254 255.255.254.0
D. The broadcast address of the subnet is 10.16.3.255 255.255.254.0.
E. The network is not subnetted.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
Increment: 2 (/23 = 11111111.11111111.11111110.00000000 = 255.255.254.0)
Network address: 10.16.2.0 (because 2 = 2 * 1 and 2 < 3)
Broadcast address: 10.16.3.255 (because 2 + 2 – 1 = 3 for the 3rd octet)
-> The lowest (first assignable) host address is 10.16.2.1 and the broadcast address of the subnet is 10.16.3.255 255.255.254.0
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the subnet address of 172.16.159.159/22?
A. 172.16.0.0
B. 172.16.128.0
C. 172.16.156.0
D. 172.16.159.0
E. 172.16.159.128
F. 172.16.192.0
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Increment: 4 (/22 = 11111111.11111111.11111100.00000000)
Network address: 172.16.156.0 (156 is multiple of 4 and 156 < 159)
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about Subnetting, please read my Subnetting Made Easy tutorial.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The junior network support staff provided the diagram as a recommended configuration for the first phase of a four-phase network expansion project. The entire network expansion will have over 1000 users on 14 network segments and has been allocated this IP address space:
192.168.1.1 through 192.168.5.255
192.168.100.1 through 198.168.100.255
What are three problems with this design? (Choose three)
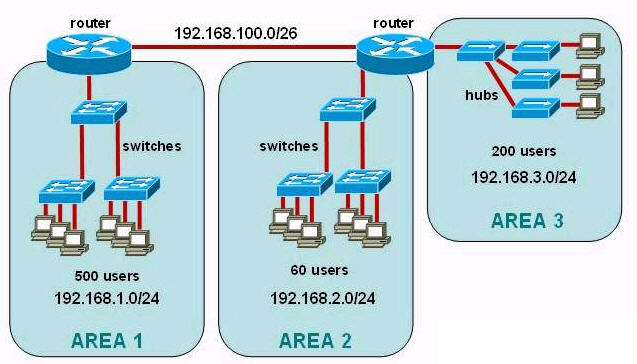
A – The AREA 1 IP address space is inadequate for the number of users.
B – The AREA 3 IP address space is inadequate for the number of users.
C – AREA 2 could use a mask of /25 to conserve IP address space.
D – The network address space that is provided requires a single network-wide mask.
E – The router-to-router connection is wasting address space.
F – The broadcast domain in AREA 1 is too large for IP to function.
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Explanation
AREA 1 has 500 users but it uses class C which only supports 254 users (from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254)-> A is correct.
AREA 3 also uses class C and as mentioned above it supports 254 users so it is enough for 200 users -> B is incorrect.
In AREA 2 there are only 60 users < 64 = 26 so we can use a subnet mask which has 6 bits 0 -> /26. Of course we can use larger subnets (like /25) for future expansion -> C is correct.
A large network should never use a single network-wide mask. It should be some different subnet masks to make the network flexible and easy to be summarized -> D is incorrect.
For router-to-router connection we should use a subnet mask of /30 which supports 2 hosts per subnet. This subnet mask is ideal for router-to-router connection -> E is correct.
There is no limit for IP to function if we know how to organize our network -> F is incorrect.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The enterprise has decided to use the network address 172.16.0.0. The network administrator needs to design a classful addressing scheme to accommodate the three subnets, with 30, 40, and 50 hosts, as shown. What subnet mask would accommodate this network?
| Net bits | Subnet mask | total-addresses per subnet |
| /20 | 255.255.240.0 | 4096 |
| /21 | 255.255.248.0 | 2048 |
| /22 | 255.255.252.0 | 1024 |
| /23 | 255.255.254.0 | 512 |
| /24 | 255.255.255.0 | 256 |
| /25 | 255.255.255.128 | 128 |
| /26 | 255.255.255.192 | 64 |
| /27 | 255.255.255.224 | 32 |
| /28 | 255.255.255.240 | 16 |
| /29 | 255.255.255.248 | 8 |
| /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 4 |
A. 255.255.255.192
B. 255.255.255.224
C. 255.255.255.240
D. 255.255.255.248
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The maximum number of hosts in this question is 50 hosts so we have to use /26 subnet mask or above.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]The network manager has requested a 300-workstation expansion of the network. The workstations are to be installed in a single broadcast domain, but each workstation must have its own collision domain. The expansion is to be as cost-effective as possible while still meeting the requirements. Which three items will adequately fulfill the request? (Choose three)
A. one IP subnet with a mask of 255.255.254.0
B. two IP subnets with a mask of 255.255.255.0
C. seven 48-port hubs
D. seven 48-port switches
E. one router interface
F. seven router interfaces
Answer: A D E[/am4show]
Explanation
To support 300 workstations in a single broadcast domain, we need to use a subnet mask which supports 512 hosts = 29 -> /23 or 255.255.254.0 in decimal form -> A is correct.
If we use 48-port switches we need 300/48 = 6.25 -> seven 48-port switches are enough because we also need trunking between them -> D is correct.
We only need one router interface and it is connected with one of seven switches -> E is correct.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which router command will configure an interface with the IP address 10.10.80.1/19?
A. router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.80.1/19
B. router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.80.1 255.255.0.0
C. router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.80.1 255.255.255.0
D. router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.80.1 255.255.224.0
E. router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.80.1 255.255.240.0
F. router(config-if)# ip address 10.10.80.1 255.255.255.240
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
/19 = 255.255.224.0. The fast way to find out this subnet mask is to remember /16 = 255.255.0.0 and we need 3 more bits 1 for 3rd octet: 1110 0000 which is 224.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A TFTP server has recently been installed in the Atlanta office. The network administrator is located in the NY office and has made a console connection to the NY router. After establishing the connection they are unable to backup the configuration file and IOS of the NY router to the TFTP server. What is the cause of this problem?
A. The NY router has an incorrect subnet mask.
B. The TFTP server has an incorrect IP address.
C. The TFTP server has an incorrect subnet mask.
D. The network administrator computer has an incorrect IP address.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements describe the IP address 10.16.3.65/23? (Choose two)
A. The subnet address is 10.16.3.0 255.255.254.0.
B. The lowest host address in the subnet is 10.16.2.1 255.255.254.0.
C. The last valid host address in the subnet is 10.16.2.254 255.255.254.0
D. The broadcast address of the subnet is 10.16.3.255 255.255.254.0.
E. The network is not subnetted.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
Increment: 2 (/23 = 11111111.11111111.11111110.00000000 = 255.255.254.0)
Network address: 10.16.2.0 (because 2 = 2 * 1 and 2 < 3)
Broadcast address: 10.16.3.255 (because 2 + 2 – 1 = 3 for the 3rd octet)
-> The lowest (first assignable) host address is 10.16.2.1 and the broadcast address of the subnet is 10.16.3.255 255.255.254.0
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The internetwork is using subnets of the address 192.168.1.0 with a subset mask of 255.255.255.224. The routing protocol in use is RIP version 1. Which address could be assigned to the FastEthernet interface on RouterA?
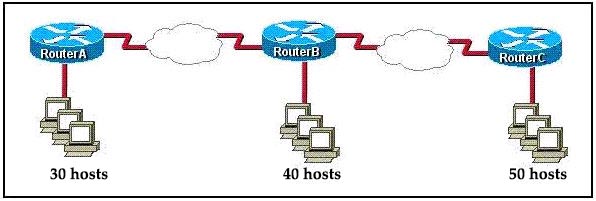
A. 192.168.1.31
B. 192.168.1.64
C. 192.168.1.127
D. 192.168.1.190
E. 192.168.1.192
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
255.255.255.224 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1110 0000 (binary form)
Increment: 32
First subnetwork: 192.168.1.0 -> 192.168.1.31 (A is incorrect because 192.168.1.31 is a broadcast address)
Second subnetwork: 192.168.1.32 -> 192.168.1.63
Third subnetwork: 192.168.1.64 -> 192.168.1.95 (B is incorrect because 192.168.1.64 is a network address)
Fourth subnetwork: 192.168.1.96 -> 192.168.1.127 (C is incorrect because 192.168.1.127 is a broadcast address)
Fifth subnetwork: 192.168.1.128 -> 192.168.1.159
Sixth subnetwork: 192.168.1.160 -> 192.168.1.191 (D is correct because 192.168.1.190 is the last assignable host address of this subnetwork)
Seventh subnetwork: 192.168.1.192 -> 192.168.1.224 (E is incorrect because 192.168.1.192 is a network address)
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]A network administrator is connecting PC hosts A and B directly through their Ethernet interfaces as shown in the graphic. Ping attempts between the hosts are unsuccessful. What can be done to provide connectivity between the hosts? (Choose two)

A. A crossover cable should be used in place of the straight-through cable.
B. A rollover cable should be used in place of the straight-through cable.
C. The subnet masks should be set to 255.255.255.192
D. A default gateway needs to be set on each host.
E. The hosts must be reconfigured to use private IP addresses for direct connections of this type.
F. The subnet masks should be set to 255.255.255.0
Answer: A F[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]If an Ethernet port on a router was assigned an IP address of 172.16.112.1/20, what is the maximum number of hosts allowed on this subnet?
A. 1024
B. 2046
C. 4094
D. 4096
E. 8190
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. After configuring two interfaces on the HQ router, the network administrator notices an error message. What must be done to fix this error?
| HQ#configure terminal HQ(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0 HQ(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.17 255.255.255.0 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown HQ(config-if)# interface serial 0/0 HQ(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.65 255.255.255.240 HQ(config-if)# no shutdown % 192.168.1.0 overlaps with FastEthernet0/0 |
A. The serial interface must be configured first.
B. The serial interface must use the address 192.168.1.2
C. The subnet mask of the serial interface should be changed to 255.255.255.0
D. The subnet mask of the FastEthernet interface should be changed to 255.255.255.240
E. The address of the FastEthernet interface should be changed to 192.168.1.66
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Host B has just been added to the network and must acquire an IP address. Which two addresses are possible addresses that will allow host B to communicate with other devices in the network? (Choose two)
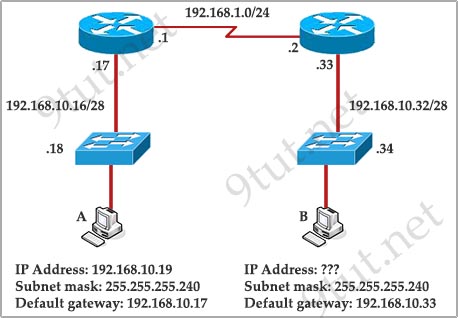
A. 192.168.10.32
B. 192.168.10.38
C. 192.168.10.46
D. 192.168.10.47
E. 192.168.10.49
F. 192.168.10.51
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
The IP address of host B must be in the range of 192.168.10.32/28 subnet, which ranges from 192.168.10.32 to 192.168.10.47 (Increment: 16), except the IP addresses of 192.168.10.32, 192.168.10.46 (which are the network and broadcast addresses of the subnet), 192.168.10.33, 192.168.10.34 (which have been assigned to the interface’s router and the switch). Therefore there are only two IP addresses of 192.168.10.38 & 192.168.10.46.
Question 12
[am4show have=’p2;’]A network administrator has subnetted the 172.16.0.0 network using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. A duplicate IP address of 172.16.2.120 has accidentally been configured on a workstation in the network. The technician must assign this workstation a new IP address within that same subnetwork. Which address should be assigned to the workstation?
A. 172.16.1.80
B. 172.16.2.80
C. 172.16.1.64
D. 172.16.2.64
E. 172.16.2.127
F. 172.16.2.128
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 13
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the maximum number of bits that can be borrowed to create subnets if a Class B network address is being used?
A. 2
B. 6
C. 8
D. 14
E. 16
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 14
[am4show have=’p2;’]The internetwork shown in the diagram is experiencing network connectivity problems. What is the cause of the problem?
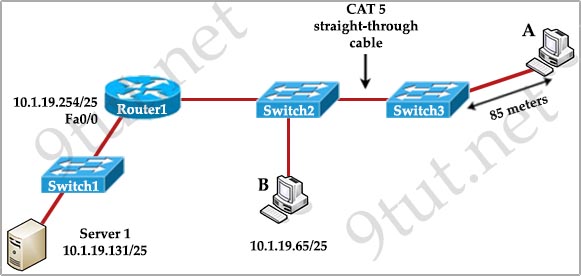
A. The cabling connecting host A to Switch3 is too long.
B. The address of host B is a broadcast address.
C. The IP address of interface Fa0/0 of Router1 is not a usable address.
D. The cable connecting Switch2 and Switch3 should be a crossover.
E. The IP address of Server 1 is in the wrong subnet.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 15
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the subnet address for the IP address 172.19.20.23/28?
A. 172.19.20.0
B. 172.19.20.15
C. 172.19.20.16
D. 172.19.20.20
E. 172.19.20.32
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
From the /28 we can find all information we need:
Increment: 16 (/28 = 11111111.11111111.11111111.11110000)
Network address: 172.19.20.16 (because 16 < 23)
Broadcast address: 172.16.20.31 (because 31 = 16 + 16 – 1)
In fact we don’t need to find out the broadcast address because the question only asks about subnet address (network address).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: The ICND1 exam requires candidates to understand basic knowledge of dynamic routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP, OSPF).
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the best practice when assigning IP addresses in a small office of six hosts?
A. Use a DHCP server that is located at the headquarters.
B. Use a DHCP server that is located at the branch office.
C. Assign the addresses by using the local CDP protocol.
D. Assign the addresses statically on each node.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]The ip helper-address command does what?
A. assigns an IP address to a host
B. resolves an IP address from a DNS server
C. relays a DHCP request across networks
D. resolves an IP address overlapping issue
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
By default, Cisco routers do not forward broadcast address. So what will happen if your PC does not in the same LAN with DHCP Server? Your PC (also a DHCP Client) will broadcast a packet but it is dropped by the router -> Your PC cannot get the IP from DHCP Server. So the “ip helper-address” command enables the DHCP broadcast to be forwarded to the DHCP server. For example, the IP address of your DHCP Server is 10.10.10.254 then we can type in the interface connecting with the DHCP Client (fa0/0 in this case) this command: “ip helper-address 10.10.10.254”.
Note: When a client boots up for the first time, it transmits a DHCPDISCOVER message on its local physical subnet. Because the client has no way of knowing the subnet to which it belongs, the DHCPDISCOVER is an all-subnets broadcast (destination IP address of 255.255.255.255, which is a layer 3 broadcast address). The client does not have a configured IP address, so the source IP address of 0.0.0.0 is used.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. As packets travel from Mary to Robert, which three devices will use the destination MAC address of the packet to determine a forwarding path? (Choose three)
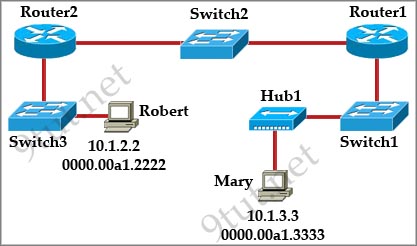
A. Hub1
B. Switch1
C. Router1
D. Switch2
E. Router2
F. Switch3
Answer: B D F[/am4show]
Explanation
Routers do not look to the destination MAC address to forward packet. It will find the next destination MAC address itself to replace the old destination MAC address of the received packet.
Hubs do not care about MAC addresses, it just flood the frames out of all its port except the port that sent it.
Therefore only three switches in the exhibit above use destination MAC address to determine the next hops.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. HostX is transferring a file to the FTP server. Point A represents the frame as it goes toward the Toronto router. What will the Layer 2 destination address be at this point?
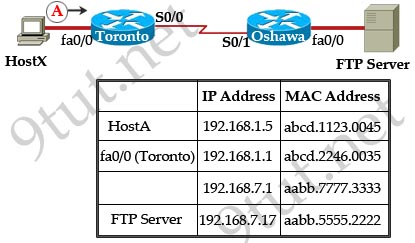
A. abcd. 1123.0045
B. 192.168.7.17
C. aabb.5555.2222
D. 192.168.1.1
E. abcd.2246.0035
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The destination MAC address at point A must be the MAC address of the interface fa0/0 of Toronto router -> E is correct.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]The command ip route 192.168.100.160 255.255.255.224 192.168.10.2 was issued on a router. No routing protocols or other static routes are configured on the router. Which statement is true about this command?
A. The interface with IP address 192.168.10.2 is on this router.
B. The command sets a gateway of last resort for the router.
C. Packets that are destined for host 192.168.100.160 will be sent to 192.168.10.2.
D. The command creates a static route for all IP traffic with the source address 192.168.100.160.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The simple syntax of static route:
ip route destination-network-address subnet-mask {next-hop-IP-address | exit-interface}
+ destination-network-address: destination network address of the remote network
+ subnet mask: subnet mask of the destination network
+ next-hop-IP-address: the IP address of the receiving interface on the next-hop router
+ exit-interface: the local interface of this router where the packets will go out
Therefore the purpose of this command is to send any packets with destination IP address in the range of 192.168.100.160/27 subnet to 192.168.10.2. In fact, answer C is a bit weird when saying “host 192.168.100.160” because 192.168.100.160 is the network address in this case and it cannot be assigned to a host. But answer C is the most suitable answer for this question.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]What does administrative distance refer to?
A. the cost of a link between two neighboring routers
B. the advertised cost to reach a network
C. the cost to reach a network that is administratively set
D. a measure of the trustworthiness of a routing information source
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the source physical address be in the frame when it reaches host B?
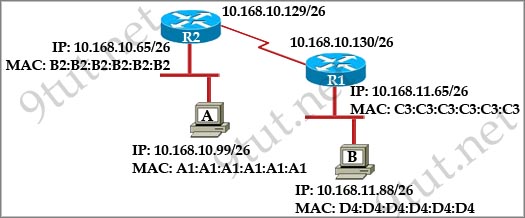
A. 10.168.10.99
B. 10.168.11.88
C. A1:A1:A1:A1:A1:A1
D. B2:B2:B2:B2:B2:B2
E. C3:C3:C3:C3:C3:C3
F. D4:D4:D4:D4:D4:D4
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
After receiving a packet, the router will keep the source and destination IP addresses while change the source MAC address (to the MAC address of its outgoing interface) and the destination MAC address (to the MAC address of the next-hop interface). Therefore when the packet reaches host B, the source MAC address must be the MAC address of the outgoing interface of R1.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Host A is sending a packet to Host B for the first time. What destination MAC address will Host A use in the ARP request?
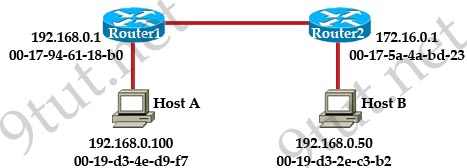
A. 192.168.0.1
B. 172.16.0.50
C. 00-17-94-61-18-b0
D. 00-19-d3-2d-c3-b2
E. ff-ff-ff-ff-ff-ff
F. 255.255.255.255
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
Host A knows the IP address of Host B but it does not know the MAC address of host B, so it have to create an ARP Request (which is a broadcast frame) to ask for the MAC address of host B. When Router1 receives this ARP Request, it answers with its own MAC address.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Host A can communicate with Host B but not with Host C or D. How can the network administrator solve this problem?
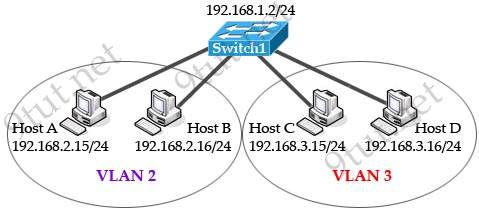
A. Configure Hosts C and D with IP addresses in the 192.168.2.0 network.
B. Install a router and configure a route to route between VLANs 2 and 3.
C. Install a second switch and put Hosts C and D on that switch while Hosts A and B remain on the original switch.
D. Enable the VLAN trunking protocol on the switch.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The host in Kiev sends a request for an HTML document to the server in Minsk. What will be the source IP address of the packet as it leaves the Kiev router?
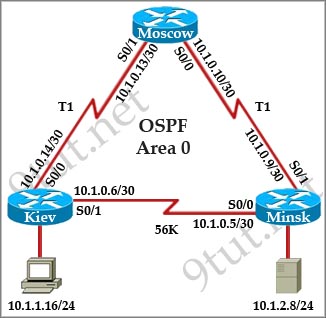
A. 10.1.0.1
B. 10.1.0.5
C. 10.1.0.6
D. 10.1.0.14
E. 10.1.1.16
F. 10.1.2.8
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
Along the routing path, the source and destination IP address will not change so the source IP will always be 10.1.1.16.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: The ICND1 exam requires candidates to understand basic knowledge of dynamic routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP, OSPF).
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Mary is sending an instant message to Robert. The message will be broken into a series of packets that will traverse all network devices. What addresses will populate these packets as they are forwarded from Router1 to Router2?
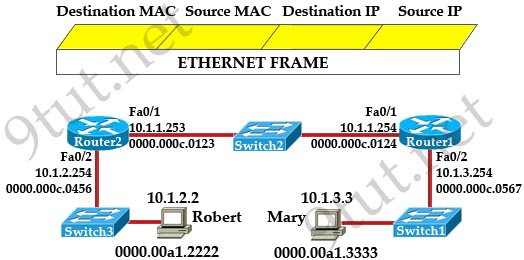
A. 
B.
C.
D.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
After receiving a packet, the router will keep the source and destination IP addresses (10.1.3.3 and 10.1.2.2, respectively) while change the source MAC address (to the MAC address of its outgoing interface) and the destination MAC address (to the MAC address of the next-hop interface). Therefore when the packet leaves Router1, the source MAC address must be the MAC address of the outgoing interface of Router1 (0000.000c.0124) and the destination MAC address must be the MAC of fa0/1 of R2 (0000.000c.0123).
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct? (Choose two)
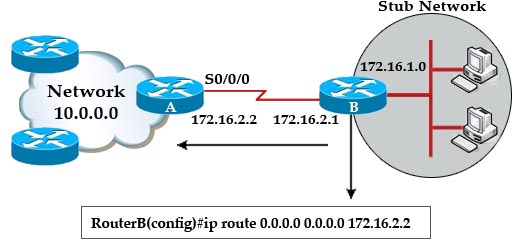
A. This is a default route.
B. Adding the subnet mask is optional for the ip route command.
C. This will allow any host on the 172.16.1.0 network to reach all known destinations beyond RouterA.
D. This command is incorrect, it needs to specify the interface, such as s0/0/0 rather than an IP address.
E. The same command needs to be entered on RouterA so that hosts on the 172.16.1.0 network can reach network 10.0.0.0.
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
A static route with 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 will become a default route. The default route means: “send all traffic to this IP address”. So the default route “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.2.2” will send all traffic to 172.16.2.2.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which command would you use to configure a static route on Router1 to network 192.168.202.0/24 with a nondefault administrative distance?
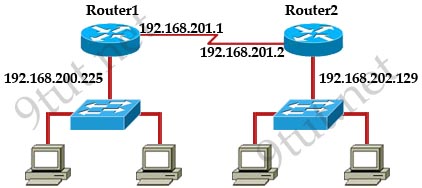
A. router1(config)#ip route 1 192.168.201.1 255.255.255.0 192.168.201.2
B. router1(config)#ip route 192.168.202.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.201.2 1
C. router1(config)#ip route 5 192.168.202.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.201.2
D. router1(config)#ip route 192.168.202.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.201.2 5
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The Administrative Distance (AD) parameter must be put at the end of the “ip route” command. The default AD is 1.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The output is from a router in a large enterprise. From the output, determine the role of the router.
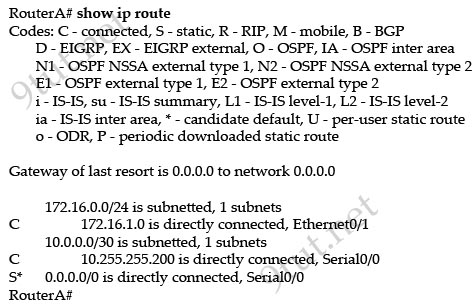
A. A Core router.
B. The HQ Internet gateway router.
C. The WAN router at the central site.
D. Remote stub router at a remote site.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
This router only have directly connected networks (symbolized by letter “C”) and one default route out of Serial0/0. Maybe this is a stub router with only one connection to the Headquarter or to the Internet.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What is the simplest way to configure routing between the regional office network 10.89.0.0/20 and the corporate network?
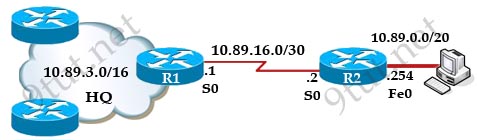
A. router1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.2
B. router2(config)#ip route 10.89.3.0 255.255.0.0 10.89.16.2
C. router1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.1
D. router2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.89.16.1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
In this topology, R2 is a stub router with only one connection to the HQ network so the best way to configure routing is to set a static route (default route) to R1.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What must be configured to establish a successful connection from Host A to switch SW-A through router RT-A?

A. VLAN 1 on RT-A
B. IP routing on SW-A
C. default gateway on SW-A
D. crossover cable connecting SW-A and RT-A
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Host A is in a different subnet of SW-A so SW-A does not know how to send data to host A so it needs to be assigned with a default gateway. The command to assign a default gateway to a switch is “ip default-gateway “. Please notice this command only has effect when “ip routing” is disabled on SW-A.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which default gateway address should be assigned to HostA?
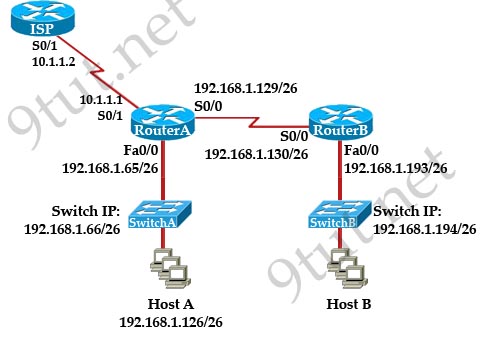
A. 192.168.1.1
B. 192.168.1.65
C. 192.168.1.66
D. 192.168.1.129
E. 10.1.1.1
F. 10.1.1.2
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The default gateway of Host A should be the connected interface of the router, except host A is connected with a Layer 3 switch. In this case, Switch A is a pure Layer 2 switch and Switch A IP address is just for management purpose.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which value is indicated by the next hop in a routing table?
A. preference of the route source
B. IP address of the remote router for forwarding the packets
C. how the route was learned
D. exit interface IP address for forwarding the packets
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which component of a routing table entry represents the subnet mask?
A. routing protocol code
B. prefix
C. metric
D. network mask
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which component of the routing table ranks routing protocols according to their preferences?
A. administrative distance
B. next hop
C. metric
D. routing protocol code
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The administrative distance of each protocol is compared to see if that route is better or not.
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which route source code represents the routing protocol with a default administrative distance of 90 in the routing table?
A. S
B. E
C. D
D. R
E. O
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Letter “D” is used to symbolize for EIGRP (with a default AD of 90). Letter “E” is not used for EIGRP because it has been used for Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) which is a obsolete routing protocol now.
Note: The ICND1 exam requires candidates to understand basic knowledge of dynamic routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP, OSPF).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]When enabled, which feature prevents routing protocols from sending hello messages on an interface?
A. virtual links
B. passive-interface
C. directed neighbors
D. OSPF areas
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which routing protocol has the smallest default administrative distance?
A. IBGP
B. OSPF
C. IS-IS
D. EIGRP
E. RIP
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The Administrative Distance (AD) of popular routing protocols is shown below. You should learn them by heart:
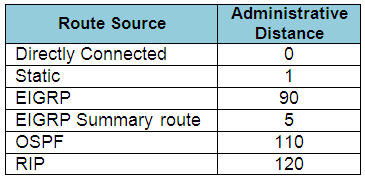
Note: The AD of iBGP is 200
The smaller the AD is, the better it is. The router will choose the routing protocol with smallest AD.
In this case EIGRP with AD of 90 is the smallest one.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about static routes is true?
A. The source interface can be configured to make routing decisions.
B. A subnet mask is entered for the next-hop address.
C. The subnet mask is 255.255 255.0 by default
D. The exit interface can be specified to indicate where the packets will be routed.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about routing protocols is true?
A. Link-state routing protocols choose a path by the number of hops to the destination.
B. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol.
C. Distance-vector routing protocols use the Shortest Path First algorithm.
D. IS-IS is a distance-vector routing protocol.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which dynamic routing protocol uses only the hop count to determine the best path to a destination?
A. IGRP
B. RIP
C. EIGRP
D. OSPF
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]A workstation has just resolved a browser URL to the IP address of a server. What protocol will the workstation now use to determine the destination MAC address to be placed into frames directed toward the server?
A. HTTP
B. DNS
C. DHCP
D. RARP
E. ARP
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
After resolving a browser URL to an IP address (via DNS server), the workstation must learn the MAC address of the server so that it can create a complete packet (a complete packet requires destination MAC and IP address, source MAC and IP address). Therefore the workstation must use ARP to find out the MAC address from the IP address.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What is the simplest way to configure routing between the regional office network 10.89.0.0/20 and the corporate network?

A. router1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.2
B. router2(config)#ip route 10.89.3.0 255.255.0.0 10.89.16.2
C. router1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.1
D. router2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.89.16.1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
In this topology, R2 is a stub router with only one connection to the HQ network so the best way to configure routing is to set a static route (default route) to R1.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the output of the corporate router routing table shown in the graphic. The corporate router receives an IP packet with a source IP address of 192.168.214.20 and a destination address of 192.168.22.3. What will the router do with this packet?
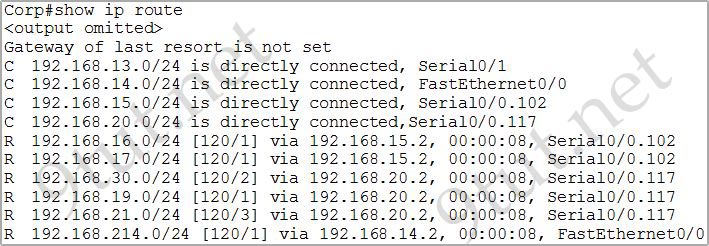
A. It will encapsulate the packet as Frame Relay and forward it out interface Serial 0/0.117.
B. It will discard the packet and send an ICMP Destination Unreachable message out interface FastEthernet 0/0.
C. It will forward the packet out interface Serial 0/1 and send an ICMP Echo Reply message out interface serial 0/0.102.
D. It will change the IP packet to an ARP frame and forward it out FastEthernet 0/0.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]The network administrator has found the following problem. The remote networks 172.16.10.0, 172.16.20.0, and 172.16.30.0 are accessed through the Central router’s serial 0/0 interface. No users are able to access 172.16.20.0. After reviewing the command output shown in the graphic, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
A. no gateway of last resort on Central
B. Central router’s not receiving 172.16.20.0 update
C. incorrect static route for 172.16.20.0
D. 172.16.20.0 not located in Central’s routing table
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
Link-state protocol uses hello packets to discover neighbors and establish adjacencies. After that, the routers begin sending out LSAs to every neighbor (each received LSA is copied and forwarded to every neighbor except the one that sent the LSA)
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]A router has learned three possible routes that could be used to reach a destination network. One route is from EIGRP and has a composite metric of 20514560. Another route is from OSPF with a metric of 782. The last is from RIPv2 and has a metric of 4. Which route or routes will the router install in the routing table?
A. the OSPF route
B. the EIGRP route
C. the RIPv2 route
D. all three routes
E. the OSPF and RIPv2 routes
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
When one route is advertised by more than one routing protocol, the router will choose to use the routing protocol which has lowest Administrative Distance. The Administrative Distances of popular routing protocols are listed below:
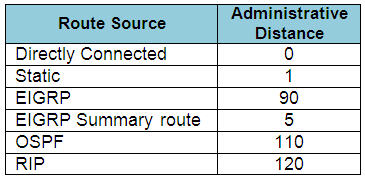
Note: The ICND1 exam requires candidates to understand basic knowledge of dynamic routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP, OSPF).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Some routers have been configured with default routes. What are some of the advantages of using default routes? (Choose two)
A. They establish routes that will never go down.
B. They keep routing tables small.
C. They require a great deal of CPU power.
D. They allow connectivity to remote networks that are not in the routing table
E. They direct traffic from the internet into corporate networks.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit, PC1 pings PC2. What three things will CORE router do with the data that is received from PC1? (Choose three)
A. The data frames will be forwarded out interface FastEthernet0/1 of CORE router.
B. The data frames will be forwarded out interface FastEthernet1/0 of CORE router.
C. CORE router will replace the destination IP address of the packets with the IP address of PC2.
D. CORE router will place the MAC address of PC2 in the destination MAC address of the frames.
E. CORE router will put the IP address of the forwarding FastEthernet interface in the place of the source IP address in the packets.
F. CORE router will put the MAC address of the forwarding FastEthernet interface in the place of the source MAC address.
Answer: B D F[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements are correct about RIP version 2? (Choose three)
A. It has the same maximum hop count as version 1.
B. It uses broadcasts for its routing updates.
C. It is a classless routing protocol.
D. It has a lower default administrative distance than RIP version 1.
E. It supports authentication.
F. It does not send the subnet mask in updates.
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Explanation
A and E are correct according to the theory of RIP.
RIP version 1 updates are broadcasts, and RIP version 2 updates are multicast to 224.0.0.9 -> B is not correct.
RIP v1 is a classful routing protocol but RIP v2 is a classless routing protocol -> C is correct.
RIPv1 and RIPv2 have the same default administrative distance of 120 -> D is not correct.
RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol so it does send the subnet mask in updates -> F is not correct.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]A technician pastes the configurations in the exhibit into the two new routers shown. Otherwise, the routers are configured with their default configurations. A ping from Host1 to Host2 fails, but the technician is able to ping the S0/0 interface of R2 from Host1. The configurations of the hosts have been verified as correct. What is the cause of the problem?
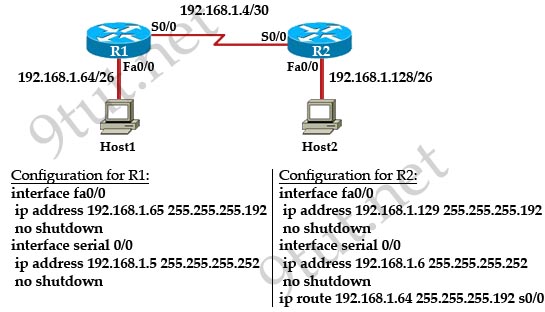
A. The serial cable on R1 needs to be replaced.
B. The interfaces on R2 are not configured properly.
C. R1 has no route to the 192.168.1.128 network.
D. The IP addressing scheme has overlapping subnetworks.
E. The ip subnet-zero command must be configured on both routers.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Host1 can ping the Serial interface of R2 because R1 has the network of 192.168.1.4/30 as directly connected route. But R1 does not know how to route to the network of Host2 (192.168.1.128/26) so R1 will drop that ping without trying to send it out S0/0 interface. To make the ping work, we have to configure a route pointing to that network (for example: ip route 192.168.1.128 255.255.255.192 s0/0 on R1).
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]After the show ip route command has been entered, the following routes are displayed. Which route will not be entered into the routing table of a neighboring router?
A. R 192.168.8.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
B. R 192.168.11.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:03, Serial1
C. C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D. R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The route 192.168.5.0/24 currently has the metric of 15 so this router will add 1 hop count before sending out to its neighboring router. With RIP, a metric of 16 means that network is down -> it will not be installed in the routing table of the neighboring router.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What value should be displayed in Box 1 of the ipconfig output of host A?
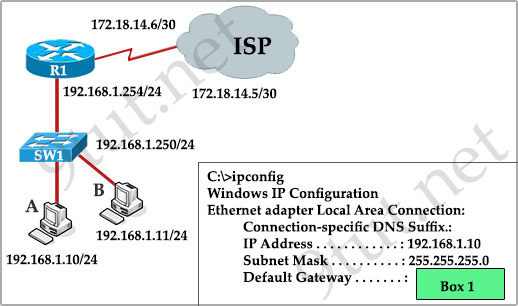
A. 172.18.14.5
B. 172.18.14.6
C. 192.168.1.10
D. 192.168.1.11
E. 192.168.1.250
F. 192.168.1.254
Answer: F[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]After you configure a default route to the Internet on a router, the route is missing from the routing table. Which option describes a possible reason for the problem?
A. The next-hop address is unreachable.
B. The default route was configured on a passive interface.
C. Dynamic routing is disabled.
D. Cisco Discovery Protocol is disabled on the interface used to reach the next hop.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The passive interface only prevents routing updates from being sent and received on that interface. It does not affect the default route. But if we configure a default route like this:
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2
Then if the next-hop address is down (unreachable) then this default route would be removed from the routing table.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which information is used to install the best route to a destination in IP routing table?
A. the tunnel ID
B. the interface number
C. the prefix length
D. the autonoums system
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the administrative distance of connected routes?
A.1
B. 0
C. 10
D. 90
Answer: B[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: Although OSPF topic is under ICND2 but some very basic OSPF questions are asked in the ICND1 so you should take some time to know about it. If you are not sure about OSPF, please read my OSPF tutorial first.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
A. It is locally significant.
B. It is globally significant.
C. It is needed to identify a unique instance of an OSPF database.
D It is an optional parameter required only if multiple OSPF processes are running on the router.
E. All routers in the same OSPF area must have the same process ID if they are to exchange routing information.
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol developed for Internet Protocol (IP) networks by the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). What is the default administrative distance of the OSPF routing protocol?
A. 90
B. 100
C. 110
D. 20
E. 130
F. 170
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statements describe the routing protocol OSPF? (Choose three)
A. It supports VLSM.
B. It is used to route between autonomous systems.
C. It confines network instability to one area of the network.
D. It increases routing overhead on the network.
E. It allows extensive control of routing updates.
F. It is simpler to configure than RIPv2.
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Explanation
Answer A and C are obviously correct. For answer E, it allows extensive control of routing updates via Link-State Advertisement (LSA). Administrators can filter these LSAs to meet their requirements easily.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]R1 is unable to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with R3. What are possible reasons for this problem? (Choose two)
A. All of the routers need to be configured for backbone Area 1.
B. R1 and R2 are the DR and BDR, so OSPF will not establish neighbor adjacency with R3.
C. A static route has been configured from R1 to R3 and prevents the neighbor adjacency from being established.
D. The hello and dead interval timers are not set to the same values on R1 and R3.
E. EIGRP is also configured on these routers with a lower administrative distance.
F. R1 and R3 are configured in different areas.
Answer: D F[/am4show]
Explanation
A is not correct because the backbone area of OSPF is always Area 0.
B is not correct because R1 or R3 must be the DR or BDR -> it has to establish neighbor adjacency with the other.
C is not correct because OSPF neighbor relationship is not established based on static routing. It uses multicast address 224.0.0.5 to establish OSPF neighbor relationship.
E is not correct because configure EIGRP on these routers (with a lower administrative distance) will force these routers to run EIGRP, not OSPF.
D and F are correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:
– Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flag
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which address are OSPF hello packets addressed to on point-to-point networks?
A. 224.0.0.5
B. 172.16.0.1
C. 192.168.0.5
D. 223.0.0.1
E. 254.255.255.255
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]RouterD# show ip interface brief

Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this router?
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.3
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]ROUTER# show ip route
| 192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 9 subnets, 3 masks C 192.168.12.64 /28 is directly connected, Loopback1 C 192.168.12.32 /28 is directly connected, Ethernet0 C 192.168.12.48 /28 is directly connected, Loopback0 O 192.168.12.236 /30 [110/128] via 192.168.12.233, 00:35:36, Serial0 C 192.168.12.232 /30 is directly connected, Serial0 O 192.168.12.245 /30 [110/782] via 192.168.12.233, 00:35:36, Serial0 O 192.168.12.240 /30 [110/128] via 192.168.12.233, 00:35:36, Serial0 O 192.168.12.253 /30 [110/782] via 192.168.12.233, 00:35:37, Serial0 O 192.168.12.249/30 [110/782] via 192.168.12.233, 00:35:37, Serial0 O 192.168.12.240/30 [110/128] via 192.168.12.233, 00:35:36, Serial0 |
To what does the 128 refer to in the router output above?
A. OSPF cost
B. OSPF priority
C. OSPF hop count 5
D. OSPF ID number
E. OSPF administrative distance
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
OSPF uses a metric referred to as cost. The cost of the entire path is the sum of the costs of the outgoing interfaces along the path. Cisco uses a simple formula to calculate OSPF cost:
OSPF cost = 108 / Bandwidth (bit)
Therefore, a 100 Mbps FastEthernet interface will have the cost of 108 / 100,000,000 (bps) = 1
Note: Cost for interfaces with bandwidth equal or larger than 10^8 bps is normalized to 1 so a 1Gbps interface will also have OSPF cost of 1.
For “O 192.168.12.240 /30 [110/128] via 192.168.12.233, 00:35:36, Serial0″ line, the first number in the brackets is the administrative distance of the information source; the second number is the metric for the route -> In this case the second number is the OSPF cost.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic. There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance.
As part of examining the router resources the OSPF DRs need to be known.
All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router.
Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two)
A. Corp-1
B. Corp-2
C. Corp-3
D. Corp4
E. Branch-1
F. Branch-2
Answer: D F[/am4show]
Explanation
There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40) & Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 90
B. 100
C. 110
D. 120
Answer: C
Explanation
The Administrative Distances (AD) of popular routing protocols are listed below:
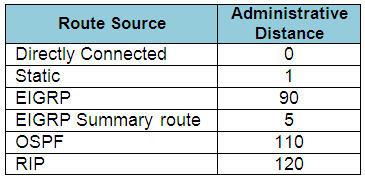
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. provides common view of entire topology
B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
C. calculates shortest path
D. utilizes event-triggered updates
E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A C D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default lease time for a DHCP binding?
A. 24 hours
B. 12 hours
C. 48 hours
D. 36 hours
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
We can use the “lease” command to specify the duration of the lease: lease {days [hours][minutes] | infinite}
The default is a one-day lease.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The DHCP settings have recently been changed on the DHCP server and the client is no longer able to reach network resources. What should be done to correct this situation?
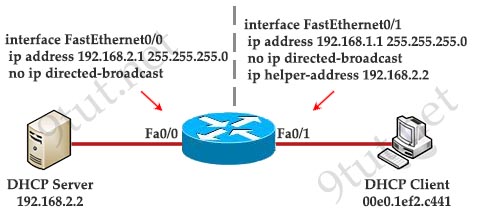
A. Verify that the DNS server address is correct in the DHCP pool.
B. Ping the default gateway to populate the ARP cache.
C. Use the tracert command on the DHCP client to first determine where the problem is located.
D. Clear all DHCP leases on the router to prevent address conflicts.
E. Issue the ipconfig command with the /release and /renew options in a command window.
Answer: E[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]You have configured the host computers on a campus LAN to receive their DHCP addresses from the local router to be able to browse their corporate site. Which statement about the network environment is true?
A. It supports a DNS server for use by DHCP clients.
B. Two host computers may be assigned the same IP address.
C. The DNS server must be configured manually on each host.
D. The domain name must be configured locally on each host computer.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The local router in this case is called a DHCP server. The main purpose of a DHCP server is to assign IP addresses to the clients. Besides that, a DHCP server can also specify the IP address of the DNS server and specify the domain name for the clients.
For more information about configuring a DHCP server, please read: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipaddr_dhcp/configuration/12-4t/dhcp-12-4t-book/config-dhcp-server.html
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about NAT/PAT, please read my Network Address Translation NAT Tutorial.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]What happens when computers on a private network attempt to connect to the Internet through a Cisco router running PAT?
A. The router uses the same IP address but a different TCP source port number for each connection.
B. An IP address is assigned based on the priority of the computer requesting the connection.
C. The router selects an address from a pool of one-to-one address mappings held in the lookup table.
D. The router assigns a unique IP address from a pool of legally registered addresses for the duration of the connection.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Port Address Translation (PAT) can support thousands of users connect to the Internet using only one real global IP address. With PAT, each computer will be assigned a separate port number so that the router can identify which computer should receive the return traffic.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]In the configuration of NAT, what does the keyword overload signify?
A. When bandwidth is insufficient, some hosts will not be allowed to access network translation.
B. The pool of IP addresses has been exhausted.
C. Multiple internal hosts will use one IP address to access external network resources.
D. If the number of available IP addresses is exceeded, excess traffic will use the specified address pool.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The keyword “overload” specifies we are using NAT Overload (PAT) in which multiple internal hosts will use only one IP address to access external network resources.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]When configuring NAT, the Internet interface is considered to be what?
A. local
B. inside
C. global
D. outside
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
On the interface connecting to the Internet of the router we have to use the command “ip nat outside” for NAT to work. It identifies that interface as the outside interface.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NAT type is used to translate a single inside address to a single outside address?
A. dynamic NAT
B. NAT overload
C. PAT
D. static NAT
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
There are two types of NAT translation: dynamic and static.
Static NAT: Designed to allow one-to-one mapping between local and global addresses. This flavor requires you to have one real Internet IP address for every host on your network
Dynamic NAT: Designed to map an unregistered IP address to a registered IP address from a pool of registered IP addresses. You don’t have to statically configure your router to map an inside to an outside address as in static NAT, but you do have to have enough real IP addresses for everyone who wants to send packets through the Internet. With dynamic NAT, you can configure the NAT router with more IP addresses in the inside local address list than in the inside global address pool. When being defined in the inside global address pool, the router allocates registered public IP addresses from the pool until all are allocated. If all the public IP addresses are already allocated, the router discards the packet that requires a public IP address.
In this question we only want to translate a single inside address to a single outside address so static NAT should be used.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about the inside interface configuration in a NAT deployment is true?
A. It is defined globally
B. It identifies the location of source addresses for outgoing packets to be translated using access or route maps.
C. It must be configured if static NAT is used
D. It identifies the public IP address that traffic will use to reach the internet.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
When we specify a NAT “inside” interface (via the “ip nat inside” command under interface mode), we are specifying the source IP addresses. Later in the “ip nat” command under global configuration mode, we will specify the access or route map for these source addresses.
For example the command:
Router(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool PoolforNAT
after the keyword “source” we need to specify one of the three keywords:
+ list: specify access list describing local addresses (but this command does not require an “inside” interface to be configured)
+ route-map: specify route-map
+ static: specify static local -> global mapping
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Under which circumstance should a network administrator implement one-way NAT?
A. when the network must route UDP traffic
B. when traffic that originates outside the network must be routed to internal hosts
C. when traffic that originates inside the network must be routed to internal hosts
D. when the network has few public IP addresses and many private IP addresses require outside access
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]How many addresses will be available for dynamic NAT translation when a router is configured with the following commands?
Router(config)#ip nat pool TAME 209.165.201.23 209.165.201.30 netmask 255.255.255.224
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 9 pool TAME
A. 7
B. 8
C. 9
D. 10
E. 24
F. 32
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]What does the “Inside Global” address represent in the configuration of NAT?
A. the summarized address for all of the internal subnetted addresses
B. the MAC address of the router used by inside hosts to connect to the Internet
C. a globally unique, private IP address assigned to a host on the inside network
D. a registered address that represents an inside host to an outside network
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the graphic:
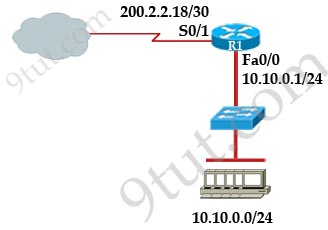
A company wants to use NAT in the network shown. Which commands will apply the NAT configuration to the proper interfaces? (Choose two)
A.
R1 (config)# interface serial0/1
R1 (config-if)# ip nat inside
B.
R1 (config)# interface serial0/1
R1 (config-if)# ip nat outside
C.
R1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R1 (config-if)# ip nat inside
D.
R1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R1 (config-if)# ip nat outside
E.
R1(config)# interface serial0/1
R1 (config-if)# ip nat outside source pool 200.2.2.18 255.255.255.252
F.
R1 (config)# interface FastEthernet0/0
R1 (config-if)# ip nat inside source 10.10.0.0 255.255.255.0
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
After configuring all the requirements for NAT, we need to apply them to “source interface” and “outgoing” interface by going to the appropriate interfaces and type the “ip nat inside” and “ip nat outside” commands.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which form of NAT maps multiple private IP addresses to a single registered IP address by using different ports?
A. static NAT
B. dynamic NAT
C. overloading
D. overlapping
E. port loading
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement describes the effect of the overload keyword in the ip nat inside source list 90 interface ethernet 0/0 overload command?
A. Addresses that match address list inside are translated to the IP address of the Ethernet 0/0 interface.
B. Hosts that match access inside are translated to an address in the Ethernet 0/0 network.
C. Hosts on the Ethernet 0/0 LAN are translated to the address pool in access list 90.
D. Addresses that match access list 90 are translated through PAT to the IP address of the Ethernet 0/0 interface
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The command ip nat inside source list 90 interface ethernet 0/0 overload means:
+ “ip nat inside”: “I want to NAT from inside to outside”
+ “list 90” means “the source IP addresses to NAT are included in Access-list 90”
+ “interface ethernet 0/0” means “NAT out of this interface”
+ “overload” means “use PAT for the IP translation”
Question 12
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NAT command can be applied to an interface?
A. ip nat inside
B. ip nat inside test access-list-number pool pool-name
C. ip nat inside source static 10.10.10.0 10.10.10.50
D. ip nat pool test 10.10.10.0 10.10.10.50 255.255.255.0
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The “ip nat inside” command can be applied to an interface to indicate this interface is the source NAT.
Question 13
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command displays the number of times that an individual router translated an inside address to an outside address?
A. show ip protocol 0
B. show ip nat translation
C. show counters
D. show ip route
E. show ip nat statistics
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The outputs of the two commands “show ip nat statistics” and “show ip nat translation” are shown below:
Router#show ip nat statistics Total active translations: 2 (0 static, 2 dynamic; 2 extended) Peak translations: 3, occurred 5d04h ago Outside interfaces: Serial1/0 Inside interfaces: Ethernet0/1 Hits: 34531 Misses: 0 CEF Translated packets: 34526, CEF Punted packets: 0 Expired translations: 11 Dynamic mappings: -- Inside Source [Id: 1] access-list nat_traffic interface Serial1/0 refcount 2 Total doors: 0 Appl doors: 0 Normal doors: 0 Queued Packets: 0
Router#show ip nat translation Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp 201.15.3.5:628 10.1.1.7:628 201.15.3.17:628 201.15.3.17:628 icmp 201.15.3.5:629 10.1.1.7:629 201.15.3.6:629 201.15.3.6:629 icmp 201.15.3.5:610 10.1.1.8:610 201.15.3.17:610 201.15.3.17:610 icmp 201.15.3.5:611 10.1.1.8:611 201.15.3.6:611 201.15.3.6:611 icmp 201.15.3.5:727 10.1.1.17:727 201.15.3.17:727 201.15.3.17:727 icmp 201.15.3.5:728 10.1.1.17:728 201.15.3.6:728 201.15.3.6:728 icmp 201.15.3.5:633 10.1.1.21:633 201.15.3.17:633 201.15.3.17:633 icmp 201.15.3.5:634 10.1.1.21:634 201.15.3.6:634 201.15.3.6:634 icmp 201.15.3.5:480 10.2.2.1:480 201.15.3.17:480 201.15.3.17:480 icmp 201.15.3.5:481 10.2.2.1:481 201.15.3.6:481 201.15.3.6:481 icmp 201.15.3.5:840 10.10.123.2:840 201.15.3.17:840 201.15.3.17:840 icmp 201.15.3.5:841 10.10.123.2:841 201.15.3.6:841 201.15.3.6:841 icmp 201.15.3.5:578 10.10.123.3:578 201.15.3.17:578 201.15.3.17:578 icmp 201.15.3.5:579 10.10.123.3:579 201.15.3.6:579 201.15.3.6:579 icmp 201.15.3.5:595 192.168.1.1:595 201.15.3.17:595 201.15.3.17:595 icmp 201.15.3.5:596 192.168.1.1:596 201.15.3.6:596 201.15.3.6:596
From that we can see the correct answer should be “show ip nat statistics”.
Question 14
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NAT term is defined as a group of addresses available for NAT use?
A. one-way nat
B. static nat
C. dynamic nat
D. nat pool
Answer: D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A TFTP server has recently been installed in the Atlanta office. The network administrator is located in the NY office and has made a console connection to the NY router. After establishing the connection they are unable to backup the configuration file and IOS of the NY router to the TFTP server. What is the cause of this problem?

A. The NY router has an incorrect subnet mask.
B. The TFTP server has an incorrect IP address.
C. The TFTP server has an incorrect subnet mask.
D. The network administrator computer has an incorrect IP address.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured a Catalyst 2950 switch for remote management by pasting into the console the configuration commands that are shown in the exhibit. However, a Telnet session cannot be successfully established from a remote host. What should be done to fix this problem?
| interface vlan 1 ip address 192.168.17.253 255.255.255.240 no shutdown exit ip default-gateway 192.168.17.1 line vty 0 15 password cisco login exit |
A. Change the first line to interface fastethernet 0/1.
B. Change the first line to interface vlan 0/1.
C. Change the fifth line to ip default-gateway 192.168.17.241.
D. Change the fifth line to ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.17.1.
E. Change the sixth line to line con 0.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The two connected ports on the switch are not turning orange or green. What would be the most effective steps to troubleshoot this physical layer problem? (Choose three)
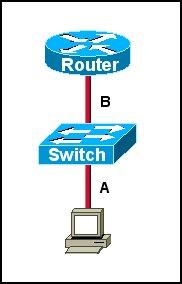
A. Ensure that the Ethernet encapsulations match on the interconnected router and switch ports.
B. Ensure that cables A and B are straight-through cables.
C. Ensure cable A is plugged into a trunk port.
D. Ensure the switch has power.
E. Reboot all of the devices.
F. Reseat all cables.
Answer: B D F[/am4show]
Explanation
The ports on the switch are not up indicating it is a layer 1 (physical) problem so we should check cable type, power and how they are plugged in.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A person is trying to send a file from a host on Network A of the JAX Company to a server on Network Z of the XYZ Company. The file transfer fails. The host on Network A can communicate with other hosts on Network A. Which command, issued from router RTA, would be the most useful for troubleshooting this problem?
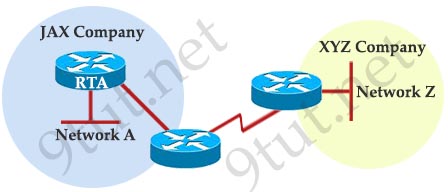
A. show flash:
B. show history
C. show version
D. show interfaces
E. show controllers serial
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A user cannot reach any web sites on the Internet, but others in the department are not having a problem. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
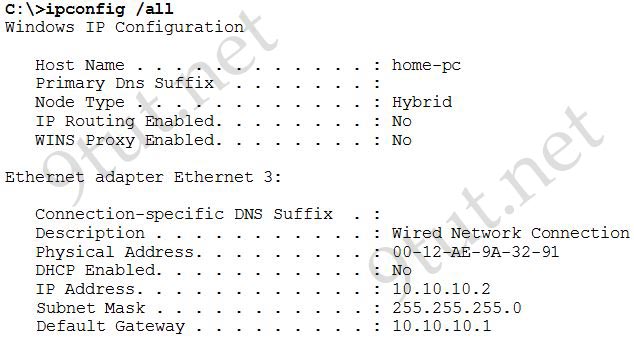
A. IP routing is not enabled.
B. The default gateway is not in the same subnet.
C. A DNS server address is not reachable by the PC.
D. A DHCP server address is not reachable by the PC.
E. NAT has not been configured on the router that connects to the Internet.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a connectivity problem on the serial interfaces. The output from the show interfaces command on both routers shows that the serial interface is up, line protocol is down. Given the partial output for the show running-config in the exhibit, what is the most likely cause of this problem?

A. The serial cable is bad.
B. The MTU is incorrectly configured.
C. The Layer 2 framing is misconfigured.
D. The IP addresses are not in the same subnet.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]While troubleshooting a connectivity issue from a PC you obtain the following information:
Local PC IP address: 10.0.0.35/24
Default Gateway: 10.0.0.1
Remote Sever: 10.5.75.250/24
You then conduct the following tests from the local PC:
Ping 127.0.0.1 – Successful
Ping 10.0.0.35 – Successful
Ping 10.0.0.1 – Unsuccessful
Ping 10.5.75.250 – Unsuccessful
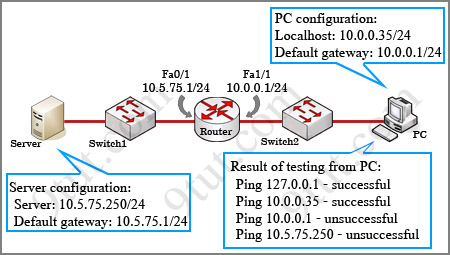
What is the underlying cause of this problem?
A. A remote physical layer problem exists.
B. The host NIC is not functioning.
C. TCP/IP has not been correctly installed on the host.
D. A local physical layer problem exists.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A host is connected to switch port fa0/3. The host and switch have been fully configured for IP connectivity as shown. However, the indicator LED on switch port fa0/3 is not on, and the host cannot communicate with any other hosts including those connected to VLAN 2 on the same switch. Based on the given information, what is the problem?
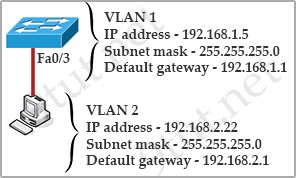
A. switch port fa0/3 is not configured as a trunk port
B. there is a bad cable
C. the switch has been assigned an incorrect subnet mask
D. switch port fa0/3 has been blocked by STP
E. the switch and the host must be in the same subnet
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:

Serial0/0 does not respond to a ping request from a host on the FastEthernet0/0 LAN. How can this problem be corrected?
A. Enable the Serial 0/0 interface.
B. Correct the IP address for Serial 0/0.
C. Correct the IP address for FastEthernet 0/0.
D. Change the encapsulation type on Serial 0/0.
E. Enable autoconfiguration on the Serial 0/0 interface.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Serial0/0 is “administratively down”, that means this interface is shutting down.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received?
| Router#telnet 10.3.1.2 Trying 10.3.1.2 … Open Password required, but none set |
A. No VTY password has been set.
B. No enable password has been set.
C. No console password has been set.
D. No enable secret password has been set.
E. The login command has not been set on CON 0
F. The login command has not been set on the VTY ports.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which two of the output fields could help you determine if a broadcast storm has occurred? (Choose two.)
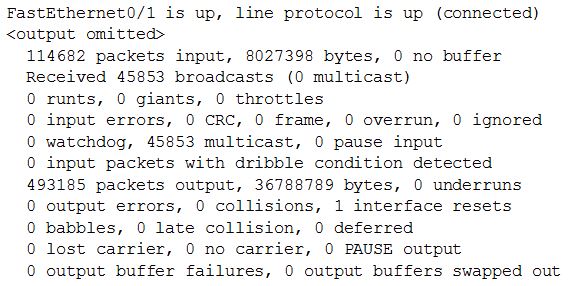
A. giants
B. no buffer
C. collisions
D. ignored
E. dribble condition
Answer: B D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Two routers named Atlanta and Brevard are connected by their serial interfaces as shown in the exhibit, but there is no data connectivity between them. The Atlanta router is known to have a correct configuration. Given the partial configurations shown in the exhibit, what is the problem on the Brevard router that is causing the lack of connectivity?
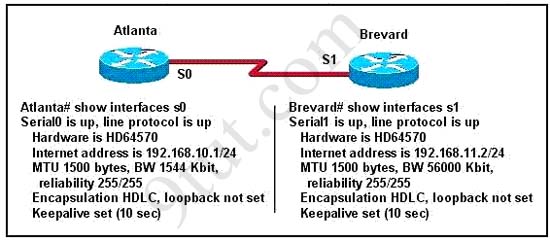
A. A loopback is not set
B. The IP address is incorrect.
C. The subnet mask is incorrect.
D. The serial line encapsulations are incompatible.
E. The maximum transmission unit (MTU) size is too large.
F. The bandwidth setting is incompatible with the connected interface.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is unable to ping from R1 to R2. Using the output of the show interfaces serial0/1 command, what should the administrator do to correct the problem?

A. Replace the serial cable between R1 and R2.
B. Reseat the serial connectors on the R1 and R2 routers.
C. Configure the serial0/1 interface on R2 with the no shutdown command.
D. Configure the serial0/1 interface on R1 with the clock rate 56000 command.
E. Configure the serial0/1 interface on R1 with the ip address 192.1.1.7 255.255.255.252 command.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Examine the network diagram and router output shown in the exhibit. Users on the BHM LAN are unable to access the server attached to the BHE router. What two things should be done to fix this problem? (Choose two)
A. Enter the configuration mode for interface fastethernet0/0.
B. Enter the configuration mode for interface serial0/0.
C. Enter the configuration mode for interface serial0/1.
D. Issue the run command.
E. Issue the enable command.
F. Issue the no shutdown command.
Answer: B F[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is unable to ping from R1 to R2. What will help correct the problem?

A. Ensure that the serial cable is correctly plugged in to the interfaces.
B. Apply the clock rate 56000 configuration command to the serial0/1 interface of R1.
C. Configure the serial0/1 interfaces on R1 and R2 with the no shutdown command.
D. Change the address of the serial0/1 interface of R1 to 192.1.1.4.
E. Change the subnet masks of both interfaces to 255.255.255.240.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What happens when the cable is too long?
A. Baby Giant
B. Late collision
C. Duplex mismatch
D. No connection
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
A late collision is defined as any collision that occurs after the first 512 bits of the frame have been transmitted. The usual possible causes are full-duplex/half-duplex mismatch, exceeded Ethernet cable length limits, or defective hardware such as incorrect cabling, non-compliant number of hubs in the network, or a bad NIC.
Late collisions should never occur in a properly designed Ethernet network. They usually occur when Ethernet cables are too long or when there are too many repeaters in the network.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1904.html
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which technology supports the stateless assignment of IPv6 addresses?
A. DNS
B. DHCPv6
C. DHCP
D. autoconfiguration
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
There are several ways to assign IPv6 to a device:
+ Static IPv6: The IPv6 address, subnet prefix length and default gateway are configured manually in the system configuration file.
+ Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6): this mode requires a DHCPv6 server in your LAN. This is the most used mode for IPv6 assignment. There are two methods of DHCPv6:
– stateless mode: Only extended information, such as primary and optional secondary DNS server, is obtained from a DHCPv6 server. IPv6 address is not assigned, so the IPv6 address from the Ethernet configuration is set for a Static address of Ethernet interface.
– stateful mode: DHCPv6 server maintains a database of leased IPv6 addresses, and assigns to the client an unused IPv6 address. The DHCPv6 server specifies also a primary and optional secondary DNS server. The DNS server is used to resolve the IP address for a known host name.
+ IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC): provides the ability to address a host based on a network prefix that is advertised from a local network router via Router Advertisements (RA). Notice that with this mode, the device which requires an IPV6 always receive a dynamic IPv6 address.
The question asks about “stateless assignment of IPv6 addresses” which means stateless mode of DHCPv6.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which entity assigns IPv6 addresses to end users?
A. ICANN
B. APNIC
C. RIR
D. ISPs
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
According to the official IANA website “Users are assigned IP addresses by Internet service providers (ISPs). ISPs obtain allocations of IP addresses from a local Internet registry (LIR) or National Internet Registry (NIR), or from their appropriate Regional Internet Registry (RIR): https://www.iana.org/numbers
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is one requirement for interfaces to run IPv6?
A. An IPv6 address must be configured on the interface.
B. An IPv4 address must be configured.
C. Stateless autoconfiguration must be enabled after enabling IPv6 on the interface.
D. IPv6 must be enabled with the ipv6 enable command in global configuration mode.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
To run IPv6 on an interface we have to configure an IPv6 on that interface somehow -> A is correct.
IPv6 must be enabled first but with the “ipv6 unicast-routing”, not “ipv6 enable” command -> D is not correct.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the requirement of configuring 6to4 tunnelling on two routers?
A. Both ipv6 and ipv4 must be configured
B. Only IPv6
C. Only IPv4
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command can you use to manually assign a static IPv6 address to a router interface?
A. ipv6 address PREFIX_1::1/64
B. ipv6 autoconfig 2001:db8:2222:7272::72/64
C. ipv6 autoconfig
D. ipv6 address 2001:db8:2222:7272::72/64
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two of these statements are true of IPv6 address representation? (Choose two)
A. The first 64 bits represent the dynamically created interface ID.
B. A single interface may be assigned multiple IPV6 addresses of any type.
C. Every IPV6 interface contains at least one loopback address.
D. Leading zeros in an IPV6 16 bit hexadecimal field are mandatory.
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
Leading zeros in IPv6 are optional do that 05C7 equals 5C7 and 0000 equals 0 -> D is not correct.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option is a valid IPv6 address?
A. 2001:0000:130F::099a::12a
B. 2002:7654:A1AD:61:81AF:CCC1
C. FEC0:ABCD:WXYZ:0067::2A4
D. 2004:1:25A4:886F::1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]How many bits are contained in each field of an IPv6 address?
A. 24
B. 4
C. 8
D. 16
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three approaches can be used while migrating from an IPv4 addressing scheme to an IPv6 scheme? (Choose three)
A. static mapping of IPv4 address to IPv6 addresses
B. configuring IPv4 tunnels between IPv6 islands
C. use DHCPv6 to map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses
D. use proxying and translation (NAT-PT) to translate IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets
E. configure IPv6 directly
F. enable dual-stack routing
Answer: B D F[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about IPv6 is true?
A. Addresses are not hierarchical and are assigned at random.
B. Broadcasts have been eliminated and replaced with multicasts.
C. There are 2.7 billion available addresses.
D. An interface can only be configured with one IPv6 address.
Answer: B[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Identify the four valid IPv6 addresses. (Choose four)
A. ::
B. ::192:168:0:1
C. 2000::
D. 2001:3452:4952:2837::
E. 2002:c0a8:101::42
F. 2003:dead:beef:4dad:23:46:bb:101
Answer: A B E F[/am4show]
Explanation
Answers B E F are correct because A and B are the short form of 0:0:0:0:192:168:0:1 and 2002:c0a8:0101:0:0:0:0:0042 while C are normal IPv6 address.
Answer A is correct because “::” is named the “unspecified” address and is typically used in the source field of a datagram that is sent by a device that seeks to have its IP address configured.
Answer C is not correct because a global-unicast IPv6 address is started with binary 001, denoted as 2000::/3 in IPv6 and it also known as an aggregatable global unicast address. The 2000:: (in particular, 2000::/3) is just a prefix and is not a valid IPv6 address.
In fact answer D is acceptable but it is considered the network portion of an IPv6 address so it is a worse choice than others.
The entire global-unicast IPv6 address range is from 2000::/128 to 3FFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF/128, resulting in a total usable space of over 42,535,295,865,117,307,932,921,825,928,971,000,000 addresses, which is only 1/8th of the entire IPv6 address space!
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements describe characteristics of IPv6 unicast addressing? (Choose two)
A. Global addresses start with 2000::/3
B. Link-local addresses start with FE00:/12
C. Link-local addresses start with FF00::/10
D. There is only one loopback address and it is ::1
E. If a global address is assigned to an interface, then that is the only allowable address for the interface.
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
Below is the list of common kinds of IPv6 addresses:
| Loopback address | ::1 |
| Link-local address | FE80::/10 |
| Site-local address | FEC0::/10 |
| Global address | 2000::/3 |
| Multicast address | FF00::/8 |
From the above table, we learn that A and D are correct while B and C are incorrect. Notice that the IPv6 unicast loopback address is equivalent to the IPv4 loopback address, 127.0.0.1. The IPv6 loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, or ::1.
E is not correct because of anycast addresses which are indistinguishable from normal unicast addresses. You can think of anycast addresses like this: “send it to nearest one which have this address”. An anycast address can be assigned to many interfaces and the first interface receives the packet destined for this anycast address will proceed the packet. A benefit of anycast addressing is the capability to share load to multiple hosts. An example of this benefit is if you are a Television provider with multiple servers and you want your users to use the nearest server to them then you can use anycast addressing for your servers. When the user initiates a connection to the anycast address, the packet will be routed to the nearest server (the user does not have to specify which server they want to use).
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement is true?
A. An IPv6 address is 64 bits long and is represented as hexadecimal characters.
B. An IPv6 address is 32 bits long and is represented as decimal digits.
C. An IPv6 address is 128 bits long and is represented as decimal digits.
D. An IPv6 address is 128 bits long and is represented as hexadecimal characters.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statements are TRUE regarding Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) addresses? (Choose three)
A. An IPv6 address is divided into eight 16-bit groups.
B. A double colon (::) can only be used once in a single IPv6 address.
C. IPv6 addresses are 196 bits in length.
D. Leading zeros cannot be omitted in an IPv6 address.
E. Groups with a value of 0 can be represented with a single 0 in IPv6 address.
Answer: A B E[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which technique can you use to route IPv6 traffic over an IPv4 infrastructure?
A. NAT
B. 6to4 tunneling
C. L2TPv3
D. dual-stack
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
“6to4 tunneling” is a technique which enables encapsulation of IPv6 packets into IPv4 for transport across an IPv4 network.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which header field is new in IPv6?
A. Version
B. Hop Limit
C. Flow Label
D. Traffic Class
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The IPv4 and IPv6 headers are shown below for your comparison. As we can see the Flow Label, Hop Limit, Traffic Class fields are all new but in fact Hop Limit in IPv6 is same as Time to live (TTL) in IPv4. Traffic Class is the equivalent of the DiffServ/DSCP portion of the IPv4 packet (in “Type of service” field) which carries the QoS markings of the packet. Just like in IPv4 the first 6 bits are designated for the DSCP value, and the next 2 bits are for ECN (Explicit Congestion Notifications) capable devices.
Flow-Label: This 20-bit field provides a special service for real-time applications. It can be used to inform routers and switches to maintain the same path for the packet flow so that packets are not reordered.
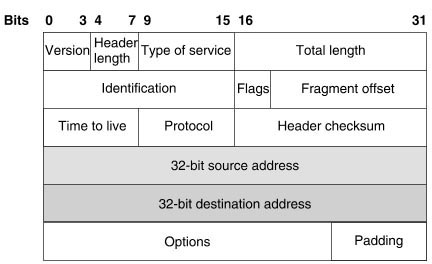 IPv4 Header fields
IPv4 Header fields
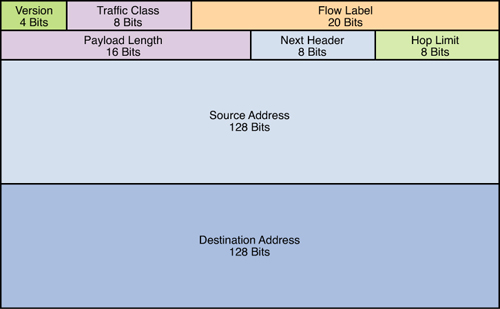 IPv6 Header fields
IPv6 Header fields
IPv6 eliminates the Header Checksum field, which handles error checking in IPv4.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which sequence begins a unique local IPv6 address in binary notation?
A. 1111000
B. 11111000
C. 11111100
D. 11100000
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
A IPv6 Unique Local Address is an IPv6 address in the block FC00::/7. It is the approximate IPv6 counterpart of the IPv4 private address. It is not routable on the global Internet. Therefore FC00::/7 is equivalent to 1111 1100 0000 0000::/7 in binary notation.
Note: In the past, Site-local addresses (FEC0::/10) are equivalent to private IP addresses in IPv4 but now they are deprecated.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NTP command configures the local device as an NTP reference clock source?
A. ntp peer
B. ntp broadcast
C. ntp master
D. ntp server
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
If you want your system to become an authoritative NTP server from which other internal routers or machines can synchronise, you can achieve this with the “ntp master” command.
Note: Use the “ntp server” to form an association with a NTP server.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which NTP concept indicates the distance between a device and the reliable time source?
A. clock offset
B. stratum
C. reference
D. dispersion
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
NTP uses a stratum to describe the distance between a network device and an authoritative time source:
+ A stratum 1 time server is directly attached to an authoritative time source (such as a radio or atomic clock or a GPS time source).
+ A stratum 2 NTP server receives its time through NTP from a stratum 1 time server.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about NTP is true?
A. each device is enabled as server by default
B. the default authentication key number is 1
C. the default stratum number is 5
D. the default source of a NTP message is the interface connected to the next-hop for server peer address
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
There is no document saying the default mode of NTP is server so we assume answer A is not correct.
There is no default authentication key number -> B is not correct.
If the network has “ntp master” configured and it cannot reach any clock with a lower stratum number, the system claims to be synchronized at the configured stratum number, and other systems synchronize to it via NTP. By default, the master clock function is disabled. When enabled, the default stratum is 8 -> Answer C is not correct.
NTP sets the source IP address for all NTP packets based on the address of the interface through which the NTP packet are sent. But there is no correct answer so maybe answer D is the best choice.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]An administrator has connected devices to a switch and, for security reasons, wants the dynamically learned MAC addresses from the address table added to the running configuration. What must be done to accomplish this?
A. Enable port security and use the keyword sticky.
B. Set the switchport mode to trunk and save the running configuration.
C. Use the switchport protected command to have the MAC addresses added to the configuration.
D. Use the no switchport port-security command to allow MAC addresses to be added to the configuration.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
This is the full command mentioned in answer A:
switchport port-security mac-address sticky [MAC]
If we don’t specify the MAC address (like in this question) then the switch will dynamically learn the attached MAC Address and place it into your running-configuration.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]The following commands are entered on the router:
Burbank(config)# enable secret fortress
Burbank(config)# line con 0
Burbank(config-line)# login
Burbank(config-line)# password n0way1n
Burbank(config-line)# exit
Burbank(config)# service password-encryption
What is the purpose of the last command entered?
A. to require the user to enter an encrypted password during the login process
B. to prevent the vty, console, and enable passwords from being displayed in plain text in the configuration files
C. to encrypt the enable secret password
D. to provide login encryption services between hosts attached to the router
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The “service password-encryption” command encrypts passwords used by “enable password” global configuration command, as well as the password line configuration command (VTY, console) that are saved in the router configuration file.
Note: The secret password (configured by the command “enable secret fortress”) is always encrypted even if the “service password-encryption” command is not used.
Also, the “service password-encryption” command encrypts both current and future passwords.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Why would a network administrator configure port security on a switch?
A. to prevent unauthorized Telnet access to a switch port
B. to prevent unauthorized hosts from accessing the LAN
C. to limit the number of Layer 2 broadcasts on a particular switch port
D. block unauthorized access to the switch management interfaces
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]A company has placed a networked PC in a lobby so guests can have access to the corporate directory. A security concern is that someone will disconnect the directory PC and re-connect their laptop computer and have access to the corporate network. For the port servicing the lobby, which three configuration steps should be performed on the switch to prevent this? (Choose three)
A. Enable port security.
B. Create the port as a trunk port.
C. Create the port as an access port.
D Create the port as a protected port.
E. Set the port security aging time to 0.
F. Statically assign the MAC address to the address table.
G. Configure the switch to discover new MAC addresses after a set time of inactivity.
Answer: A C F[/am4show]
Explanation
By configuring the port connected with the directory PC as access port the network administrator will mitigate a lot of security issues because access port does not have as much privilege as a trunk port -> C is correct.
The port security feature can also help mitigate security issue because it can learn the MAC address of the directory PC. When another laptop is plugged into the port, the switch will automatically block or shut down that port (if suitable configuration is used) -> A is correct. But nowadays a hacker can fake the MAC address of the directory PC.
By statically assigning the MAC address to the address table, only that MAC address can access to the network -> F is correct.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the effect of using the service password-encryption command?
A. Only the enable password will be encrypted.
B. Only the enable secret password will be encrypted.
C. Only passwords configured after the command has been entered will be encrypted.
D. It will encrypt the secret password and remove the enable secret password from the configuration.
E. It will encrypt all current and future passwords.
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The “service password-encryption” command encrypts passwords used by “enable password” global configuration command, as well as the password line configuration command (VTY, console) that are saved in the router configuration file.
The “service password-encryption” command encrypts both current and future passwords.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]How can you ensure that only the MAC address of a server is allowed by switch port Fa0/1?
A. Configure port Fa0/1 to accept connections only from the static IP address of the server.
B. Configure the server MAC address as a static entry of port security.
C. Use a proprietary connector type on Fa0/1 that is incomputable with other host connectors.
D. Bind the IP address of the server to its MAC address on the switch to prevent other hosts from spoofing the server IP address.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The command to configure port security on a switch is (in interface configuration mode):
switchport port-security mac-address sticky [MAC]
In this case we will type the server MAC address. That MAC address will be stored in the address table, and added to the switch running configuration.
Note: If we don’t specify the MAC address then the switch will dynamically learn the attached MAC Address and place it into your running-configuration
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator made the entries that are shown and then saved the configuration. From a console connection, what password or password sequence is required for the administrator to access privileged mode on Router1?
| Router# configure terminal Router(config)# hostname Router1 Router1(config)# enable secret sanfran Router1(config)# enable password cisco Router1(config)# line vty 0 4 Router1(config-line)# password sanjose Route r1(config-line)# |
A. cisco
B. sanfran
C. sanjose
D. either cisco or sanfran
E. either cisco or sanjose
F. sanjose and sanfran
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
In the configuration above we have three passwords:
+ The “enable secret” password: sanfran
+ The “enable password” password: cisco
+ The VTY line password: sanjose
The two first “enable secret” and “enable password” are used to set password for entering privilege mode (an example of privilege mode: Router#). Both of them will be stored in the running configuration. But the password in “enable secret” command is always encrypted using MD5 hash while the password in “enable password” is in plain text.
Note: If you want to encrypt “enable password” you can use the command “service password-encryption” but it will be encrypted with a very basic form of encryption called vigenere cipher, which is very weak.
When you configure both an enable and a secret password, the secret password will be used -> B is correct.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]What should be part of a comprehensive network security plan?
A. Allow users to develop their own approach to network security
B. Physically secure network equipment from potential access by unauthorized individuals
C. Encourage users to use personal information in their passwords to minimize the likelihood of passwords being forgotten
D. Delay deployment of software patches and updates until their effect on end-user equipment is well known and widely reported
E. Minimize network overhead by deactivating automatic antivirus client updates
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
All other answers are not recommended for a network security plan so only B is the correct answer.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two recommended ways of protecting network device configuration files from outside network security threats? (Choose two)
A. Allow unrestricted access to the console or VTY ports.
B. Use a firewall to restrict access from the outside to the network devices.
C. Always use Telnet to access the device command line because its data is automatically encrypted.
D. Use SSH or another encrypted and authenticated transport to access device configurations.
E. Prevent the loss of passwords by disabling password encryption.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]From which of the following attacks can Message Authentication Code (MAC) shield your network?
A. DoS
B. DDoS
C. spoofing
D. SYN floods
Answer: C[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statements are true regarding ICMP packets? (Choose two)
A. They acknowledge receipt of TCP segments.
B. They guarantee datagram delivery
C. TRACERT uses ICMP packets.
D. They are encapsulated within IP datagrams.
E. They are encapsulated within UDP datagrams
Answer: C D[/am4show]
Explanation
Tracert (or traceroute) is used to trace the path between the sender and the destination host. Traceroute works by sending packets with gradually increasing Time-to-Live (TTL) value, starting with TTL value = 1. The first router receives the packet, decrements the TTL value and drops the packet because it then has TTL value zero. The router sends an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source. The next set of packets are given a TTL value of 2, so the first router forwards the packets, but the second router drops them and replies with ICMP Time Exceeded. Proceeding in this way, traceroute uses the returned ICMP Time Exceeded messages to build a list of routers that packets traverse, until the destination is reached and returns an ICMP Echo Reply message -> C is correct.
ICMP is encapsulated in an IP packet. In particular, the ICMP message is encapsulated in the IP payload part of an IP datagram -> D is correct.
Note: The TRACERT command on Windows Operating System uses ICMP while MAC OS X and Linux TRACEROUTE use UDP.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. An administrator cannot connect from R1 to R2. To troubleshoot this problem, the administrator has entered the command shown in the exhibit. Based on the output shown, what could be the problem?

A. The serial interface is configured for half duplex.
B. The serial interface does not have a cable attached.
C. The serial interface has the wrong type of cable attached.
D. The serial interface is configured for the wrong frame size.
E. The serial interface has a full buffer.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The output above is unclear. Normally when we use this command we can see the type of serial connection on this interface, for example “V.35 DCE cable. Below is an example of the same command as above:
|
RouterA#show controllers serial 0 |
Or
|
RouterB#show controllers serial 0 |
but in this case we only get “V.35 cable”. So in fact we are not sure about the answer C. But the output above also does not have any information to confirm other answers are correct or not.
Just for your information, the V.35 male and V.35 female cable are shown below:


Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]How many simultaneous Telnet sessions does a Cisco router support by default?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
F. 6
Answer: E[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of the following is a characteristic of full-duplex communication?
A. It is a CSMA/CD network.
B. It is a CSMA/CA network.
C. It is point-to-point only.
D. Hub communication is done via full duplex.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which set of conditions comprises a successful ping attempt between two connected routers configured with IP addresses on the same subnet?
A. The destination host receives an echo reply from the source host within one second and the source host receives an echo request from the destination host.
B. The destination host receives an echo request from the source host within one second.
C. The destination host receives an echo reply from the source host within one second and the source host receives an echo reply from the destination host within two seconds.
D. The destination host receives an echo request from the source host and the source host receives an echo request from the destination host within one second.
E. The destination host receives an echo request from the source host and the source host receives an echo reply from the destination host within two seconds.
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The ping command first sends an echo request packet to an address, then waits for a reply. The ping is successful only if:
+ The echo request gets to the destination, and
+ The destination is able to get an echo reply back to the source within a predetermined time called a timeout. The default value of this timeout is two seconds on Cisco routers.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which device allows users to connect to the network using a single or double radio?
A. access point
B. switch
C. wireless controller
D. firewall
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Many Cisco access points offer single or double (dual) radio (2.4 and 5.0 GHz).
Note: The wireless controller automates wireless configuration and management functions. It does not connect directly to users.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Various protocols are listed on the left On the right are applications for the use of those protocols. Drag the protocol on the left to an associated function for that protocol on the right (Not all options are used)
Answer:
[/am4show]+ ARP: A PC sends packets to the default gateway IP address the first time since the PC turned on.
+ ICMP: The network administrator is checking basic IP connectivity from a workstation to a server.
+ DNS: The TCP/IP protocol stack must find an IP address for packets destined for a URL.
+ DHCP: A network device will automatically assign IP addresses to workstations.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Move the protocol or service on the left to a situation on the right where it would be used. (Not all options are used)
Answer:
[/am4show]+ NAT: A PC with address 10.1.5.10 must access devices on the Internet.
+ DHCP: Only routers and servers require static IP addresses. Easy IP administration is required.
+ DNS: A PC only knows a server as MediaServer. IP needs to send data to that server.
+ OSPF: A protocol is needed to replace current static routes with automatic route updates.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Drag the definition on the left to the correct term on the right. Not all definitions on the left will be used.
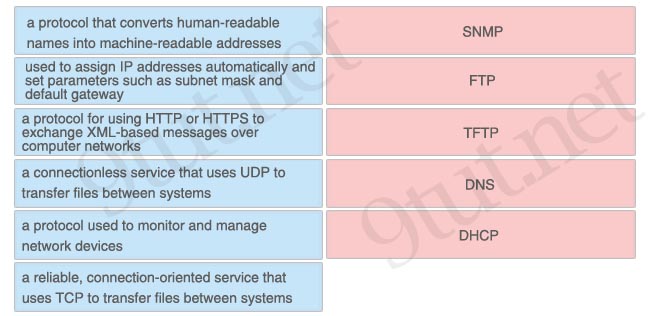
Answer:
[/am4show]+ SNMP: a protocol used to monitor and manage network devices
+ FTP: a reliable, connection-oriented service that uses TCP to transfer files between systems
+ TFTP: a connectionless service that uses UDP to transfer files between systems
+ DNS: a protocol that converts human-readable names into machine-readable addresses
+ DHCP: used to assign IP addresses automatically and set parameters such as subnet mask and default gateway
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Drag the appropriate command on the left to the configuration task it accomplishes (not all options are used)
Answer:
[/am4show]
| service password-encryption | encrypt all clear text passwords |
| line console 0 password friendS0nly |
protect access to the user mode prompt |
| enable secret noWay1n4u | set privileged mode encrypted password |
| line vty 0 4 password 2hard2Guess |
set password to allow Telnet connections |
| enable password uwi11NeverNo | set privileged mode clear text password |
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]On the left are various network protocols. On the right are the layers of the TCP/IP model. Assuming a reliable connection is required, move the protocols on the left to the TCP/IP layers on the right to show the proper encapsulation for an email message sent by a host on a LAN. (Not all options are used)
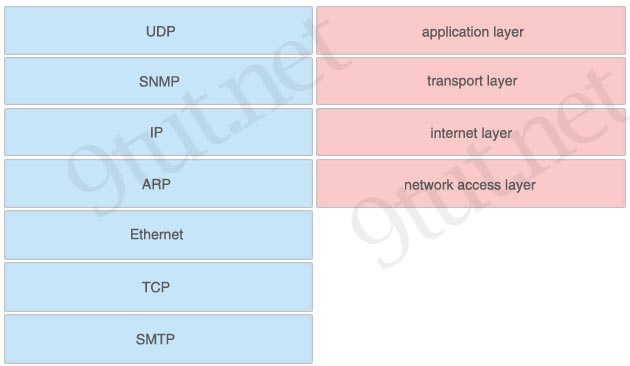
Answer:
[/am4show]+ application layer: SMTP
+ transport layer: TCP
+ internet layer: IP
+ network access layer: Ethernet
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question
[am4show have=’p2;’]RouterA and SwitchA have been configured to operate in a private network which will connect to the Internet. you have been asked to review the configuration prior to cabling and implementation.
This task requires the use of various commands to access and check the running configuration of the two devices. No configuration changes are necessary (and the configuration command has been disabled for these two devices).[/am4show]
The ICND1 100-105 exam has come to replace the old ICND1 100-101 exam. We create the “Share your ICND1 v3.0 Experience” for everyone to share their experience after taking this exam.
Please share with us your experience after taking the ICND1 100-105 exam, your materials, the way you learned, your recommendations… But please DO NOT share any information about the detail of the exam or your personal information, your score, exam date and location, your email…