test
[watupro 1]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about OSPF, please read my OSPF tutorial first.
Question
This item contains several questions that you must answer. You can view these questions by clicking on the corresponding button to the left. Changing questions can be accomplished by clicking the numbers to the left of each question. In order to complete the questions, you will need to refer to the topology.
To gain access to the topology, click on the topology button at the bottom of the screen. When you have finished viewing the topology, you can return to your questions by clicking on the Questions button to the left.
Each of the windows can be minimized by clicking on the [-]. You can also reposition a window by dragging it by the title bar.
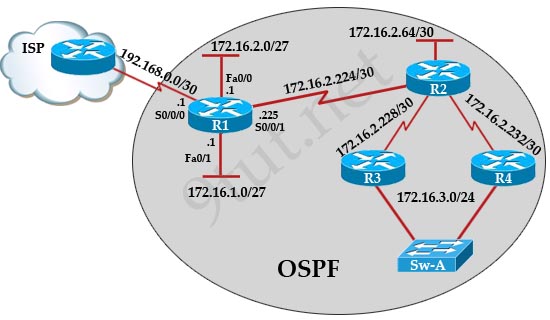
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]R1 is configured with the default configuration of OSPF.
From the following list of IP addresses configured on R1, which address will the OSPF process select as the router ID?
A. 192.168.0.1
B. 172.16.1.1
C. 172.16.2.1
D. 172.16.2.225
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The Router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router and is chosen using the following sequence:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
+ The router ID can be manually assigned
In this case, because a loopback interface is not configured so the highest active IP address 192.168.0.1 is chosen as the router ID.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]After the network has converged, what type of messaging, if any, occurs between R3 and R4?
A. No messages are exchanged.
B. Hellos are sent every 10 seconds.
C. The full database from each router is sent every 30 seconds.
D. The routing table from each router is sent every 60 seconds.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
HELLO messages are used to maintain adjacent neighbors so even when the network is converged, hellos are still exchanged. On broadcast and point-to-point links, the default is 10 seconds, on NBMA the default is 30 seconds.
Although OSPF is a link-state protocol but the full database from each router is sent every 30 minutes (not seconds) -> C and D are not correct.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]To allow or prevent load balancing to network 172.16.3.0/24, which of the following commands could be used in R2? (Choose two)
A. R2(config-if)#clock rate
B. R2(config-if)#bandwidth
C. R2(config-if)#ip ospf cost
D. R2(config-if)#ip ospf priority
E. R2(config-router)#distance ospf
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]R1 is unable to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with R3. What are possible reasons for this problem? (Choose two)
A. All of the routers need to be configured for backbone Area 1
B. R1 and R2 are the DR and BDR, so OSPF will not establish neighbor adjacency with R3
C. A static route has been configured from R1 to R3 and prevents the neighbor adjacency from being established.
D. The hello and dead interval timers are not set to the same values on R1 and R3
E. EIGRP is also configured on these routers with a lower administrative distance
F. R1 and R3 are configured in different areas
Answer: D F[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]OSPF is configured using default classful addressing. With all routers and interfaces operational, how many networks will be in the routing table of R1 that are indicated to be learned by OSPF?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
E. 6
F. 7
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Although OSPF is configured using default classful addressing but OSPF is a link-state routing protocol so it will always send the subnet mask of each network in their advertised routes. Therefore R1 will learn the the complete subnets. Four networks list below will be in the routing table of R1:
+ 172.16.2.64/30
+ 172.16.2.228/30
+ 172.16.2.232/30
+ 172.16.3.0/24
Note: Other networks will be learned as “Directly connected” networks (marked with letter “C”)
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about named ACLs is true?
A. They support standard and extended ACLs.
B. They are used to filter usernames and passwords for Telnet and SSH.
C. They are used to filter Layer 7 traffic.
D. They support standard ACLs only.
E. They are used to rate limit traffic destined to targeted networks.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The syntax of a named ACL is:
| ip access-list {standard | extended} {name | number} |
Therefore we can configure a standard acl with keyword “standard” and configure an extended acl with keyword “extended”. For example this is how to configure an named extended access-list:
| Router(config)#ip access-list extended in_to_out permit tcp host 10.0.0.1 host 187.100.1.6 eq telnet |
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which identification number is valid for an extended ACL?
A. 1
B. 64
C. 99
D. 100
E. 299
F. 1099
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Below is the range of standard and extended access list:
| Access list type | Range |
| Standard | 1-99, 1300-1999 |
| Extended | 100-199, 2000-2699 |
In most cases we only need to remember 1-99 is dedicated for standard access lists while 100 to 199 is dedicated for extended access lists.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What three pieces of information can be used in an extended access list to filter traffic? (Choose three)
A. VLAN number
B. TCP or UDP port numbers
C. source switch port number
D. source IP address and destination IP address
E. protocol
F. source MAC address and destination MAC address
Answer: B D E[/am4show]
Explanation
The syntax of an extended acl is:
| access-list access-list-number {permit | deny} protocol source-IP {source-mask} destination-IP {destination-mask} [eq destination-port] |
-> We can define protocol, source & destination IP addresses, destination port number.
For example, we will create an extended ACL that will permit FTP traffic (port 20, 21) from network 10.0.0.0/8 to reach 187.100.1.6 but deny other traffic to go through:
Router(config)#access-list 101 permit tcp 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 187.100.1.6 0.0.0.0 eq 21
Router(config)#access-list 101 permit tcp 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 187.100.1.6 0.0.0.0 eq 20
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about access lists that are applied to an interface is true?
A. you can apply only one access list on any interface
B. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 3 protocol
C. you can place as many access lists as you want on any interface
D. you can configure one access list, per direction, per layer 2 protocol
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
We can have only 1 access list per protocol, per direction and per interface. It means:
+ We can not have 2 inbound access lists on an interface
+ We can have 1 inbound and 1 outbound access list on an interface
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]When you are troubleshooting an ACL issue on a router, which command can help you to verify which interfaces are affected by the ACL?
A. show ip access-lists
B. show access-lists
C. show interface
D. show ip interface
E. list ip interface
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]In which solution is a router ACL used?
A. filtering packets that are passing through a router
B. to change the default administrative distance of a route in the route table
C. protecting a server from unauthorized access
D. controlling path selection, based on the route metric
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit.
| R1# show access-lists Extended IP access list 175 10 deny tcp any any time-range nonworkhours (active) 20 permit tcp any any time-range workhours (inactive) |
While you troubleshoot a connectivity issue to a PC behind R1, you enter the show access-lists command to generate this output. Which reason for the problem is most likely true?
A. The permit all ACL entry on R1 is inactive.
B. The ACL of R1 is misconfigured.
C. A deny all ACL entry is currently active on R1.
D. An implicit deny is causing R1 to block network traffic.
Answer: D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two circumstances can cause collision domain issues on VLAN domain? (Choose two)
A. duplex mismatches on Ethernet segments in the same VLAN
B. multiple errors on switchport interfaces
C. congestion on the switch inband path
D. a failing NIC in an end device
E. an overloaded shared segment
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
On an Ethernet connection, a duplex mismatch is a condition where two connected devices operate in different duplex modes, that is, one operates in half duplex while the other one operates in full duplex. Duplex mismatch can easily cause collision domain issue as the device that operates in full duplex mode turns off CSMA/CD. So it is eager to send data immediately without checking if the link is free to use -> A is correct.
An “inband path” is the path which provides path for management traffic (like CDP, VTP, PAgP…) but we are not sure why congestion on the switch inband path can cause collision domain issues. Maybe congestion on inband path prevents the JAM signal (sent when a collision occurs on the link) to be sent correctly on the link.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements are typical characteristics of VLAN arrangements? (Choose three)
A. A new switch has no VLANs configured.
B. Connectivity between VLANs requires a Layer 3 device.
C. VLANs typically decrease the number of collision domains.
D. Each VLAN uses a separate address space.
E. A switch maintains a separate bridging table for each VLAN.
F. VLANs cannot span multiple switches.
Answer: B D E[/am4show]
Explanation
By default, all ports on a new switch belong to VLAN 1 (default & native VLAN). There are also some well-known VLANs (for example: VLAN 1002 for fddi-default; VLAN 1003 for token-ring…) configured by default -> A is not correct.
To communicate between two different VLANs we need to use a Layer 3 device like router or Layer 3 switch -> B is correct.
VLANs don’t affect the number of collision domains, they are the same -> C is not correct. Typically, VLANs increase the number of broadcast domains.
We must use a different network (or sub-network) for each VLAN. For example we can use 192.168.1.0/24 for VLAN 1, 192.168.2.0/24 for VLAN 2 -> D is correct.
A switch maintains a separate bridging table for each VLAN so that it can send frame to ports on the same VLAN only. For example, if a PC in VLAN 2 sends a frame then the switch look-ups its bridging table and only sends frame out of its ports which belong to VLAN 2 (it also sends this frame on trunk ports) -> E is correct.
We can use multiple switches to expand VLAN -> F is not correct.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default VLAN on an access port?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 10
D. 1024
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
If we configure an access port as follows:
| Switch(config)#interface fa0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access |
Then this interface, by default, will belong to VLAN 1. Of course we can assign another VLAN to this port via the “switchport access vlan {vlan-number}” command.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are three valid reasons to assign ports to VLANs on a switch? (Choose three)
A. to make VTP easier to implement
B. to isolate broadcast traffic
C. to increase the size of the collision domain
D. to allow more devices to connect to the network
E. to logically group hosts according to function
F. to increase network security
Answer: B E F[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What command can you enter to assign an interface to the default VLAN?
A. Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 1
B. Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 1
C. Switch(config-if)# vlan 1
D. Switch(config)# int vlan 1
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The “switchport access vlan 1” assigns VLAN 1 to this interface. In fact, by default all access ports belong to VLAN 1 so this command is hidden in the switch configuration.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about switch access ports is true?
A. They drop packets with 802.1Q tags.
B. A VLAN must be assigned to an access port before it is created.
C. They can receive traffic from more than one VLAN with no voice support
D. By default, they carry traffic for VLAN 10.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
A VLAN does not need to be assigned to any port -> B is not correct.
An access port can only receive traffic from one VLAN -> C is not correct.
If not assigned to a specific VLAN, an access port carries traffic for VLAN 1 by default -> D is not correct.
An access port will drop packets with 802.1Q tags -> A is correct. Notice that 802.1Q tags are used to packets moving on trunk links.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature facilitates the tagging of frames on a specific VLAN?
A. Routing
B. hairpinning
C. switching
D. encapsulation
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three options are types of slow Vlan connectivity? (Choose three)
A. Slow broadcast domain connectivity.
B. Slow routing domain connectivity.
C. Slow default gateway connectivity.
D. Slow application domain connectivity.
E. Slow collision domain connectivity.
F. Slow inter Vlan connectivity.
Answer: A E F[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about VLAN configuration is true?
A. The switch must be in config-vlan mode before you configure an extended VLAN.
B. Dynamic inter-vlan routing is supported on VLAN 2 through VLAN 4064.
C. A switch in VTP transparent mode saves the VLAN database to the running configuration only.
D. The switch must be in VTP server or transparent mode before you configure a VLAN.
Answer: D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about DTP is true?
A. It uses the native VLAN.
B. It negotiates a trunk link after VTP has been configured.
C. It uses desirable mode by default.
D. It sends data on VLAN 1.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Control traffic like CDP, DTP, PAgP, and VTP uses VLAN 1 to operate, even if you change the native VLAN.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]How can you disable DTP on a switch port?
A. Configure the switch port as a trunk.
B. Add an interface on the switch to a channel group.
C. Change the operational mode to static access.
D. Change the administrative mode to access.
Answer: A (no correct answer, in fact)[/am4show]
Explanation
Although some books and websites said DTP is disabled if the switch port is configured as trunk or access mode (via the command “switchport mode trunk” or “switchport mode access”) but in fact DTP is still running in these modes. Please read at http://packetlife.net/blog/2008/sep/30/disabling-dynamic-trunking-protocol-dtp/. The only way to disable DTP on a switch port is to use the “switchport nonegotiate” command. But notice this command can only be used after configuring that switch port in “trunk” or “access” mode.
Therefore this is a question with no correct answer but if we have to choose an answer, we will choose answer A. At least it is correct in theory.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements about DTP are true? (Choose three)
A. It is enabled by default.
B. It is a universal protocol.
C. It is a proprietary protocol.
D. It is disabled by default.
E. It is a Layer 3-based protocol.
F. It is a Layer 2-based protocol.
Answer: A C F[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the DTP’s default mode in a switch?
A. ON
B. OFF
C. Dynamic Desirable
D. Dynamic Auto
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) is used to negotiate forming a trunk between two Cisco devices.
In fact this question is unclear as it does not ask about a specific switch model. The default DTP configuration for Cisco Catalyst 2960 and 3560 switches is dynamic auto while older 3550 switches run Dynamic Desirable as the default mode. So in this question we should follow the “newer” switches (which is “dynamic auto” mode).
New switches are only set to “dynamic auto” mode by default so they are safer as they do not try to form a trunk aggressively.
Therefore in this question “dynamic auto” is the best choice.
Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=2181837&seqNum=8
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
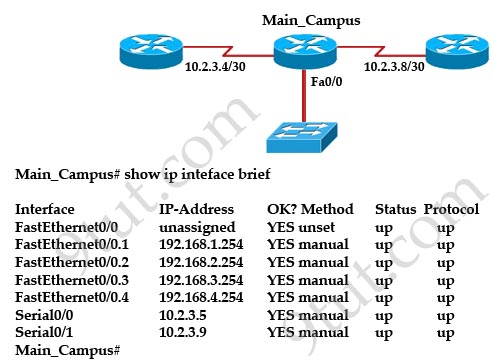
What can be determined about the interfaces of the Main_Campus router from the output shown?
A. The LAN interfaces are configured on different subnets.
B. Interface FastEthernet 0/0 is configured as a trunk.
C. The Layer 2 protocol of interface Serial 0/1 is NOT operational.
D. The router is a modular router with five FastEthernet interfaces.
E. Interface FastEthernet 0/0 is administratively deactivated.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
We can’t confirm answer B is totally correct but all other answers are wrong so B is the best choice.
+ We only have 1 LAN interface on Main_Campus router with 4 subinterfaces -> answer A is not correct (although it is a bit unclear).
+ The “protocol” column of interface Serial0/1 is up so its Layer 2 is operating correctly -> answer C is not correct.
+ This router has only 1 FastEthernet interface -> answer D is not correct.
+ The “status” column of Fa0/0 is currently “up” so it is operating -> answer E is not correct.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A technician has configured the FastEthernet 0/1 interface on Sw11 as an access link in VLAN 1. Based on the output from the show vlan brief command issued on Sw12, what will be the result of making this change on Sw11?
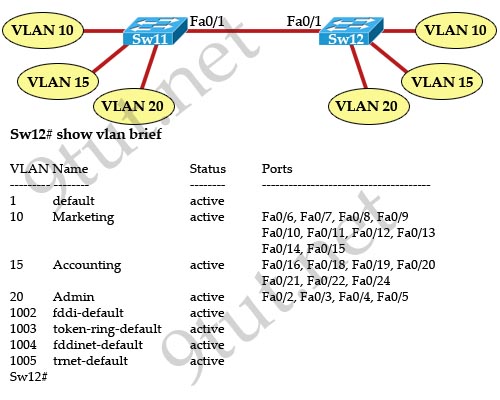
A. Only the hosts in VLAN 1 on the two switches will be able to communicate with each other.
B. The hosts in all VLANs on the two switches will be able to communicate with each other.
C. Only the hosts in VLAN 10 and VLAN 15 on the two switches will be able to communicate with each other.
D. Hosts will not be able to communicate between the two switches.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Fa0/1 of Switch11 is configured as an access link of VLAN1 so only frames in VLAN1 can communicate through the two switches. But from the output above we see there is no interface belongs to VLAN1 on Switch12 -> no hosts can communicate between the two switches.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three)
A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default.
B. 802.1Q trunking ports can also be secure ports.
C. 802.1Q trunks can use 10 Mb/s Ethernet interfaces.
D. 802.1Q trunks require full-duplex, point-to-point connectivity.
E. 802.1Q trunks should have native VLANs that are the same at both ends.
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three commands must you enter to create a trunk that allows VLAN 20? (Choose three)
A. Switch(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic auto
B. Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
C. Switch(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 20
D. Switch(config-if)#switchport mode dynamic desirable
E. Switch(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
F. Switch(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 20
Answer: B C E[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. While troubleshooting a switch, you executed the “show interface port-channel 1 etherchannel” command and it returned this output. Which information is provided by the Load value?

A. the percentage of use of the link
B. the preference of the link
C. the session count of the link
D. the number source-destination pairs on the link
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The way EtherChannel load balancing works is that the switch assigns a hash result from 0-7 based on the configured hash method ( load balancing algorithm ) for the type of traffic. This hash result is commonly called as Result Bundle Hash (RBH).
Now we need to convert Load value from Hexadecimal to Binary numbers. Therefore:
+ Gi1/1: 36 (Hex) = 00110110 (Bin) -> Bits 1, 2, 4, 5 are chosen (read from right to left, start from 0)
+ Gi1/2: 84 (Hex) = 10000100 (Bin) -> Bits 2, 7 are chosen
+ Gi1/3: 16 (Hex) = 00010110 (Bin) -> Bits 1, 2, 4 are chosen
Therefore if the RBH is 5, it will choose Gi1/1. If RBH is 4, it will choose Gi1/1 and Gi1/3 interfaces. If RBH is 2 it will choose all three above interfaces. And the bit sharing ratio is 3:3:2 (from “No of bits” column) hence two links has higher probability of getting utilized as compared to the third link.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two actions must you take to configure a PAgP EtherChannel between two switches, S1 and S2? (Choose two)
A. Configure the channel-group 1 mode auto command on S1.
B. Configure the channel-group 1 mode desirable command on S2.
C. Configure the channel-group 1 mode active command on S2.
D. Configure the channel-group 1 mode on command on S2.
E. Configure the channel-group 1 mode active command on S1.
Answer: A B[/am4show]
Explanation
In PAgP we only have two modes: auto and desirable.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which protocol provides a method of sharing VLAN configuration information between two Cisco switch?
A. VTP
B. 802.1Q
C. RSTP
D. STP
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which protocol supports sharing the VLAN configuration between two or more switches?
A. multicast
B. STP
C. VTP
D. split-horizon
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
With VTP, switches can learn VLAN configuration of other switches dynamically.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two characteristics of a switch that is configured as a VTP client? (Choose two)
A. If a switch that is configured to operate in client mode cannot access a VTP server, then the switch reverts to transparent mode.
B. The local vlan configuration is updated only when an update that has a higher configuration revision number is received.
C. VTP advertisements are not forwarded to neighboring switches that are configured in vtp transparent mode.
D. When switches in vtp client mode are rebooted, they send a vtp advertisement request to the vtp servers.
E. VTP client is the default vtp mode.
F. On switches that are configured to operate in client mode, vlans can be created, deleted or renamed locally.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements about VTP features are true? (Choose three)
A. VTP works at Layer 3 of the OSI model and requires that a management VLAN IP address be configured.
B. When properly configured, VTP minimizes VLAN misconfigurations and configuration inconsistencies.
C. When properly configured, VTP maintains VLAN configuration consistency and accelerates trunk link negotiation.
D. Each broadcast domain on a switch can have its own unique VTP domain.
E. VTP pruning is used to increase available bandwidth in trunk links.
F. To configure a switch to be part of two VTP domains, each domain must have its own passwords.
G. Client, server, and transparent are valid VTP modes.
Answer: B E G[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which IEEE standard does PVST+ use to tunnel information?
A. 802.1x
B. 802.1q
C. 802.1w
D. 802.1s
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
Cisco developed PVST+ to allow strolling numerous STP instances, even over an 802.1Q network via the use of a tunneling mechanism. PVST+ utilizes Cisco gadgets to hook up with a Mono Spanning Tree area to a PVST+ region. No particular configuration is needed to attain this. PVST+ affords assist for 802.1Q trunks and the mapping of a couple of spanning trees to the single spanning tree of popular 802.1Q switches strolling Mono Spanning Tree.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is one benefit of PVST+?
A. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches in the network.
B. PVST+ automatically selects the root bridge location, to provide optimization.
C. PVST+ allows the root switch location to be optimized per vlan.
D. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) maintains a spanning tree instance for each VLAN configured in the network. It means a switch can be the root bridge of a VLAN while another switch can be the root bridge of other VLANs in a common topology. For example, Switch 1 can be the root bridge for Voice data while Switch 2 can be the root bridge for Video data. If designed correctly, it can optimize the network traffic.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which spanning-tree feature places a port immediately into a forwarding stated?
A. BPDU guard
B. PortFast
C. loop guard
D. UDLD
E. Uplink Fast
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
When you enable PortFast on the switch, spanning tree places ports in the forwarding state immediately, instead of going through the listening, learning, and forwarding states.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]If primary and secondary root switches with priority 16384 both experience catastrophic losses, which tertiary switch can take over?
A. a switch with priority 20480
B. a switch with priority 8192
C. a switch with priority 4096
D. a switch with priority 12288
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
This is a tricky question. We know the switch with lowest value of priority is elected the root switch. Therefore in this question the switches with priority of 4096, 8192, 12288 (which are lower than the current value of the root bridge 16384) are not joining the root bridge election by somehow. The only suitable answer is the switch with priority 20480 will become the root bridge.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which factors generate bridge ID? (Choose two)
A. MAC address
B. IP Address
C. STP Priority
D. Bridge Priority
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
The switches compare their Bridge ID with each other to find out who will be the root bridge. The root bridge is the bridge with the lowest bridge ID.
Bridge ID = Bridge Priority + MAC Address
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which process is associated with spanning-tree convergence?
A. determining the path cost
B. electing designated ports
C. learning the sender bridge ID
D. assigning the port ID
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
SPT must performs three steps to provide a loop-free network topology:
1. Elects one root bridge
2. Select one root port per nonroot bridge
3. Select one designated port on each network segment -> Answer B is correct.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which term describes a spanning-tree network that has all switch ports in either the blocking or forwarding state?
A. redundant
B. spanned
C. provisioned
D. converged
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Spanning Tree Protocol convergence (Layer 2 convergence) happens when bridges and switches have transitioned to either the forwarding or blocking state. When layer 2 is converged, root bridge is elected and all port roles (Root, Designated and Non-Designated) in all switches are selected.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which switch provides the spanning-tree designated port role for the network segment that services the printers?
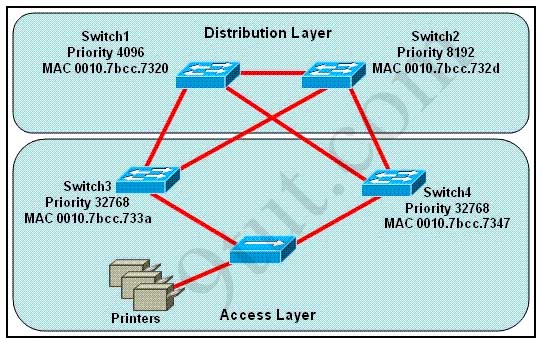
A. Switch1
B. Switch2
C. Switch3
D. Switch4
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
First, the question asks what switch services the printers, so it can be Switch 3 or Switch 4 which is connected directly to the Printers.
Next, by comparing the MAC address of Switch 3 and Switch 4 we found that the MAC of Switch 3 is smaller. Therefore the interface connected to the Printers of Switch 3 will become designated interface and the interface of Switch 4 will be blocked. The picture below shows the roles of all ports:
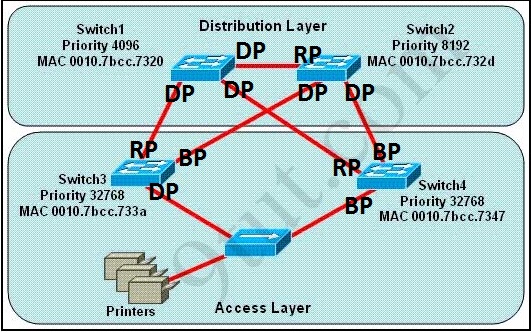
DP: Designated Port
RP: Root Port
BP: Blocked Port
(Please notice that Switch 1 will become the root bridge because of its lowest priority, not Switch 3)
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]If primary and secondary root switches with priority 16384 both experience catastrophic losses, which tertiary switch can take over?
A. a switch with priority 20480
B. a switch with priority 8192
C. a switch with priority 4096
D. a switch with priority 12288
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
This is a tricky question. We know the switch with lowest value of priority is elected the root switch. Therefore in this question the switches with priority of 4096, 8192, 12288 (which are lower than the current value of the root bridge 16384) are not joining the root bridge election by somehow. The only suitable answer is the switch with priority 20480 will become the root bridge.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What kind of data message is send to elect the root bridge?
A. BPDU
B. Segment
C. Packets
D. Hello
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which type does a port become when it receives the best BPDU on a bridge?
A. the backup port
B. the root port
C. the designated port
D. the alternate port
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which value can you modify to configure a specific interface as the preferred forwarding interface?
A. the VLAN priority
B. the hello time
C. the port priority
D. the interface number
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which VLAN bridge priority value is assigned by the set spantree root command?
A. 8192
B. 16384
C. 28672
D. 32768
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements about the spanning-tree bridge ID are true? (Choose two)
A. It is composed of a 4-bit bridge priority and a 12-bit system ID extension.
B. The bridge ID is transmitted in the IP header to elect the root bridge.
C. The system ID extension is a value between 1 and 4095.
D. It is composed of an 8-bit bridge priority and a 16-bit system ID extension.
E. The bridge priority must be incremented in blocks of 4096.
Answer: A E[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
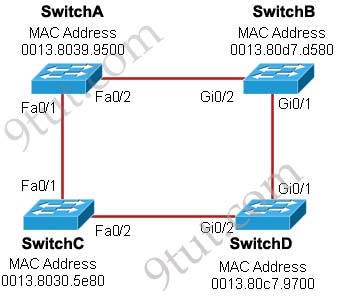
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)
A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F[/am4show]
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
In the exhibit you also see FastEthernet port is connecting to GigabitEthernet port. In this case GigabitEthernet port will operate as a FastEthernet port so the link can be considered as FastEthernet to FastEthernet connection.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again

SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 19 (the cost value of 100Mbps link although the port on Switch D is GigabitEthernet port) and advertises this value (19) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 23. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 38 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:
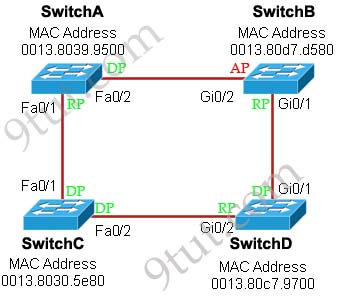
+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
Question 2
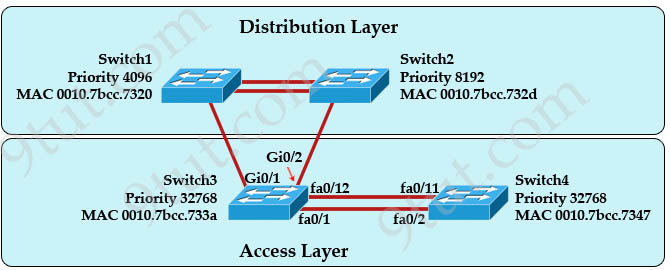
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. At the end of an RSTP election process, which access layer switch port will assume the discarding role?
A. Switch3, port fa0/1
B. Switch3, port fa0/12
C. Switch4, port fa0/11
D. Switch4, port fa0/2
E. Switch3, port Gi0/1
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
In this question, we only care about the Access Layer switches (Switch3 & 4). Switch 3 has a lower bridge ID than Switch 4 (because the MAC of Switch3 is smaller than that of Switch4) so both ports of Switch3 will be in forwarding state. The alternative port will surely belong to Switch4.
Switch4 will need to block one of its ports to avoid a bridging loop between the two switches. But how does Switch4 select its blocked port? Well, the answer is based on the BPDUs it receives from Switch3. A BPDU is superior than another if it has:
1. A lower Root Bridge ID
2. A lower path cost to the Root
3. A lower Sending Bridge ID
4. A lower Sending Port ID
These four parameters are examined in order. In this specific case, all the BPDUs sent by Sswitch3 have the same Root Bridge ID, the same path cost to the Root and the same Sending Bridge ID. The only parameter left to select the best one is the Sending Port ID (Port ID = port priority + port index). In this case the port priorities are equal because they use the default value, so Switch4 will compare port index values, which are unique to each port on the switch, and because Fa0/12 is inferior to Fa0/1, Switch4 will select the port connected with Fa0/1 (of Switch3) as its root port and block the other port -> Port fa0/11 of Switch4 will be blocked (discarding role).
If you are still not sure about this question, please read my RSTP tutorial.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]At which layer of the OSI model is RSTP used to prevent loops?
A. data link
B. network
C. physical
D. transport
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements about RSTP are true? (Choose three)
A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconvening time after a link failure.
B. RSTP expands the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
D. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
E. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
F. RSTP uses the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
Answer: A B D[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two switch states are valid for 802.1w? (Choose two)
A. listening
B. backup
C. disabled
D. learning
E. discarding
Answer: D E[/am4show]
Explanation
IEEE 802.1w is Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). There are only three port states left in RSTP that correspond to the three possible operational states. The 802.1D disabled, blocking, and listening states are merged into the 802.1w discarding state.
* Discarding – the port does not forward frames, process received frames, or learn MAC addresses – but it does listen for BPDUs (like the STP blocking state)
* Learning – receives and transmits BPDUs and learns MAC addresses but does not yet forward frames (same as STP).
* Forwarding – receives and sends data, normal operation, learns MAC address, receives and transmits BPDUs (same as STP).
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two of these statements regarding RSTP are correct? (Choose two)
A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
B. RSTP defines new port roles.
C. RSTP defines no new port states.
D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (choose two)
A. discarding
B. learning
C. disabled
D. forwarding
E. listening
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
RSTP only has 3 port states that are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
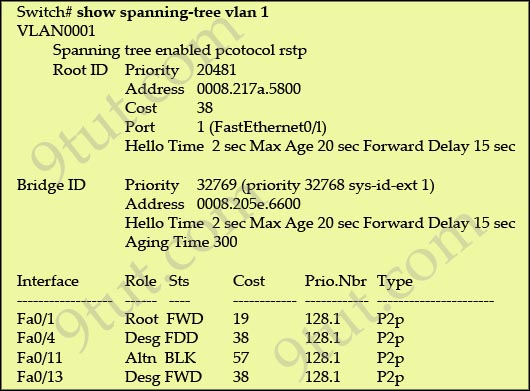
Why has this switch not been elected the root bridge for VLAN1?
A. It has more than one internee that is connected to the root network segment.
B. It is running RSTP while the elected root bridge is running 802.1d spanning tree.
C. It has a higher MAC address than the elected root bridge.
D. It has a higher bridge ID than the elected root bridge.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
As we can see from the output above, the priority of the root bridge is 20481 while that of the local bridge is 32769.
Question 9
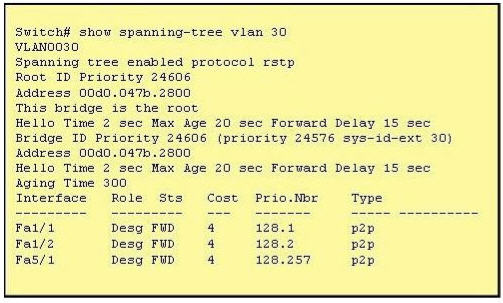
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The output that is shown is generated at a switch. Which three of these statements are true? (Choose three)
A. All ports will be in a state of discarding, learning or forwarding.
B. Thirty VLANs have been configured on this switch.
C. The bridge priority is lower than the default value for spanning tree.
D. All interfaces that are shown are on shared media.
E. All designated ports are in a forwarding state.
F. The switch must be the root bridge for all VLANs on this switch.
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output, we see that all ports are in Designated role (forwarding state) -> A and E are correct.
The command “show spanning-tree vlan 30″ only shows us information about VLAN 30. We don’t know how many VLAN exists in this switch -> B is not correct.
The bridge priority of this switch is 24606 which is lower than the default value bridge priority 32768 -> C is correct.
All three interfaces on this switch have the connection type “p2p”, which means Point-to-point environment – not a shared media -> D is not correct.
The only thing we can specify is this switch is the root bridge for VLAN 30 but we can not guarantee it is also the root bridge for other VLANs -> F is not correct.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Each of these four switches has been configured with a hostname, as well as being configured to run RSTP. No other configuration changes have been made. Which three of these show the correct RSTP port roles for the indicated switches and interfaces? (Choose three)

A. SwitchA, Fa0/2, designated
B. SwitchA, Fa0/1, root
C. SwitchB, Gi0/2, root
D. SwitchB, Gi0/1, designated
E. SwitchC, Fa0/2, root
F. SwitchD, Gi0/2, root
Answer: A B F[/am4show]
Explanation
The question says “no other configuration changes have been made” so we can understand these switches have the same bridge priority. Switch C has lowest MAC address so it will become root bridge and 2 of its ports (Fa0/1 & Fa0/2) will be designated ports -> E is incorrect.
Because SwitchC is the root bridge so the 2 ports nearest SwitchC on SwitchA (Fa0/1) and SwitchD (Gi0/2) will be root ports -> B and F are correct.
Now we come to the most difficult part of this question: SwitchB must have a root port so which port will it choose? To answer this question we need to know about STP cost and port cost.
In general, “cost” is calculated based on bandwidth of the link. The higher the bandwidth on a link, the lower the value of its cost. Below are the cost values you should memorize:
| Link speed | Cost |
| 10Mbps | 100 |
| 100Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
SwitchB will choose the interface with lower cost to the root bridge as the root port so we must calculate the cost on interface Gi0/1 & Gi0/2 of SwitchB to the root bridge. This can be calculated from the “cost to the root bridge” of each switch because a switch always advertises its cost to the root bridge in its BPDU. The receiving switch will add its local port cost value to the cost in the BPDU.
In the exhibit you also see FastEthernet port is connecting to GigabitEthernet port. In this case GigabitEthernet port will operate as a FastEthernet port so the link can be considered as FastEthernet to FastEthernet connection.
One more thing to notice is that a root bridge always advertises the cost to the root bridge (itself) with an initial value of 0.
Now let’s have a look at the topology again

SwitchC advertises its cost to the root bridge with a value of 0. Switch D adds 19 (the cost value of 100Mbps link although the port on Switch D is GigabitEthernet port) and advertises this value (19) to SwitchB. SwitchB adds 4 (the cost value of 1Gbps link) and learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/1 port with a total cost of 23. The same process happens for SwitchA and SwitchB learns that it can reach SwitchC via Gi0/2 with a total cost of 38 -> Switch B chooses Gi0/1 as its root port -> D is not correct.
Now our last task is to identify the port roles of the ports between SwitchA & SwitchB. It is rather easy as the MAC address of SwitchA is lower than that of SwitchB so Fa0/2 of SwitchA will be designated port while Gi0/2 of SwitchB will be alternative port -> A is correct but C is not correct.
Below summaries all the port roles of these switches:

+ DP: Designated Port (forwarding state)
+ RP: Root Port (forwarding state)
+ AP: Alternative Port (blocking state)
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
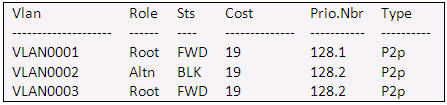
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Given the output shown from this Cisco Catalyst 2950, what is the most likely reason that interface FastEthernet 0/10 is not the root port for VLAN 2?
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastethernet0/10
A. This switch has more than one interface connected to the root network segment in VLAN 2.
B. This switch is running RSTP while the elected designated switch is running 802.1d Spanning Tree.
C. This switch interface has a higher path cost to the root bridge than another in the topology.
D. This switch has a lower bridge ID for VLAN 2 than the elected designated switch.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option describes how a switch in rapid PVST+ mode responds to a topology change?
A. It immediately deletes dynamic MAC addresses that were learned by all ports on the switch.
B. It sets a timer to delete all MAC addresses that were learned dynamically by ports in the same STP instance.
C. It sets a timer to delete dynamic MAC addresses that were learned by all ports on the switch.
D. It immediately deletes all MAC addresses that were learned dynamically by ports in the same STP instance.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Rapid PVST+—This spanning-tree mode is the same as PVST+ except that is uses a rapid convergence based on the IEEE 802.1w standard. To provide rapid convergence, the rapid PVST+ immediately deletes dynamically learned MAC address entries on a per-port basis upon receiving a topology change. By contrast, PVST+ uses a short aging time for dynamically learned MAC address entries.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which port state is introduced by Rapid-PVST?
A. learning
B. listening
C. discarding
D. forwarding
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
PVST+ is based on IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). But PVST+ has only 3 port states (discarding, learning and forwarding) while STP has 5 port states (blocking, listening, learning, forwarding and disabled). So discarding is a new port state in PVST+.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command enables RSTP on a switch?
A. spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
B. spanning-tree uplinkfast
C. spanning-tree backbonefast
D. spanning-tree mode mst
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 5
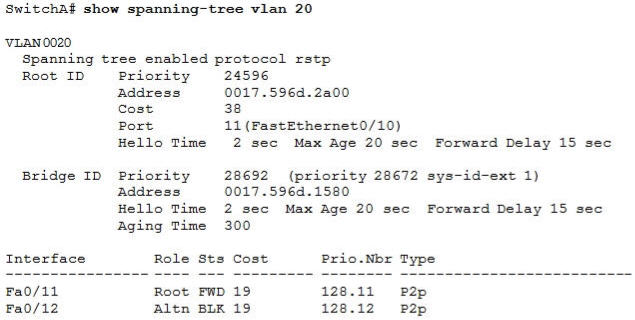
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true?
A. The Fa0/11 role confirms that SwitchA is the root bridge for VLAN 20.
B. VLAN 20 is running the Per VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol.
C. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.1580.
D. SwitchA is not the root bridge, because not all of the interface roles are designated.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Only non-root bridge can have root port. Fa0/11 is the root port so we can confirm this switch is not the root bridge -> A is not correct.
From the output we learn this switch is running Rapid STP, not PVST -> B is not correct.
0017.596d.1580 is the MAC address of this switch, not of the root bridge. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.2a00 -> C is not correct.
All of the interface roles of the root bridge are designated. SwitchA has one Root port and 1 Alternative port so it is not the root bridge -> D is correct.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
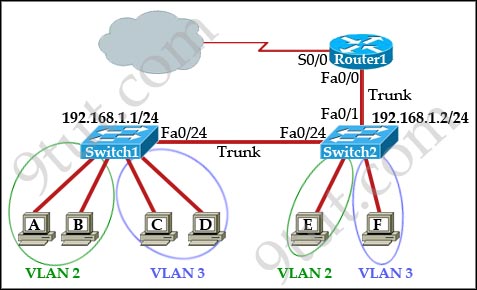
Which two statements are true about interVLAN routing in the topology that is shown in the exhibit? (Choose two)
A. Host E and host F use the same IP gateway address.
B. Routed and Switch2 should be connected via a crossover cable.
C. Router1 will not play a role in communications between host A and host D.
D. The FastEthernet 0/0 interface on Router1 must be configured with subinterfaces.
E. Router1 needs more LAN interfaces to accommodate the VLANs that are shown in the exhibit.
F. The FastEthernet 0/0 interface on Router1 and Switch2 trunk ports must be configured using the same encapsulation type.
Answer: D F[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about slow inter VLAN forwarding is true?
A. The VLAN is experiencing slowness in the point-to-point collisionless connection.
B. The VLANs are experiencing slowness because multiple devices are connected to the same hub.
C. The local VLAN is working normally, but traffic to the alternate VLAN is forwarded slower than expected.
D. The entire VLAN is experiencing slowness.
E. The VLANs are experiencing slowness due to a duplex mismatch.
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
The causes of slow interVLAN are usually duplex mismatch or collision domain issues, user misconfiguration. For more information please read: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/virtual-lans-vlan-trunking-protocol-vlans-vtp/23637-slow-int-vlan-connect.html#troubleshoot_slow_interv
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which configuration can you apply to enable encapsulation on a subinterface?
A. interface FastEthernet 0/0
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ip address 10.1.1.30 255.255.255.0
B. interface FastEthernet 0/0.30
ip address 10.1.1.30 255.255.255.0
C. interface FastEthernet 0/0.30
description subinterface vlan 30
D. interface FastEthernet 0/0.30
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ip address 10.1.1.30 255.255.255.0
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
To enabe encapsulation on a subinterface we have type the “encapsulation” command under that subinterface, not the main interface. An example of configuring encapsulation on subinterface of Fa0/1 is shown below:
|
Router(config)#interface f0/0 (Note: The main interface f0/0 doesn’t need an IP address but it must be turned on) Router(config)#interface f0/0.0 |
Note: In the “encapsulation dot1q 10”, number 10 is the VLAN applied to that subinterface. Or you can understand that the subinterface belongs to that VLAN.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
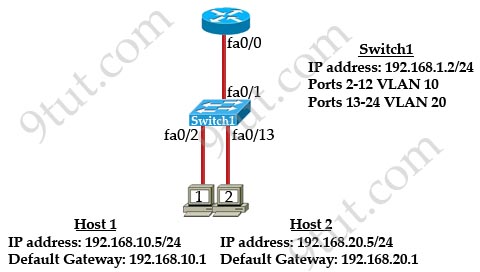
What commands must be configured on the 2950 switch and the router to allow communication between host 1 and host 2? (Choose two)
A. Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shut down
B. Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0.1
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 10
Router(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-subif)#interface fastethernet 0/0.2
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 20
Router(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
C. Router (config)#router eigrp 100
Router(config-router)#network 192.168.10.0
Router(config-router)#network 192.168.20.0
D. Switch1(config)# vlan database
Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp domain XYZ
Switch1(config-vlan)# vtp server
E. Switch1(config) # interface fastEthernet 0/1
Switch1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
F. Switch1(config)# interface vlan 1
Switch1(config-if)# ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:

C-router is to be used as a “router-on-a-stick” to route between the VLANs. All the interfaces have been properly configured and IP routing is operational. The hosts in the VLANs have been configured with the appropriate default gateway. What can be said about this configuration?
A. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router eigrp 123
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
B. No further routing configuration is required.
C. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router ospf 1
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
D. These commands need to be added to the configuration:
C-router(config)# router rip
C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
Answer: B[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The show interfaces serial 0/1 command was issued on the R10-1 router. Based on the output displayed which statement is correct?
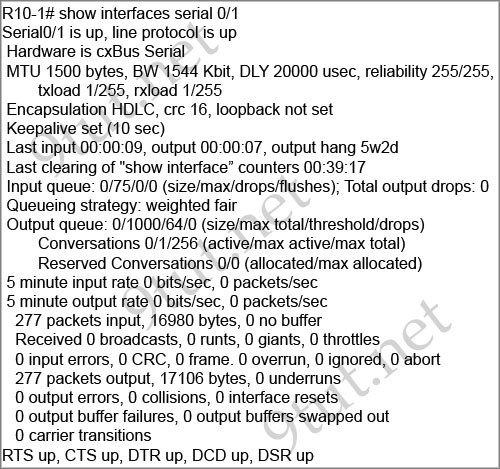
A. The cable connected to the serial 0/1 interface of the R10-1 router is a DTE cable.
B. The R10-1 router can ping the router interface connected to the serial 0/1 interface.
C. The clock rate used for interface serial 0/1 of the R10-1 router is 1,544,000 bits per second.
D. The CSU used with the serial 0/1 interface of the R10-1 router has lost connection to the service provider.
E. The interface of the remote router connected to the serial 0/1 interface of the R10-1 router is using the default serial interface encapsulation.
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output, we see the the line “Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is up”. That means the link is good and the interface is functioning normally. Also the encapsulation used on this interface is HDLC -> The other end must use the same encapsulation. Otherwise the line protocol will go down.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two options are valid WAN connectivity methods? (Choose two)
A. PPP
B. WAP
C. DSL
D. L2TPv3
E. Ethernet
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which device classes are used over serial links?
A. DCE
B. DTE
C. LCP
D. HDLC
E. PPP
F. LMI
Answer: A B[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which WAN technology uses labels to make decisions about data forwarding?
A. Metro Ethernet
B. Frame Relay
C. MPLS
D. ISDN
E. VSAT
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which WAN solution is secured by default?
A. VPN
B. DSL
C. LCP
D. PPP
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which WAN topology provides a direct connection from each site to all other sites on the network?
A. single-homed
B. full mesh
C. point-to-point
D. hub-and-spoke
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]After you configure a GRE tunnel between two networks, the tunnel comes up normally, but workstations on each side of the tunnel cannot communicate. Which reason for the problem is most likely the true?
A. The tunnel source address is incorrect.
B. The tunnel destination address is incorrect.
C. The route between the networks is undefined.
D. The IP MTU is incorrect.
E. The distance configuration is missing.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default encapsulation type for Cisco WAN serial interfaces?
A. GRE
B. PPP
C. Frame Relay
D. IEEE 802.1Q
E. HDLC
Answer: E[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature does PPP use to encapsulate multiple protocols?
A. NCP
B. LCP
C. IPCP
D. IPXP
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements about using the CHAP authentication mechanism in a PPP link are true? (Choose two)
A. CHAP uses a two-way handshake.
B. CHAP uses a three-way handshake.
C. CHAP authentication periodically occurs after link establishment.
D. CHAP authentication passwords are sent in plaintext.
E. CHAP authentication is performed only upon link establishment.
F. CHAP has no protection from playback attacks.
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) can use either Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) or Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) for authentication. CHAP is used upon initial link establishment and periodically to make sure that the router is still communicating with the same host. CHAP passwords arc exchanged as message digest algorithm 5 (MD5) hash values.
The three-way handshake steps are as follows:
Challenge: The authenticator generates a frame called a Challenge and sends it to the initiator. This frame contains a simple text message (sometimes called the challenge text). The message has no inherent special meaning so it doesn’t matter if anyone intercepts it. The important thing is that after receipt of the Challenge both devices have the same challenge message.
Response: The initiator uses its password (or some other shared “secret” that the authenticators also knows) to encrypt the challenge text. It then sends the encrypted challenge text as a Response back to the authenticator.
Success or Failure: The authenticator performs the same encryption on the challenge text that the initiator did. If the authenticator gets the same result that the initiator sent it in the Response, the authenticator knows that the initiator had the right password when it did its encryption, so the authenticator sends back a Success message. Otherwise, it sends a Failure message.
(Reference: CCNA Quick Reference Sheets)
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the purpose of LCP?
A. to perform authentication
B. to negotiate control options
C. to encapsulate multiple protocols
D. to specify asynchronous versus synchronous
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command is used to enable CHAP authentication with PAP as the fallback method on a serial interface?
A. (config-if)# authentication ppp chap fallback ppp
B. (config-if)# authentication ppp chap pap
C. (config-if)# ppp authentication chap pap
D. (config-if)# ppp authentication chap fallback ppp
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The command “ppp authentication chap pap” command indicates the CHAP authentication is used first. If it fails or is rejected by other side then uses PAP instead. If you want to use PAP first (then CHAP) you can use the “ppp authentication pap chap” command.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are three reasons that an organization with multiple branch offices and roaming users might implement a Cisco VPN solution instead of point-to-point WAN links? (Choose three)
A. reduced cost
B. better throughput
C. broadband incompatibility
D. increased security
E. scalability
F. reduced latency
Answer: A D E[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which Layer 2 protocol encapsulation type supports synchronous and asynchronous circuits and has built-in security mechanisms?
A. HDLC
B. PPP
C. X.25
D. Frame Relay
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
PPP supports both synchronous (like analog phone lines) and asynchronous circuits (such as ISDN or digital links). With synchronous circuits we need to use clock rate.
Note: Serial links can be synchronous or asynchronous. Asynchronous connections used to be only available on low-speed (<2MB) serial interfaces, but now, there are the new HWICs (High-Speed WAN Interface Cards) which also support asynchronous mode. To learn more about them please visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/modules/ps5949/ps6182/prod_qas0900aecd80274424.html.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which PPP subprotocol negotiates authentication options?
A. NCP
B. ISDN
C. SUP
D. LCP
E. DLCI
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Link Control Protocol (LCP) is a subprotocol within the Point-to-Point Protocol protocol suite that is responsible for link management. During establishment of a PPP communication session, LCP establishes the link, configures PPP options, and tests the quality of the line connection between the PPP client and PPP server. LCP automatically handles encapsulation format options and varies packet sizes over PPP communication links.
LCP also negotiates the type of authentication protocol used to establish the PPP session. Different authentication protocols are supported for satisfying the security needs of different environments.
Other subprotocol within PPP is Network Control Protocol (NCP), which is used to allow multiple Network layer protocols (routed protocols) to be used on a point-to-point connection.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]At which layer of the OSI model does PPP perform?
A. Layer 2
B. Layer 3
C. Layer 4
D. Layer 5
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Layer 2 includes the popular WAN standards, such as the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), High-Level Data-Link Control (HDLC) and Frame Relay protocols.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which type of interface can negotiate an IP address for a PPPoE client?
A. Ethernet
B. dialer
C. serial
D. Frame Relay
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
In the Dialer interface, we can use the “ip address negotiated” command to ask for an IP address from the PPPoE Server.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which part of the PPPoE server configuration contains the information used to assign an IP address to a PPPoE client?
A. virtual-template interface
B. DHCP
C. dialer interface
D. AAA authentication
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The picture below shows all configuration needed for PPPoE:
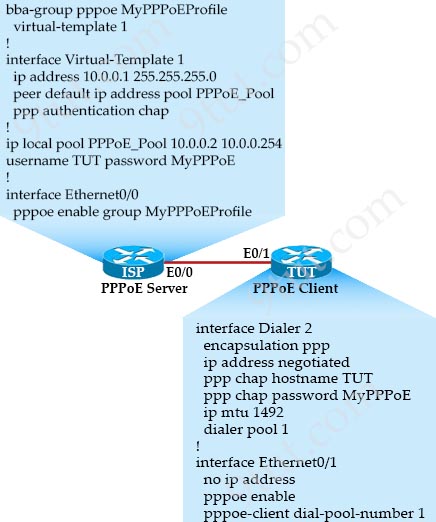
There is no Dialer interface on the PPPoE Server so answer “Dialer interface” is not correct. The most suitable answer is “Virtual Template” interface as it contains the pool which is used to assign IP address to the PPPoE Client. But this question is weird because according to the CCNAv3 syllabus, candidates only need to grasp the PPPoE on client-side, not sure why this question asked about PPPoE on Server side. For more information about PPPoE, please read our PPPoE tutorial.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command do you enter to enable an interface to support PPPoE on a client?
A. Dev1(config)# bba-group pppoe bba 1
B. Dev1(config-if)# pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1
C. Dev1(config-if)# pppoe enable group bba1
D. Dev1(config-if)# pppoe enable
Answer: D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which type of topology is required by DMVPN?
A. ring
B. full mesh
C. hub-and-spoke
D. partial mesh
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
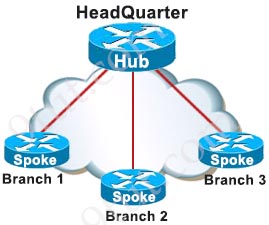
The topology of DMVPN is always hub-and-spoke as all Spokes are required to connect to the Hub router directly.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about MPLS is true?
A. It operates in Layer 1.
B. It operates between Layer 2 and Layer 3.
C. It operates in Layer 3.
D. It operates in Layer 2.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
MPLS operates at a layer that lies between traditional definitions of Layer 2 (data link layer) and Layer 3 (network layer), and thus is often referred to as a “layer 2.5” protocol.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements about HSRP operation are true? (Choose three)
A. The virtual IP address and virtual MAC address are active on the HSRP Master router.
B. The HSRP default timers are a 3 second hello interval and a 10 second dead interval.
C. HSRP supports only clear-text authentication.
D. The HSRP virtual IP address must be on a different subnet than the routers’ interfaces on the same LAN.
E. The HSRP virtual IP address must be the same as one of the router’s interface addresses on the LAN.
F. HSRP supports up to 255 groups per interface, enabling an administrative form of load balancing.
Answer: A B F[/am4show]
Explanation
The virtual MAC address of HSRP version 1 is 0000.0C07.ACxx, where xx is the HSRP group number in hexadecimal based on the respective interface. For example, HSRP group 10 uses the HSRP virtual MAC address of 0000.0C07.AC0A. HSRP version 2 uses a virtual MAC address of 0000.0C9F.FXXX (XXX: HSRP group in hexadecimal)
For more information about HSRP operation, please read our HSRP tutorial.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is a valid HSRP virtual MAC address?
A. 0000.5E00.01A3
B. 0007.B400.AE01
C. 0000.0C07.AC15
D. 0007.5E00.B301
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
With HSRP, two or more devices support a virtual router with a fictitious MAC address and unique IP address. There are two version of HSRP.
+ With HSRP version 1, the virtual router’s MAC address is 0000.0c07.ACxx , in which xx is the HSRP group.
+ With HSRP version 2, the virtual MAC address if 0000.0C9F.Fxxx, in which xxx is the HSRP group.
Note: Another case is HSRP for IPv6, in which the MAC address range from 0005.73A0.0000 through 0005.73A0.0FFF.
-> C is correct.
(Good resource for HSRP: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/5_x/nx-os/unicast/configuration/guide/l3_hsrp.html)
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three options are the HSRP states for a router? (Choose three)
A. initialize
B. learn
C. secondary
D. listen
E. speak
F. primary
Answer: B D E[/am4show]
Explanation
HSRP consists of 6 states:
| State | Description |
| Initial | This is the beginning state. It indicates HSRP is not running. It happens when the configuration changes or the interface is first turned on |
| Learn | The router has not determined the virtual IP address and has not yet seen an authenticated hello message from the active router. In this state, the router still waits to hear from the active router. |
| Listen | The router knows both IP and MAC address of the virtual router but it is not the active or standby router. For example, if there are 3 routers in HSRP group, the router which is not in active or standby state will remain in listen state. |
| Speak | The router sends periodic HSRP hellos and participates in the election of the active or standby router. |
| Standby | In this state, the router monitors hellos from the active router and it will take the active state when the current active router fails (no packets heard from active router) |
| Active | The router forwards packets that are sent to the HSRP group. The router also sends periodic hello messages |
Please notice that not all routers in a HSRP group go through all states above. In a HSRP group, only one router reaches active state and one router reaches standby state. Other routers will stop at listen state.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]What about HSRP IP Address is true?
A. If its part of the LAN
B. Part of all other networks
C. Local to the interface
D. Appears in the routing table
E. Acts as default route for that interface
Answer: E[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of the following HSRP router states does an active router enter when it is preempted by a higher priority router?
A. active
B. speak
C. learn
D. listen
E. init
F. standby
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
First we should review all the HSRP States:
| State | Description |
| Initial | This is the beginning state. It indicates HSRP is not running. It happens when the configuration changes or the interface is first turned on |
| Listen | The router knows both IP and MAC address of the virtual router but it is not the active or standby router. For example, if there are 3 routers in HSRP group, the router which is not in active or standby state will remain in listen state. |
| Speak | The router sends periodic HSRP hellos and participates in the election of the active or standby router. |
| Standby | In this state, the router monitors hellos from the active router and it will take the active state when the current active router fails (no packets heard from active router) |
| Active | The router forwards packets that are sent to the HSRP group. The router also sends periodic hello messages |
Now let’s take an example of a router passing through these states. Suppose there are 2 routers A and B in the network; router A is turned on first. It enters the initial state. Then it moves to listen state in which it tries to hear if there are already active or standby routers for this group. After learning no one take the active or standby state, it determines to take part in the election by moving to speak state. Now it starts sending hello messages containing its priority. These messages are sent to the multicast address 224.0.0.2 (which can be heard by all members in that group). When it does not hear a hello message with a higher priority it assumes the role of active router and moves to active state. In this state, it continues sending out periodic hello messages.
Now router B is turned on. It also goes through initial and listen state. In listen state, it learns that router A has been already the active router and no other router is taking standby role so it enters speak state to compete for the standby router -> it promotes itself as standby router.
Now to our main question! We want router B to become active router so we set a higher priority number than the priority of A and ask router B to take over the role of active router (with the preempt command). Now router A will fall back to the speak state to compete for active or standby state -> it becomes standby router because its priority is now lower than that of router A. (Therefore answer B is correct).
Note: Suppose router A is in active state while router B is in standby state. If router B does not hear hello messages from router A within the holdtime, router B goes into speak state to announce its priority to all HSRP members and compete for the active state. But if at some time it receives a message from the active router that has a lower priority than its priority (because the administrator change the priority in either router), it can take over the active role by sending out a hello packet with parameters indicating it wants to take over the active router. This is called a coup hello message.
(Reference and good resource: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk648/tk362/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094a91.shtml)
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which protocol specified by RFC 2281 provides network redundancy for IP networks, ensuring that user traffic immediately and transparently recovers from first-hop failures in network edge devices or access circuits?
A. ICMP
B. IRDP
C. HSRP
D. STP
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
HSRP is a Cisco-proprietary protocol developed to allow several routers or multilayer switches to appear as a single gateway IP address. This protocol is described in RFC 2281.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option is the benefit of implementing an intelligent DNS for a cloud computing solution?
A. It reduces the need for a backup data center.
B. It can redirect user requests to locations that are using fewer network resources.
C. It enables the ISP to maintain DNS records automatically.
D. It eliminates the need for a GSS.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The Domain Name System (DNS) is used to resolve human-readable domain names like www.microsoft.com into machine-readable IP addresses like 104.43.195.251. DNS also provides other information about domain names, such as mail services.
Suppose Microsoft has some data centers located at different locations. For example one in USA and one in Canada. With normal DNS, only the data center in USA is chosen as the “active” server and the DNS server will return the IP address of the data center in USA when being asked.
With the use of intelligent DNS, the DNS server may return the IP addresses of the data center in USA or in Canada, depends on some rules (user’s geographical location, data center’s available resources…). Thus intelligent DNS helps share the load among the data centers -> Answer B is correct.
The Global Site Selector (GSS) is a crucial component of any data center architecture that requires a secure site-to-site global load balancing. The GSS allows businesses to deploy global Internet and intranet applications with the confidence that all application users will be quickly rerouted to a standby data center during a primary data center outage or overload.
Therefore GSS works in the same way as intelligent DNS but we are not sure about the answer “it eliminates the need for a GSS”. Maybe GSS can cooperate with intelligent DNS for better performance.
Note: The traffic flow itself (between the client and the server) never traverses the GSS or intelligent DNS. The GSS/DNS simply tells the client which server to target by resolving a name to an IP address.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about QoS default behavior is true?
A. Ports are untrusted by default.
B. VoIP traffic is passed without being tagged.
C. Video traffic is passed with a well-known DSCP value of 46.
D. Packets are classified internally with an environment.
E. Packets that arrive with a tag are untagged at the edge of an administrative domain.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
By default, all ports are in the untrusted state when QoS is enabled.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-6000-series-switches/24055-173.html
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option describes the purpose of traffic policing?
A. It prioritizes routing protocol traffic.
B. It remarks traffic that is below the CIR
C. It drops traffic that exceeds the CIR.
D. It queues and then transmits traffic that exceeds the CIR.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
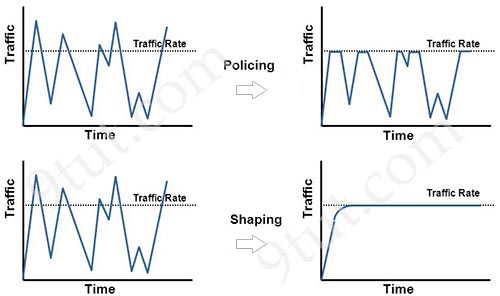
The following diagram illustrates the key difference between traffic policing and traffic shaping. Traffic policing propagates bursts. When the traffic rate reaches the configured maximum rate (or committed information rate), excess traffic is dropped (or remarked). The result is an output rate that appears as a saw-tooth with crests and troughs. In contrast to policing, traffic shaping retains excess packets in a queue and then schedules the excess for later transmission over increments of time. The result of traffic shaping is a smoothed packet output rate.
Note: Committed information rate (CIR): The minimum guaranteed data transfer rate agreed to by the routing device.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option is a benefit of switch stacking?
A. It provides redundancy with no impact on resource usage.
B. It simplifies adding and removing hosts.
C. It supports better performance of high-needs applications.
D. It provides higher port density with better resource usage.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Switch stacking technology allows the network engineer to make that stack of physical switches act like one switch. The stacking cables together make a ring between the switches. That is, the switches connect in series, with the last switch connecting again to the first.
Answer B is not correct as switch stacking is about connecting switches together so that they act as one switch, not about adding and removing hosts.
Answer C is not correct because switch stacking has nothing to do with performance of high-needs applications.
Surely switch stacking provides redundancy as stacking creates a ring of connection with two opposite paths. Whenever a frame is ready for transmission onto the path, a calculation is made to see which path has the most available bandwidth. The entire frame is then copied onto this half of the path.
With switch stacking, STP, CDP and VTP would run on one switch, not multiple switches. Also there would be one MAC address table, and it would reference all ports on all physical switches so we may say switch stacking has better resource usage. Also if we consider all stacking switches as one logical switch then surely the port density is increase very much. Therefore answer D is the most suitable one.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]If host Z needs to send data through router R1 to a storage server, which destination MAC address does host Z use to transmit packets?
A. the host Z MAC address
B. the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to the storage server
C. the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to host Z
D. the MAC address of the storage server interface
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Host Z will use ARP to get the MAC address of the interface on R1 that connects to it and use this MAC as the destination MAC address. It use the IP address of the storage server as the destination IP address.
For example in the topology below, host A will use the MAC address of E0 interface of the router as its destination MAC address to reach the Email Server.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. RTA is configured with a basic configuration. The link between the two routers is operational and no routing protocols are configured on either router. The line shown in the exhibit is then added to router RTA. Should interface Fa0/0 on router RTB shut down, what effect will the shutdown have on router RTA?
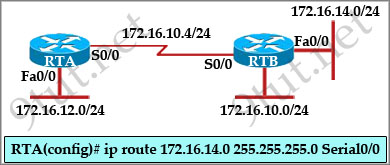
A. A route to 172.16.14.0/24 will remain in the RTA routing table.
B. A packet to host 172.16.14.225 will be dropped by router RTA
C. Router RTA will send an ICMP packet to attempt to verify the route.
D. Because router RTB will send a poison reverse packet to router RTA, RTA will remove the route.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Static routes remain in the routing table even if the specified gateway becomes unavailable. If the specified gateway becomes unavailable, you need to remove the static route from the routing table manually. However, static routes are removed from the routing table if the specified interface goes down, and are reinstated when the interface comes back up.
Therefore the static route will only be removed from the routing table if the S0/0 interface on RTA is shutdown.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/asa84/configuration/guide/route_static.html)
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]A router is running three routing processes: RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP, each configured with default characteristics. Each process learns a route to the same remote network.
If there are no static routes to the destination and none of the routes were redistributed, which route will be placed in the IP routing table?
A. the route learned through EIGRP
B. the route learned through OSPF
C. the route learned through RIP
D. the route with the lowest metric
E. all three routes with the router load balancing
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which parameter would you tune to affect the selection of a static route as a backup, when a dynamic protocol is also being used?
A. hop count
B. administrative distance
C. link bandwidth
D. link delay
E. link cost
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
By default a static route has the Administrative Distance (AD) of 1, which is always preferred to dynamic routing protocols. In some cases we may want to use dynamic routing protocols and set static routes as a backup route when the “dynamic” routes fail -> we can increase the AD of that static route to a higher value than the AD of the dynamic routing protocols.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]A router receives information about network 192.168.10.0/24 from multiple sources. What will the router consider the most reliable information about the path to that network?
A. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
B. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24
C. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
D. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
E. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
F. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
Answer: E[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement is true, as relates to classful or classless routing?
A. RIPV1 and OSPF are classless routing protocols.
B. Classful routing protocols send the subnet mask in routing updates.
C. Automatic summarization at classful boundaries can cause problems on discontigous networks.
D. EIGRP and OSPF are classful routing protocols and summarize routes by default.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Discontiguous networks are networks that have subnets of a major network separated by a different major network. Below is an example of discontiguous networks where subnets 10.10.1.0/24 and 10.10.2.0/24 are separated by a 2.0.0.0/8 network.
If we configure automatic summarization at classful boundaries, users on network 10.10.1.0/24 cannot communicate with users on network 10.10.2.0/24.
If you are not clear about automatic summarization please read the last part of this tutorial: http://www.9tut.com/eigrp-routing-protocol-tutorial.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two are advantages of static routing when compared to dynamic routing? (Choose two)
A. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing tables.
B. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
C. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
D. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
E. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
F. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables using automatic updates.
G. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
Answer: A E[/am4show]
Explanation
Static routing can only be configured for each route manually so it is more secure than dynamic routing which only needs to declare which networks to run -> A is correct.
Also static route does not use any complex algorithm to find out the best path so no routing updates need to be sent out -> reduce routing traffic load. Static routing is useful especially in stub network links.
Note: Stub network (or stub router) is used to describe a network (or router) that does not have any information about other networks except a default route. This type of network (or router) usually has only one connection to the outside.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]A technician pastes the configurations in the exhibit into the two new routers shown. Otherwise, the routers are configured with their default configurations. A ping from Host1 to Host2 fails, but the technician is able to ping the S0/0 interface of R2 from Host1. The configurations of the hosts have been verified as correct. What is the cause of the problem?
A. The serial cable on R1 needs to be replaced.
B. The interfaces on R2 are not configured properly.
C. R1 has no route to the 192.168.1.128 network.
D. The IP addressing scheme has overlapping subnetworks.
E. The ip subnet-zero command must be configured on both routers.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Host1 can ping the Serial interface of R2 because R1 has the network of 192.168.1.4/30 as directly connected route. But R1 does not know how to route to the network of Host2 (192.168.1.128/26) so R1 will drop that ping without trying to send it out S0/0 interface. To make the ping work, we have to configure a route pointing to that network (for example: ip route 192.168.1.128 255.255.255.192 s0/0 on R1).
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]How does a router handle an incoming packet whose destination network is missing from the Routing table?
A. It discards the packet.
B. It broadcasts the packet to each network on the router.
C. It routes the packet to the default route.
D. It broadcasts the packet to each interface on the router.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two drawbacks of implementing a link-state routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. the sequencing and acknowledgment of link-state packets
B. the requirement for a hierarchical IP addressing scheme for optimal functionality
C. the high volume of link-state advertisements in a converged network
D. the high demand on router resources to run the link-state routing algorithm
E. the large size of the topology table listing all advertised routes in the converged network
Answer: B D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit, Host A pings interface S0/0 on router 3, what is the TTL value for that ping?
A. 253
B. 252
C. 255
D. 254
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
From the CCNA ICND2 Exam book: “Routers decrement the TTL by 1 every time they forward a packet; if a router decrements the TTL to 0, it throws away the packet. This prevents packets from rotating forever.” I want to make it clear that before the router forwards a packet, the TTL is still remain the same. For example in the topology above, pings to S0/1 and S0/0 of Router 2 have the same TTL.
The picture below shows TTL values for each interface of each router and for Host B. Notice that Host A initializes ICMP packet with a TTL of 255:
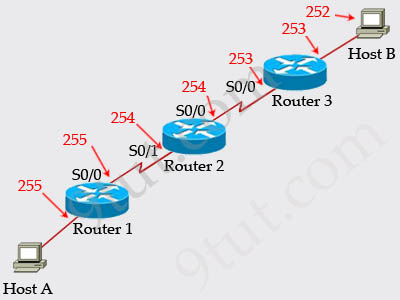
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two drawbacks of implementing a link-state routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. the sequencing and acknowledgment of link-state packets
B. the requirement for a hierarchical IP addressing scheme for optimal functionality
C. the high volume of link-state advertisements in a converged network
D. the high demand on router resources to run the link-state routing algorithm
E. the large size of the topology table listing all advertised routes in the converged network
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements describe the process identifier that is used in the command to configure OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
Router(config)# router ospf 1
A. All OSPF routers in an area must have the same process ID.
B. Only one process number can be used on the same router.
C. Different process identifiers can be used to run multiple OSPF processes
D. The process number can be any number from 1 to 65,535.
E. Hello packets are sent to each neighbor to determine the processor identifier.
Answer: C D[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are three characteristics of the OSPF routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. It converges quickly.
B. OSPF is a classful routing protocol.
C. It uses cost to determine the best route.
D. It uses the DUAL algorithm to determine the best route.
E. OSPF routers send the complete routing table to all directly attached routers.
F. OSPF routers discover neighbors before exchanging routing information.
Answer: A C F[/am4show]
Explanation
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol so it converges more quickly than distance-vector protocol. OSPF uses cost to determine the best route. The popular formula to calculate OSPF cost is: cost = 108 / Bandwidth [ in bps] (in fact the formal formula is: cost = reference bandwidth / configured bandwidth of interface in kbps. On Cisco routers, the reference bandwidth defaults to 100000 kbps)
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements about the OSPF Router ID are true? (Choose two)
A. It identifies the source of Type 1 LSA
B. It should be the same on all routers in an OSPF routing instance
C. By default, the lowest IP address on the router becomes the OSPF router ID
D. The router automatically chooses the IP address of a loopback as the OSPF Router ID
E. It is created using the MAC Address of the loopback interface
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output of the “show ip ospf database”:

We can see OSPF Router ID will be used as source of Type 1 LSA (1.1.1.1 & 2.2.2.2). Also the router will chose the highest loopback interface as its OSPF router ID (if available).
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two enhancements that OSPFv3 supports over OSPFv2? (Choose two)
A. It requires the use of ARP.
B. It can support multiple IPv6 subnets on a single link.
C. It supports up to 2 instances of OSPFv3 over a common link.
D. It routes over links rather than over networks.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
Unlike OSPFv2 which form adjacencies using their IPv4 interface addresses, OSPFv3 use the link-local addresses (FE80::/10) to form adjacencies. Therefore it can support multiple IPv6 subnets on a single link as an interface can have multiple IPv6 addresses (and two nodes can communicate with each other even if they do not share a common IP subnet.) -> B is correct.
IPv6 uses the term “link” instead of “subnet” or “network” to define a medium used to communicate between nodes at the link layer -> D is correct.
OSPFv3 can support more than 1 instance over a common link. For example you can run instance 1 on an interface with the command:
Router(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 100 area 0 instance 1
-> C is not correct.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]You enter the “show ipv6 route” command on an OSPF device and the device displays a route. Which conclusion can you draw about the environment?
A. OSPF is distributing IPv6 routes to BGP.
B. The router is designated as an ABR.
C. The router is designated as totally stubby.
D. OSPFv3 is in use.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The “show ipv6 route” displays the current contents of the IPv6 routing table. This device is running OSPF so we can deduce it is running OSPFv3 (OSPF for IPv6). An example of the “show ip v6 route” is shown below:

Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are OSPF default hello and dead timers? (Choose two)
A. The hello timer is 10 seconds.
B. The hello timer is 60 seconds.
C. The dead timer is 40 seconds.
D. The dead timer is 120 seconds.
E. The hello timer is 20 seconds.
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
By default, OSPF uses a 10-second hello timer and 40-second hold (dead) timer on broadcast and point-to-point links, and a 30-second hello timer and 120-second hold timer for all other network types.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Router edge-1 is unable to establish OSPF neighbor adjacency with router ISP-1. Which two configuration changes can you make on edge-1 to allow the two routers to establish adjacency? (Choose two)

A. Set the subnet mask on edge-1 to 255 255.255.252.
B. Reduce the MTU on edge-1 to 1514.
C. Set the OSPF cost on edge-1 to 1522.
D. Reduce the MTU on edge-1 to 1500.
E. Configure the ip ospf mtu-ignore command on the edge-1 Gi0/0 interface.
Answer: D E[/am4show]
Explanation
In order to become OSPF neighbor following values must be match on both routers:
+ Area ID
+ Authentication
+ Hello and Dead Intervals
+ Stub Flag
+ MTU Size
Therefore we need to adjust the MTU size on one of the router so that they are the same. Or we can tell OSPF to ignore the MTU size check with the command “ip ospf mtu-ignore”.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0? (Choose two)
A. Router(config)# router ospf 0
B. Router(config)# router ospf 1
C. Router(config)# router ospf area 0
D. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 0
E. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
F. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Explanation
In the router ospf command, the ranges from 1 to 65535 so o is an invalid number -> B is correct but A is not correct.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit.
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic. There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance.
As part of examining the router resources the OSPF DRs need to be known.
All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router.
Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two)
A. Corp-1
B. Corp-2
C. Corp-3
D. Corp-4
E. Branch-1
F. Branch-2
Answer: D F[/am4show]
Explanation
There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40) & Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The network is converged. After link-state advertisements are received from Router_A, what information will Router_E contain in its routing table for the subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96?
A. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, FastEthernet0/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
B. 208.149.23.64[110/1] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/3] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
C. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, FastEthernet0/0
D. 208.149.23.64[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:07, Serial1/0
208.149.23.96[110/13] via 190.173.23.10, 00:00:00:16, Serial1/0
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
Router_E learns two subnets subnets 208.149.23.64 and 208.149.23.96 via Router_A through FastEthernet interface. The interface cost is calculated with the formula 108 / Bandwidth. For FastEthernet it is 108 / 100 Mbps = 108 / 100,000,000 = 1. Therefore the cost is 12 (learned from Router_A) + 1 = 13 for both subnets -> B is not correct.
The cost through T1 link is much higher than through T3 link (T1 cost = 108 / 1.544 Mbps = 64; T3 cost = 108 / 45 Mbps = 2) so surely OSPF will choose the path through T3 link -> Router_E will choose the path from Router_A through FastEthernet0/0, not Serial1/0 -> C & D are not correct.
In fact, we can quickly eliminate answers B, C and D because they contain at least one subnet learned from Serial1/0 -> they are surely incorrect.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What OSPF command, when configured, will include all interfaces into area 0?
A. network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0
B. network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
C. network 255.255.255.255 0.0.0.0 area 0
D. network all-interfaces area 0
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The ‘network … area …’ command under OSPF process has the following meaning: It searches all the active interfaces, if the IP address of that interface belong to the ‘network …’ configured under OSPF process then the router will run OSPF on that interface. Therefore when we configure ‘network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0’ command, all interfaces are matched -> OSPF is enabled on all active interfaces on the router.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two benefits of using a single OSPF area network design? (Choose two)
A. It is less CPU intensive for routers in the single area.
B. It reduces the types of LSAs that are generated.
C. It removes the need for virtual links.
D. It increases LSA response times.
E. It reduces the number of required OSPF neighbor adjacencies.
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]What can cause two OSPF neighbors to be stuck in the EXSTART state?
A. There is a low bandwidth connection between neighbors.
B. The neighbors have different MTU settings.
C. The OSPF interfaces are in a passive state.
D. There is only layer one connectivity between neighbors.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which parameter or parameters are used to calculate OSPF cost in Cisco routers?
A. Bandwidth, Delay and MTU
B. Bandwidth
C. Bandwidth and MTU
D. Bandwidth, MTU, Reliability, Delay and Load
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The well-known formula to calculate OSPF cost is
Cost = 108 / Bandwidth
so B is the correct answer.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router?
A. 16
B. 2
C. unlimited
D. 4
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The default number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router is 4. We can change this default value by using “maximum-paths” command:
Router(config-router)#maximum-paths 2
Note: Cisco routers support up to 16 equal-cost paths
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
Link-state protocol uses hello packets to discover neighbors and establish adjacencies. After that, the routers begin sending out LSAs to every neighbor (each received LSA is copied and forwarded to every neighbor except the one that sent the LSA)
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit.

If the router Cisco returns the given output and has not had its router ID set manually, what value will OSPF use as its router ID?
A. 192.168.1.1
B. 172.16.1.1
C. 1.1.1.1
D. 2.2.2.2
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
A. 90
B. 100
C. 110
D. 120
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The Administrative Distances (AD) of popular routing protocols are listed below:
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]When a router undergoes the exchange protocol within OSPF, in what order does it pass through each state?
A. exstart state > loading state > exchange state > full state
B. exstart state > exchange state > loading state > full state
C. exstart state > full state > loading state > exchange state
D. loading state > exchange state > full state > exstart state
Answer: B[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The network associate is configuring OSPF on the Core router. All the connections to the branches should be participating in OSPF. The link to the ISP should NOT participate in OSPF and should only be advertised as the default route. What set of commands will properly configure the Core router?
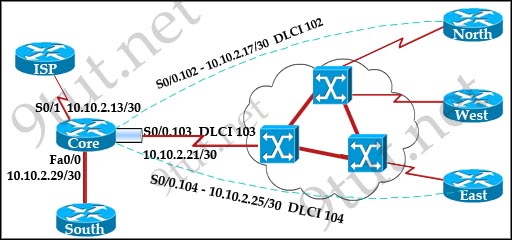
A. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
B. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.10.2.13 0.0.0.242 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
C. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
D. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.10.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The question states that the link to ISP should not participate in OSPF -> answers A, B are not correct.
In answer D, the “network 10.10.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0” does not cover the IP address of S0/0.103 (10.10.2.21) -> D is not correct.
The default-information originate command advertises a default route to other routers, telling something like “please send me your unknown traffic”. So in this case, besides a full routing table, other routers will also receive a default route from Core router.
But please notice that Core router needs to have a default route in its routing table. That is why the command “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14” is added to Core router. By adding the “always” (after “default-information originate” command) the default route will be advertised even if there is no default route in the routing table of router Core.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
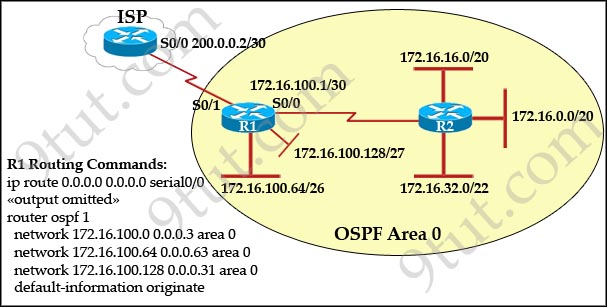
Assume that all of the router interfaces are operational and configured correctly. How will router R2 be affected by the configuration of R1 that is shown in the exhibit?
A. Router R2 will not form a neighbor relationship with R1.
B. Router R2 will obtain a full routing table, including a default route, from R1.
C. R2 will obtain OSPF updates from R1, but will not obtain a default route from R1.
D. R2 will not have a route for the directly connected serial network, but all other directly connected networks will be present, as well as the two networks connected to R1.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The default-information originate command advertises a default route to other routers, telling something like “please send me your unknown traffic”. So in this case, besides a full routing table, R2 will also receive a default route from R1 -> B is correct.
Note: But in this question, the static route should be “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/1″ (not serial0/0), that may cause a routing loop.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true about the loopback address that is configured on RouterB? (Choose two)
A. It ensures that data will be forwarded by RouterB.
B. It provides stability for the OSPF process on RouterB.
C. It specifies that the router ID for RouterB should be 10.0.0.1.
D. It decreases the metric for routes that are advertised from RouterB.
E. It indicates that RouterB should be elected the DR for the LAN.
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
A loopback interface never comes down even if the link is broken so it provides stability for the OSPF process (for example we use that loopback interface as the router-id) -> B is correct.
The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
-> The loopback interface will be chosen as the router ID of RouterB -> C is correct.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit.
R1 routing commands:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0
router ospf 1
network 172.16.100.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 172.16.100.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
network 172.16.100.128 0.0.0.31 area 0
default-information originate
Assuming that all router interfaces are operational and correctly configured, that OSPF has been correctly configured on router R2, how will the default route configured on R1 affect the operation of R2?
A. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R1 will be dropped.
B. Any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in the routing table of router R2 will be directed to R1. R1 will then send that packet back to R2 and a routing loop will occur.
C. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately.
D. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately because of the lack of a gateway on R1.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
First, notice that the more-specific routes will always be favored over less-specific routes regardless of the administrative distance set for a protocol. In this case, because we use OSPF for three networks (172.16.100.0 0.0.0.3, 172.16.100.64 0.0.0.63, 172.16.100.128 0.0.0.31) so the packets destined for these networks will not be affected by the default route.
The default route configured on R1 “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0″ will send any packet whose destination network is not referenced in the routing table of router R1 to R2, it doesn’t drop anything so answers A, B and C are not correct. D is not correct too because these routes are declared in R1 and the question says that “OSPF has been correctly configured on router R2″, so network directly connected to router R2 can communicate with those three subnetworks.
As said above, the default route configured on R1 will send any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in its routing table to R2; R2 in turn sends it to R1 because it is the only way and a routing loop will occur.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]RouterD# show ip interface brief

Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this router?
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.3
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command is used to display the collection of OSPF link states?
A. show ip ospf link-state
B. show ip ospf lsa database
C. show ip ospf neighbors
D. show ip ospf database
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The output of the “show ip ospf database” is shown below:
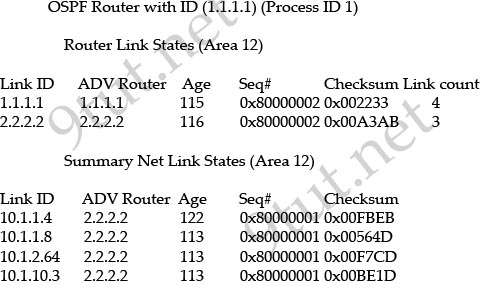
From the output above we can see LSA Type 1 (Router Link State) and LSA Type 3 (Summary Net Link State).
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement describes the process ID that is used to run OSPF on a router?
A. It is globally significant and is used to represent the AS number.
B. It is locally significant and is used to identify an instance of the OSPF database.
C. It is globally significant and is used to identify OSPF stub areas.
D. It is locally significant and must be the same throughout an area.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit.
A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF.
Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three)
A. FastEthernet0/0
B. FastEthernet0/1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: B C D[/am4show]
Explanation
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63″ equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.168.12.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF -> B C D are correct.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default values for hello and dead packets in OSPF?
A. hello 10
B. hello 60
C. dead 40
D. dead 120
Answer: A C[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which configuration enables OSPF for network 192.168.1.0/24?
A. router ospf
router-id 192.168.1.0
B. router ospf 1
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
C. router ospf 1
neighbor 192.168.1.0
D. router ospf 1
area 0 virtual-link 192.168.1.0
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which purpose of the network command in OSPF configuration mode is true?
A. It defines a wildcard mask to identify the size of the network.
B. It defines the area ID.
C. It defines the network by its classful entry.
D. It defines which networks are used for virtual links.
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which EIGRP for IPv6 command can you enter to view the link-local addresses of the neighbors of a device?
A. show ipv6 eigrp 20 interfaces
B. show ipv6 route eigrp
C. show ipv6 eigrp neighbors
D. show ip eigrp traffic
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The “show ipv6 eigrp neighbors” command displays the neighbors discovered by the EIGRPv6. Notice that the neighbors are displayed by their link-local addresses.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Based on the exhibited routing table, how will packets from a host within the 192.168.10.192/26 LAN be forwarded to 192.168.10.1?
A. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1
B. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1
C. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1 to R2
D. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1 AND from R3 to R1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
From the routing table we learn that network 192.168.10.0/30 is learned via 2 equal-cost paths (192.168.10.9 &192.168.10.5) -> traffic to this network will be load-balancing.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option describes a difference between EIGRP for IPv4 and IPv6?
A. Only EIGRP for IPv6 advertises all connected networks.
B. Only EIGRP for IPv6 requires a router ID to be configured under the routing process
C. AS numbers are configured in EIGRP but not in EIGRPv3.
D. Only EIGRP for IPv6 is enabled in the global configuration mode.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
To configure EIGRP for IPv6 we must explicitly specify a router ID before it can start running. For example:
| ipv6 router eigrp 1 eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 no shutdown |
Notice that EIGRP for IPv6 router-id must be an IPv4 address. EIGRP for IPv4 can automatically pick-up an IPv4 to use as its EIGRP router-id with this rule:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback interface is selected as the router ID.
+ If there are not any loopback addresses configured, the highest IP address assigned to any other active interface is chosen as the router ID
EIGRPv3 also uses the AS number (for example: ipv6 eigrp 1 under interface mode).
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. If the router R1 returns the given output and has not had its router ID set manually, what address will EIGRP use as its router ID?

A. 192.168.1.2
B. 172.16.4.1
C. 192.168.10.2
D. 1.1.1.1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]When running EIGRP what is required for RouterA to exchange routing updates with RouterC?
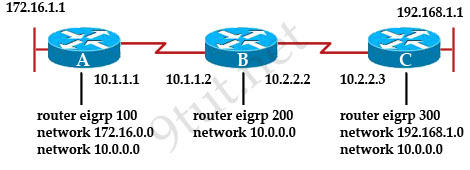
A. AS numbers must be changed to match on all the routers.
B. Loopback interface must be configured so a DR is elected.
C. The no auto-summary command is needed on Router A and Router C.
D. Router B needs to have two network statements, one for each connected network.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
We notice that 3 routers are using different AS numbers so they do not become neighbors and cannot exchange their routing updates. We need to choose only one AS number and use it on all 3 routers to make them exchange routing updates.
In this case we don’t need to use the “no auto-summary” command because network 10.0.0.0 is not separated by another major network.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. A packet with a source IP address of 192.168.2.4 and a destination IP address of 10.1.1.4 arrives at the HokesB router. What action does the router take?
A. forwards the received packet out the Serial0/0 interface
B. forwards a packet containing an EIGRP advertisement out the Serial0/1 interface
C. forwards a packet containing an ICMP message out the FastEthemet0/0 interface
D. forwards a packet containing an ARP request out the FastEthemet0/1 interface
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
When a packet with destination IP address of 10.1.1.4 arrives at HokesB, it will look up in the routing table to find the most specific path. In this case no path is found so HokesB must inform to the source host that the destination is unreachable on the interface it has received this packet (it is Fa0/0 because the network 192.168.2.0/28 is learned from this interface). So the best answer here should be C – send an ICMP message out of Fa0/0.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Given the output from the show ip eigrp topology command, which router is the feasible successor?
|
Router# show ip eigrp topology 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.255 IP-EIGRP topology entry for 10.0.0.5/32 State is Passive, Query origin flag is 1, 1 Successor(s), FD is 41152000 |
A.
10.1.0.3 (Serial0), from 10.1.0.3, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (46866176/46354176), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 56 Kbit
Total delay is 45000 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 2
B.
10.0.0.2 (Serial0.1), from 10.0.0.2, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (53973248/128256), Route is Internal
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 48 Kbit
Total delay is 25000 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 1
C.
10.1.0.1 (Serial0), from 10.1.0.1, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (46152000/41640000), Route is Internal Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 64 Kbit
Total delay is 45000 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 2
D.
10.1.1.1 (SerialO.1), from 10.1.1.1, Send flag is 0x0
Composite metric is (46763776/46251776), Route is External
Vector metric:
Minimum bandwidth is 56 Kbit
Total delay is 41000 microseconds
Reliability is 255/255
Load is 1/255
Minimum MTU is 1500
Hop count is 2
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
First we must notice that all the 4 answers are parts of the “show ip eigrp topology” output. As you can see, there are 2 parameters in the form of [FD/AD] in each answer. For example answer C has [46152000/41640000], it means that the FD of that route is 46152000 while the AD is 41640000.
To become a feasible successor, a router must meet the feasibility condition:
“To qualify as a feasible successor, a router must have an AD less than the FD of the current successor route“
In four answer above, only answer B has an AD of 128256 and it is smaller than the FD of the current successor route (41152000) so it is the feasible successor -> B is correct.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which type of EIGRP route entry describes a feasible successor?
A. a backup route, stored in the routing table
B. a primary route, stored in the routing table
C. a backup route, stored in the topology table
D. a primary route, stored in the topology table
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Feasible successor is a route whose Advertised Distance is less than the Feasible Distance of the current best path. A feasible successor is a backup route, which is not stored in the routing table but stored in the topology table.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are the two default metrics used by EIGRP for route selection? (Choose two)
A. Bandwidth
B. Delay
C. Reliability
D. Load
E. MTU
Answer: A B[/am4show]
Explanation
The formula to caculate EIGRP metric is:
metric = [K1 * bandwidth + (K2 * bandwidth)/(256 – load) + K3 * delay] * [K5/(reliability + K4)]
By default, K1 = 1, K2 = 0, K3 = 1, K4 = 0, K5 = 0 which means that the default values use only bandwidth & delay parameters while others are ignored. The metric formula is now reduced to:
metric = bandwidth + delay
Note: But remember the bandwidth here is defined as the slowest bandwidth in the route to the destination & delay is the sum of the delays of each link.
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit.
Which three EIGRP routes will be present in the router R4’s routing table? (Choose three)
A. 172.16.1.0/24
B. 10.1.10.0/30
C. 10.0.0.0/8
D. 10.1.11.0/30
E. 172.16.0.0/16
F. 192.168.1.0/24
Answer: C E F[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]What does a router do if it has no EIGRP feasible successor route to a destination network and the successor route to that destination network is in active status?
A. It routes all traffic that is addressed to the destination network to the interface indicated in the routing table.
B. It sends a copy of its neighbor table to all adjacent routers.
C. It sends a multicast query packet to all adjacent neighbors requesting available routing paths to the destination network.
D. It broadcasts Hello packets to all routers in the network to re-establish neighbor adjacencies.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
When a router has no EIGRP feasible successor and the successor route to that destination network is in active status (the successor route is down, for example) a route recomputation occurs. A route recomputation commences with a router sending a query packet to all neighbors. Neighboring routers can either reply if they have feasible successors for the destination or optionally return a query indicating that they are performing a route recomputation. While in Active state, a router cannot change the next-hop neighbor it is using to forward packets. Once all replies are received for a given query, the destination can transition to Passive state and a new successor can be selected.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f07.shtml#rout_states)
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement describes an EIGRP feasible successor route?
A. A primary route, added to the routing table
B. A backup route, added to the routing table
C. A primary route, added to the topology table
D. A backup route, added to the topology table
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. How will the router handle a packet destined for 192.0.2.156?

A. The router will drop the packet.
B. The router will return the packet to its source.
C. The router will forward the packet via Serial2.
D. The router will forward the packet via either Serial0 or Serial1.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output we see a line “Gateway of last resort is 192.168.4.1 to network 0.0.0.0”. Gateway of last resort refers to the next-hop router of a router’s current default route. Therefore all the traffic through this router to destination networks not matching any other networks or subnets in the routing table will be sent to 192.168.4.1 (which is on Serial2) -> packet destined for 192.0.2.156 (or an unknown destination) will be forwarded via Serial2.
An weird thing in the output above is the missing of the asterisk mask (*) which represents for the candidate default route. To set the “Gateway of last resort is 192.168.4.1 to network 0.0.0.0” as the output above we can use these commands:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.4.1
ip default-network 192.168.4.0
But these commands will create an static routing in the routing table with an asterisk mask. Maybe the output shown above is missing that route.
For more information about the command ip default-network please visit: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094374.shtml.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. From RouterA, a network administrator is able to ping the serial interface of RouterB but unable to ping any of the subnets attached to RouterB. Based on the partial outputs in the exhibit, what could be the problem?
A. EIGRP does not support VLSM.
B. The EIGRP network statements are incorrectly configured.
C. The IP addressing on the serial interface of RouterA is incorrect.
D. The routing protocol has summarized on the classful boundary.
E. EIGRP has been configured with an invalid autonomous system number.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output of “show ip route” command on RouterB, we learn that RouterB does not learn any networks in RouterA. Also the “172.16.0.0/26 is a summary, 00:00:03, Null0” line tells us this netwok is summarized.
Note: EIGRP performs auto-summarization each time it crosses a border between two major networks. For example, RouterA has networks of 172.16.x.x. It will perform auto-summarization when sending over network 10.1.1.0/30, which is in different major network (172.16.0.0/16 and 10.0.0.0/8 are called major networks in this case).
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The Lakeside Company has the internetwork in the exhibit. The Administrator would like to reduce the size of the routing table to the Central Router. Which partial routing table entry in the Central router represents a route summary that represents the LANs in Phoenix but no additional subnets?
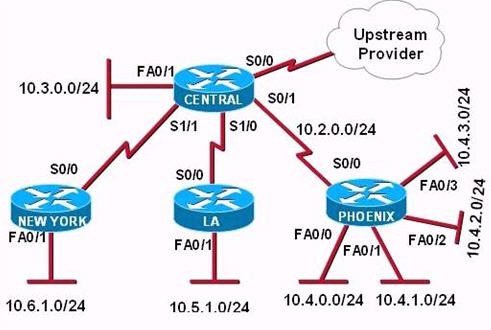
A – 10.0.0.0 /22 is subnetted, 1 subnet
D 10.0.0.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2 6w0d, serial 0/1
B – 10.0.0.0 /28 is subnetted, 1 subnet
D 10.2.0.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2 6w0d, serial 0/1
C – 10.0.0.0 /30 is subnetted, 1 subnet
D 10.2.2.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2 6w0d, serial 0/1
D – 10.0.0.0 /22 is subnetted, 1 subnet
D 10.4.0.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2 6w0d, serial 0/1
E – 10.0.0.0 /28 is subnetted, 1 subnet
D 10.4.4.0 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2 6w0d, serial 0/1
F – 10.0.0.0 /30 is subnetted, 1 subnet
D 10.4.4.4 [90/20514560] via 10.2.0.2 6w0d, serial 0/1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
All the above networks can be summarized to 10.0.0.0 network but the question requires to “represent the LANs in Phoenix but no additional subnets” so we must summarized to 10.4.0.0 network. The Phoenix router has 4 subnets so we need to “move left” 2 bits of “/24”-> /22 is the best choice -> D is correct.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]The company uses EIGRP as the routing protocol.
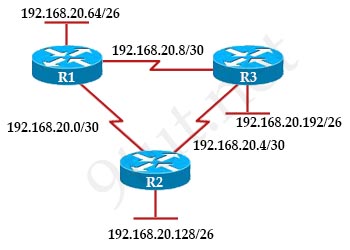
R3# show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192 168.20.0/24 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.20.64/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.20.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
D 192.168.20.0/30 [90/2681856] via 192.168.20.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
C 192.168.20.4/30 is directly connected, Serial 0/1
C 192.168.20.8/30 is directly connected, Serial 0/0
C 192.168.20.192/26 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.20.128/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.20.5,00:03 31, Serial 0/1
What path will packets take from a host on 192.168.20.192/26 network to a host on the LAN attached to router R1?
A. The path of the packets will be R3 to R2 to R1.
B. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1 to R2.
C. The path of the packets will be both R3 to R2 to R1 and R3 to R1.
D. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
From the line “D 192.168.20.64/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.20.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0″ we can see the IP address 192.168.20.9 belongs to network 192.168.20.8/30 and this network is between R1 and R3 -> Packet from 192.168.20.192/26 network destined to a host on the LAN attached to router R1 will go directly from R3 to R1.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statements are true about EIGRP successor routes? (Choose two)
A. A successor route is used by EIGRP to forward traffic to a destination.
B. Successor routes are saved in the topology table to be used if the primary route fails.
C. Successor routes are flagged as “active” in the routing table.
D. A successor route may be backed up by a feasible successor route.
E. Successor routes are stored in the neighbor table following the discovery process.
Answer: A D[am4show have=’p2;’]
Explanation
C is not correct because successor routes are not flagged as “active”, they are always the best route to reach remote networks and are always used to send packets.
A and D are correct because successor route is the best and primary route to a remote network. It is stored in the routing table and topology table. If this route fails, a backup route (called feasible successor route) in the topology table will be used to route traffic to a destination.
E is not correct because neighbor table only contains a list of directly connected EIGRP routers that have an adjacency with this router, it doesn’t contain successor routes.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]What address is a feasible successor?
A. 172.16.4.0
B. 10.1.4.4
C. 10.1.2.2
D. 172.16.3.0
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency. The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked.
What command will display the required information?
A. Router# show ip eigrp topology
B. Router# show ip eigrp interfaces
C. Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
D. Router# show ip eigrp neighbors
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Below is an example of the “show ip eigrp neighbors” command (from 9tut.com)
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which routing protocols are compatible with stubs? (Choose two)
A. OSPF
B. EIGRP
C. EGP
D. BGP
E. IS-IS
F. RIP
Answer: A B[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three checks must you perform when troubleshooting EIGRPv6 adjacencies? (Choose three)
A. Verify that IPv6 is enabled.
B. Verify that the network command has been configured.
C. Verify that auto summary is enabled.
D. Verify that the interface is up.
E. Verify that an IPv4 address has been configured.
F. Verify that the router ID has been configured.
Answer: A D F[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command do you enter to view EIGRPv6 adjacencies?
A. show ipv6 eigrp 1 interface
B. show ipv6 route eigrp
C. show ipv6 eigrp neighbors
D. show running-configuration eigrp
Answer: C[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two components are used to identify a neighbor in a BGP configuration? (Choose two)
A. autonomous system number
B. version number
C. router ID
D. subnet mask
E. IP address
Answer: A E[/am4show]
Explanation
This is an example of how to configure BGP neighbor between two routers (suppose all interfaces are configured correctly)

| R1(config)#router bgp 1 R1(config-router)#neighbor 11.0.0.2 remote-as 2 |
R2(config)#router bgp 2 R2(config-router)#neighbor 11.0.0.1 remote-as 1 |
So as you see, we need the neighbor’s IP address and neighbor’s AS number for the BGP neighbor relationship.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about the IP SLAs ICMP Echo operation is true?
A. The frequency of the operation specified in milliseconds.
B. It is used to identify the best source interface from which to send traffic.
C. It is configured in enable mode.
D. It is used to determine the frequency of ICMP packets.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The ICMP Echo operation measures end-to-end response time between a Cisco router and any devices using IP. Response time is computed by measuring the time taken between sending an ICMP Echo request message to the destination and receiving an ICMP Echo reply. Many customers use IP SLAs ICMP-based operations, in-house ping testing, or ping-based dedicated probes for response time measurements.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about the IP SLAs ICMP Echo operation is true?
A. It is configured in enable mode.
B. It is used to determine the one-way delay between devices
C. It is used to identify the best source interface from which to send traffic to a destination.
D. The frequency of the operation is specified in milliseconds.
Answer: B[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which protocol authenticates connected devices before allowing them to access the LAN?
A. 802.1d
B. 802.11
C. 802.1w
D. 802.1x
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
802.1x is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control (PNAC). It is part of the IEEE 802.1 group of networking protocols. It provides an authentication mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is a difference between TACACS+ and RADIUS in AAA?
A. Only TACACS+ allows for separate authentication.
B. Only RADIUS encrypts the entire access-request packet.
C. Only RADIUS uses TCP.
D. Only TACACS+ couples authentication and authorization.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
TACACS+ is an AAA protocol developed by Cisco. TACACS+ separates the authentication, authorization, and accounting steps. This architecture allows for separate authentication solutions while still using TACACS+ for authorization and accounting. For example, it is possible to use the Kerberos Protocol for authentication and TACACS+ for authorization and accounting. After an AAA client passes authentication through a Kerberos server, the AAA client requests authorization information from a TACACS+ server without the necessity to re-authenticate the AAA client by using the TACACS+ authentication mechanism.
Authentication and authorization are not separated in a RADIUS transaction. When the authentication request is sent to a AAA server, the AAA client expects to have the authorization result sent back in reply.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]What can be done to secure the virtual terminal interfaces on a router? (Choose two)
A. Administratively shut down the interface.
B. Physically secure the interface.
C. Create an access list and apply it to the virtual terminal interfaces with the access-group command.
D. Configure a virtual terminal password and login process.
E. Enter an access list and apply it to the virtual terminal interfaces using the access-class command.
Answer: D E[/am4show]
Explanation
It is a waste to administratively shut down the interface. Moreover, someone can still access the virtual terminal interfaces via other interfaces -> A is not correct.
We can not physically secure a virtual interface because it is “virtual” -> B is not correct.
To apply an access list to a virtual terminal interface we must use the “access-class” command. The “access-group” command is only used to apply an access list to a physical interface -> C is not correct; E is correct.
The most simple way to secure the virtual terminal interface is to configure a username & password to prevent unauthorized login -> D is correct.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which protocol is an open standard protocol framework that is commonly used in VPNs, to provide secure end-to-end communications?
A. RSA
B. L2TP
C. IPsec
D. PPTP
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
One of the most widely deployed network security technologies today is IPsec over VPNs. It provides high levels of security through encryption and authentication, protecting data from unauthorized access.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which IPsec security protocol should be used when confidentiality is required?
A. MD5
B. PSK
C. AH
D. ESP
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three options are types of Layer 2 network attack? (Choose three.)
A. ARP attacks
B. brute force attacks
C. spoofing attacks
D. DDOS attacks
E. VLAN hopping
F. botnet attacks
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option describes a drawback of proxy ARP?
A. It overwrites MAC addresses
B. It can make it more difficult for the administrator to locale device misconfigurations
C. It dynamically establishes layer 2 tunneling protocol which increase network overhead
D. If proxy ARP is configured on multiple devices , the internal L2 network may become vulnerable to DDOS
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]What type of attack is when trusted source replace MAC tables with untrusted?
A. DHCP snooping
B. port snooping
C.
D.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three response does TACAS+ give while querying..something like that. (Choose three)
A. error
B. accept
C. continue
D. persist
E. fault
Answer: A B C[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature can validate address requests and filter out invalid messages?
A. IP Source Guard
B. port security
C. DHCP snooping
D. dynamic ARP inspection
Answer: C[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]The following configuration is applied to a Layer 2 Switch:
interface fastethernet 0/4
switchport mode access
switchport port-security
switchport port-security mac-address 0000.1111.1111
switchport port-security maximum 2
What is the result of the above configuration being applied to the switch?
A. A host with a mac address of 0000.1111.1111 and up to two other hosts can connect to FastEthernet 0/4 simultaneously
B. A host with a mac address of 0000.1111.1111 and one other host can connect to FastEthernet 0/4 simultaneously
C. Violating addresses are dropped and no record of the violation is kept
D. The switch can send an SNMP message to the network management station
E. The port is effectively shutdown
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which of these correctly describes the results of port security violation of an unknown packet?
| Switch(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 3 Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky Switch(config-if)#end |
A. port enabled; unknown packets dropped; no SNMP or syslog messages
B. port enabled; unknown packets dropped; SNMP or syslog messages
C. port disabled; no SNMP or syslog messages
D. port disabled; SNMP or syslog messages
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The default violation mode is shutdown, which will shutdown the port when the maximum number of secure MAC addresses is exceeded. It also sends an SNMP trap, logs a syslog message, and increments the violation counter.
The three violation modes are listed below:
+protect – When the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the limit allowed on the port, packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until you remove a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses or increase the number of maximum allowable addresses. You are not notified that a security violation has occurred.
+restrict – When the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the limit allowed on the port, packets with unknown source addresses are dropped until you remove a sufficient number of secure MAC addresses or increase the number of maximum allowable addresses. In this mode, you are notified that a security violation has occurred. Specifically, an SNMP trap is sent, a syslog message is logged, and the violation counter increments.
+shutdown – In this mode, a port security violation causes the interface to immediately become error-disabled, and turns off the port LED. It also sends an SNMP trap, logs a syslog message, and increments the violation counter. When a secure port is in the error-disabled state, you can bring it out of this state by entering the errdisable recovery cause psecure-violation global configuration command, or you can manually re-enable it by entering the shutdown and no shutdown interface configuration commands. This is the default mode.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12.2SX/configuration/guide/port_sec.html)
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What three actions will the switch take when a frame with an unknown source MAC address arrives at the interface? (Select three)

A. Send an SNMP trap.
B. Send a syslog message.
C. Increment the Security Violation counter.
D. Forward the traffic.
E. Write the MAC address to the startup-config.
F. Shut down the port.
Answer: A B C[/am4show]
Explanation
Notice that the Violation Mode is Restrict. In this mod, when the number of port secure MAC addresses reaches the maximum limit allowed on the port, packets with unknown source addresses are dropped. You have to remove the secure mac-addresses below the maximum allowed number in order to learn a new MAC or allowing a host on the port. Also a SNMP trap is sent, a syslog message is logged in the syslog server and the violation counter increases.
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12.2SX/configuration/guide/port_sec.html)
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]A network administrator needs to configure port security on a switch. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
A. The network administrator can apply port security to dynamic access ports
B. The network administrator can configure static secure or sticky secure mac addresses in the voice vlan.
C. The sticky learning feature allows the addition of dynamically learned addresses to the running configuration.
D. The network administrator can apply port security to EtherChannels.
E. When dynamic mac address learning is enabled on an interface, the switch can learn new addresses up to the maximum defined.
Answer: C E[/am4show]
Explanation
Follow these guidelines when configuring port security:
+ Port security can only be configured on static access ports, trunk ports, or 802.1Q tunnel ports. -> A is not correct.
+ A secure port cannot be a dynamic access port.
+ A secure port cannot be a destination port for Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN).
+ A secure port cannot belong to a Fast EtherChannel or Gigabit EtherChannel port group. -> D is not correct
+ You cannot configure static secure or sticky secure MAC addresses on a voice VLAN. -> B is not correct.
+ When you enable port security on an interface that is also configured with a voice VLAN, you must set the maximum allowed secure addresses on the port to at least two.
+ If any type of port security is enabled on the access VLAN, dynamic port security is automatically enabled on the voice VLAN.
+ When a voice VLAN is configured on a secure port that is also configured as a sticky secure port, all addresses seen on the voice VLAN are learned as dynamic secure addresses, and all addresses seen on the access VLAN (to which the port belongs) are learned as sticky secure addresses.
+ The switch does not support port security aging of sticky secure MAC addresses.
+ The protect and restrict options cannot be simultaneously enabled on an interface.
Note: Dynamic access port or Dynamic port VLAN membership must be connected to an end station. This type of port can be configured with the “switchport access vlan dynamic” command in the interface configuration mode. Please read more about Dynamic access port here: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3550/software/release/12-1_19_ea1/configuration/guide/3550scg/swvlan.html#wp1103064
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The following commands are executed on interface fa0/1 of 2950Switch.
2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security
2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky
2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1
The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives on interface fa0/1. What two functions will occur when this frame is received by 2950Switch? (Choose two)
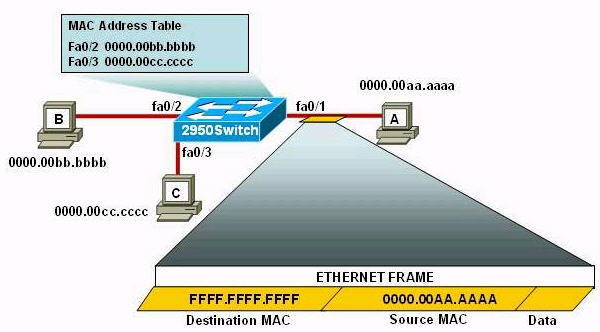
A. The MAC address table will now have an additional entry of fa0/1 FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
B. Only host A will be allowed to transmit frames on fa0/1.
C. This frame will be discarded when it is received by 2950Switch.
D. All frames arriving on 2950Switch with a destination of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be forwarded out fa0/1.
E. Hosts B and C may forward frames out fa0/1 but frames arriving from other switches will not be forwarded out fa0/1.
F. Only frames from source 0000.00bb.bbbb, the first learned MAC address of 2950Switch, will be forwarded out fa0/1.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Explanation
The first command 2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security is to enable the port-security in a switch port.
In the second command 2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky, we need to know the full syntax of this command is switchport port-security mac-address sticky [MAC]. The STICKY keyword is used to make the MAC address appear in the running configuration and you can save it for later use. If you do not specify any MAC addresses after the STICKY keyword, the switch will dynamically learn the attached MAC Address and place it into your running-configuration. In this case, the switch will dynamically learn the MAC address 0000.00aa.aaaa of host A and add this MAC address to the running configuration.
In the last command 2950Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1 you limited the number of secure MAC addresses to one and dynamically assigned it (because no MAC address is mentioned, the switch will get the MAC address of the attached MAC address to interface fa0/1), the workstation attached to that port is assured the full bandwidth of the port.Therefore only host A will be allowed to transmit frames on fa0/1 -> B is correct.
After you have set the maximum number of secure MAC addresses for interface fa0/1, the secure addresses are included in the “Secure MAC Address” table (this table is similar to the Mac Address Table but you can only view it with the show port-security address command). So in this question, although you don’t see the MAC address of host A listed in the MAC Address Table but frames with a destination of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be forwarded out of fa0/1 interface -> D is correct.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which version of SNMP first allowed user-based access?
A. SNMPv3 with RBAC
B. SNMPv3
C. SNMPv1
D. SNMPv2
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The user-based access control implemented by SNMPv3 is based on contexts and user names, rather than on IP addresses and community strings. It is a partial implementation of the view-based access control model (VACM).
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the first step you perform to configure an SNMPv3 user?
A. Configure server traps.
B. Configure the server group.
C. Configure the server host.
D. Configure the remote engine ID.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The first step we need to do when configuring an SNMPv3 user is to configure the server group to enable authentication for members of a specified named access list via the “snmp-server group” command. For example:
| Router(config)# snmp-server group MyGroup v3 auth access snmp_acl |
In this example, the SNMP server group MyGroup is configured to enable user authentication for members of the named access list snmp_acl.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature can you use to restrict SNMP queries to a specific OID tree?
A. a server group
B. a view record
C. a community
D. an access group
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the minimum command to turn on encryption on SNMP?
A. SNMPV3authpriv
B. SMNPV3authnopriv
C. SNMPV3noauthpriv
D. SMNPV2authnopriv
E. SNMPV2NOAUTHPRIV
F. SNMPV2AUTHNOPRIV
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature can you use to monitor traffic on a switch by replicating it to another port or ports on the same switch?
A. copy run start
B. traceroute
C. the ICMP Echo IP SLA
D. SPAN
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) is used to analyze network traffic passing through ports on a switch. For example we can configure the Switch to monitor its interface Fa0/0, which connects to the Core, by sending all traffic to/from Fa0/0 to its Fa0/1 interface. At Fa0/1 interface we connect to a computer and use such a software like Wireshark to capture the packets.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
If you configure syslog messages without specifying the logging trap level, which log messages will the router send?
A. error conditions only
B. warning and error conditions only
C. normal but significant conditions only
D. all levels except debugging
E. informational messages only
Answer: D
Explanation
Syslog levels are listed below
| Level | Keyword | Description |
| 0 | emergencies | System is unusable |
| 1 | alerts | Immediate action is needed |
| 2 | critical | Critical conditions exist |
| 3 | errors | Error conditions exist |
| 4 | warnings | Warning conditions exist |
| 5 | notification | Normal, but significant, conditions exist |
| 6 | informational | Informational messages |
| 7 | debugging | Debugging messages |
The highest level is level 0 (emergencies). The lowest level is level 7. By default, the router will send informational messages (level 6). That means it will send all the syslog messages from level 0 to 6.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two pieces of information are provided by the “show controllers serial 0” command? (Choose two)
A. the type of cable that is connected to the interface.
B. The uptime of the interface
C. the status of the physical layer of the interface
D. the full configuration of the interface
E. the interface’s duplex settings
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
Below is an example of the output of this command:
The “show controllers serial …” command tells us about the type of the cable (in the case V.35 DTE cable) and the status of the physical layer of the interface. In above output we learn that there is an cable attached on S0/0 interface. If no cable is found we will see the line “No DTE cable” instead.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the best way to verify that a host has a path to other hosts in different networks?
A. Ping the loopback address.
B. Ping the default gateway.
C. Ping the local interface address.
D. Ping the remote network.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]While you were troubleshooting a connection issue, a ping from one VLAN to another VLAN on the same switch failed. Which command verifies that IP routing is enabled on interfaces and the local VLANs are up?
A. show ip interface brief
B. show ip nat statistics
C. show ip statistics
D. show ip route
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The “show ip nat statistics” only gives us information about NAT translation. We cannot know if IP routing is enabled or the VLANs are up not not.
The “show ip statistics” command does not exist.
With the “show ip interface brief” we can see if the interface VLANs are up or not but cannot see if IP routing is enabled or not. So let’s see what information can be learned with the “show ip route” command.
By using the command “show ip route” we will learn if IP routing is enabled. If it is not enabled we will see this output:
After enabling ip routing (via the “ip routing” in global configuration mode) we can see all the interfaces. For example:
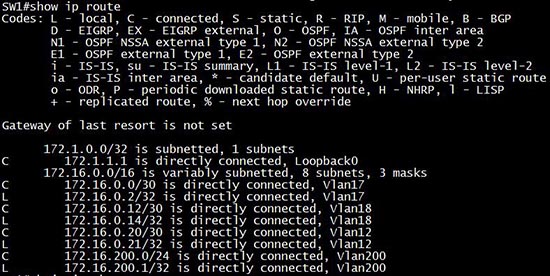
If we shut down an interface VLAN (Vlan18)
Sw1(config)#interface vlan 18
Sw1(config-if)#shutdown
then we will not see it in the routing table any more.
Therefore if the statement “local VLANs are up” means “the interface VLANs are up” then the “show ip route” is the best answer in this case.
Note: The IOS used to test is IOSv15.1
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command would you use on a Cisco router to verify the Layer 3 path to a host?
A. tracert address
B. traceroute address
C. telnet address
D. ssh address
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
To check the connectivity between a host and a destination (through some networks) we can use both “tracert” and “traceroute” commands. But the difference between these two commands is the “tracert” command can display a list of near-side router interfaces in the path between the source and the destination. The “traceroute” command has the same function of the “tracert” command but it is used on Cisco routers only, not on a PC -> B is correct.
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]A network administrator has configured access list 173 to prevent Telnet and ICMP traffic from reaching a server with the address of 192.168.13.26. Which commands can the administrator issue to verify that the access list is working properly? (Choose three)
A. Router# ping 192.168.13.26
B. Router# debug access-list 173
C. Router# show open ports 192.168.13.26
D. Router# show access-lists
E. Router# show ip interface
Answer: A D E[/am4show]
Explanation
Answer B is not correct because “debug access-list ” command does not exist.
The reason answer E is correct because this command can help us see if the access-list was applied to the correct interface or not.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit:
Assuming that the entire network topology is shown, what is the operational status of the interfaces of R2 as indicated by the command output shown?
A. One interface has a problem.
B. Two interfaces have problems.
C. The interfaces are functioning correctly.
D. The operational status of the interfaces cannot be determined from the output shown.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The subnet of Fa0/0 of R2 is 172.16.109.0/26 (range from 172.16.109.0 to 172.16.109.63) which covers the subnet of S0/1 interface 172.16.109.4/30 so in fact the answer C is not correct. But from the output of the “show ip interface brief” command we see both Fa0/0 and S0/1 interfaces’ statuses are ‘up/up’ -> they are working normally. So we think there is a typo in the subnet mask of Fa0/0. It should not be ‘/26’ but longer one, ‘/28’, for example. So you should still choose answer C in this question.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Hosts in network 192.168.2.0 are unable to reach hosts in network 192.168.3.0. Based on the output from RouterA, what are two possible reasons for the failure? (Choose two)
A. The cable that is connected to S0/0 on RouterA is faulty.
B. Interface S0/0 on RouterB is administratively down.
C. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is configured with an incorrect subnet mask.
D. The IP address that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB is not in the correct subnet.
E. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is not receiving a clock signal from the CSU/DSU.
F. The encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB does not match the encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterA.
Answer: E F[/am4show]
Explanation
From the output we see the Serial0/0 of RouterA is in “status up/protocol down” state which indicates a Layer 2 problem so the problem can be:
+ Keepalives mismatch
+ Encapsulation mismatch
+ Clocking problem
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which interface counter can you use to diagnose a duplex mismatch problem?
A. runts
B. CRC errors
C. no carrier
D. late collisions
E. deferred
F. giants
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
At the end of each frame there is a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field. FCS can be analyzed to determine if errors have occurred. FCS uses cyclic redundancy check (CRC) algorithm to detect errors in the transmitted frames. Before sending data, the sending host generates a CRC based on the header and data of that frame. When this frame arrives, the receiving host uses the same algorithm to generate its own CRC and compare them. If they do not match then a CRC error will occur. CRC errors (and input errors in general) are often caused by duplex mismatch or Physical layer issues (like faulty cable, faulty network interface card or excessive interference during the transmission,…).
On an Ethernet connection, a duplex mismatch is a condition where two connected devices operate in different duplex modes, that is, one operates in half duplex while the other one operates in full duplex.
Note:
+ Runts are frames which do not meet the minimum frame size of 64 bytes. Runts are usually created by collisions.
+ Giants: frames that are larger than 1,518 bytes
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two Cisco IOS commands, used in troubleshooting, can enable debug output to a remote location? (Choose two)
A. no logging console
B. logging host ip-address
C. terminal monitor
D. show logging | redirect flashioutput.txt
E. snmp-server enable traps syslog
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Routers R1 and R2 are on the same network segment, and both routers use interface GigabitEthernet0/0. If R1 loses communication to R2, which two items should you check as you begin troubleshooting? (Choose two)
A. Verify that R2 is using 802.1q encapsulation.
B. Verify that the GigabitEthernet0/0 interfaces on R1 and R2 are configured with the same subnet mask.
C. Verify that the R1 GigabitEthernet0/0 interface is up and line protocol is down.
D. Verify that R1 and R2 both are using HDLC encapsulation.
E. Verify that R1 GigabitEthernet0/0 interface is up and line protocol is up.
Answer: B E[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]After you configure a new router to connect to a host through the GigabitEthernet0/0 port of the router, you log in to the router and observe that the new link is down. Which action corrects the problem?
A. Use a crossover cable between the host and R1.
B. Use a straight through cable between the host and R1.
C. Configure the host to use R1 as the default gateway.
D. Use a rollover cable between the host and R1.
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command enables IPv6 forwarding on a Cisco router?
A. ipv6 local
B. ipv6 host
C. ipv6 unicast-routing
D. ipv6 neighbor
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
An example of configuring RIPng (similar to RIPv2 but is used for IPv6) is shown below:
Router(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing (Enables the forwarding of IPv6 unicast datagrams globally on the router)
Router(config)#interface fa0/0
Router(config-if)#ipv6 rip 9tut enable (9tut is the process name of this RIPng)
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]The network administrator has been asked to give reasons for moving from IPv4 to IPv6. What are two valid reasons for adopting IPv6 over IPv4? (Choose two)
A. telnet access does not require a password
B. nat
C. no broadcast
D. change of destination address in the IPv6 header
E. change of source address in the IPv6 header
F. autoconfiguration
Answer: C F[/am4show]
Explanation
With IPv6, devices can build a link-local address automatically. But notice this address is only used for communications within the local subnetwork, routers do not forward these addresses.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which of these represents an IPv6 link-local address?
A. FE08::280e:611:a:f14f.3d69
B. FE81::280f.512b:e14f:3d69
C. FE80::380e:611a:e14f:3d69
D. FEFE:0345:5f1b::e14d:3d69
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The range of IPv6 link-local address (similar to the Windows auto-configuration IP address of 169.254.x.x.) is FE80::/10. For more information about IPv6, please read my IPv6 tutorial.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three approaches can be used while migrating from an IPv4 addressing scheme to an IPv6 scheme? (Choose three)
A. enable dual-stack routing
B. configure IPv6 directly
C. configure IPv4 tunnels between IPv6 islands
D. use proxying and translation to translate IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets
E. statically map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses
F. use DHCPv6 to map IPv4 addresses to IPv6 addresses
Answer: A C D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which component of the Cisco SDN solution serves as the centralized management system?
A. Cisco OpenDaylight
B. Cisco ACI
C. Cisco APIC
D. Cisco IWAN
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) is the main architectural component of the Cisco ACI solution. It is the unified point of automation and management for the Cisco ACI fabric, policy enforcement, and health monitoring. The Cisco APIC is a centralized clustered controller that optimizes performance, supports any application anywhere, and unifies operation of physical and virtual environments. The controller manages and operates a scalable multitenant Cisco ACI fabric.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two options are primary responsibilities of the APIC-EM controller? (Choose two)
A. It automates network actions between different device types.
B. It provides robust asset management.
C. It tracks license usage and Cisco IOS versions.
D. It automates network actions between legacy equipment.
E. It makes network functions programmable.
Answer: A E[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which Cisco platform can verify ACLs?
A. Cisco Prime Infrastructure
B. Cisco Wireless LAN Controller
C. Cisco APIC-EM
D. Cisco IOS-XE
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
In the “CCNA Routing and Switching ICND2 200-105 Official Cert Guide, Academic Edition” there is a section named “Verify ACLs using the APIC-EM Path Trace ACL analysis tool” so APIC-EM should be the correct answer.
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command should you enter to allow carrying voice, options:
A. switchport ?? (VLAN 10, maybe?)
B. switchport access
C. switchport trunk
D. switchport host
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the correct DSCP value used for voice traffic?
A. Expedited Forwarding (EF), 46, 101110
B. Assured Forwarding (AF), 31, 011010
C. Assured Forwarding (AF), 36, 100110
D. Expedited Forwarding (EF), 36, 101110
Answer: A[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which feature can you implement to reserve bandwidth for VoIP calls across the call path?
A. PQ
B. Round Robin
C. CBWFQ
D. RSPV
Answer: D[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statement about proxy ARP are true ? (Choose two)
A. It is supported on networks without ARP.
B. It allows machines to spoof packets.
C. It requires larger ARP tables.
D. It reduces the amount of ARP traffic.
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which two statements about Ethernet standards are true? (Choose two)
A. Ethernet is defined by IEEE standard 802.2.
B. Ethernet is defined by IEEE standard 802.3.
C. Ethernet 10BASE-T does not support full-duplex.
D. When an Ethernet network uses CSMA/CD, it terminates transmission as soon as a collision occurs.
E. When an Ethernet network uses CSMA/CA. it terminates transmission as soon as a collision occurs.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]If three devices are plugged into one port on a switch and two devices are plugged into a different port, how many collision domains are on the switch?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
Answer: A[/am4show]
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Drag the term on the left to its definition on the right (not all options are used)
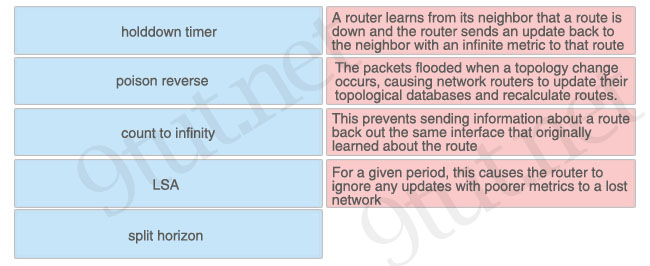
Answer:
+ poison reverse: A router learns from its neighbor that a route is down and the router sends an update back to the neighbor with an infinite metric to that route
+ LSA: The packets flooded when a topology change occurs, causing network routers to update their topological databases and recalculate routes
+ split horizon: This prevents sending information about a routeback out the same interface that originally learned about the route
+ holddown timer: For a given period, this causes the router to ignore any updates with poorer metrics to a lost network[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]The above provides some descriptions, while the below provides some routing protocols. Drag the above items to the proper locations.
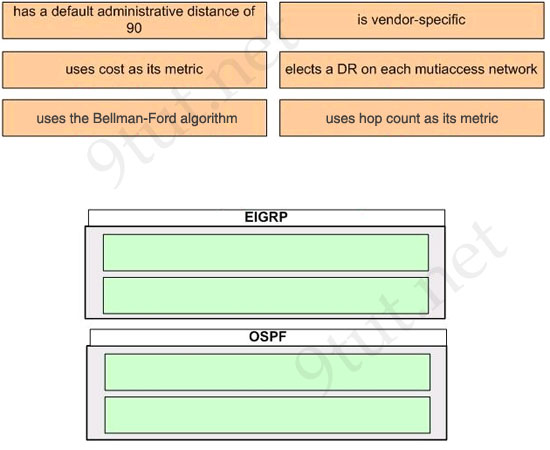
Answer:
EIGRP:
+ has a default administrative distance of 90
+ is vendor-specific
OSPF:
+ uses cost as its metric
+ elects a DR on each multiaccess network[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Drag each description on the left to the appropriate term on the right. Not all the descriptions are used.
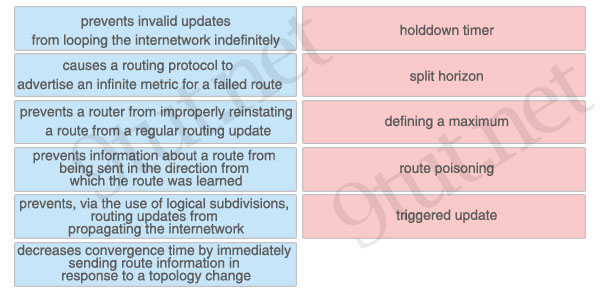
Answer:
+ holddown timer: prevents a router from improperly reinstating a route from a regular routing update
+ split horizon: prevents information about a route from being sent in the direction from which the route was learned
+ defining a maximum: prevents invalid updates from looping the internetwork indefinitely
+ route poisoning: causes a routing protocol to advertise an infinite metric for a failed route
+ triggered update: decreases convergence time by immediately sending route information in response to a topology change[/am4show]
The new ICND2 200-105 exam has come to replace the old ICND2 200-101 exam. We create the “Share your ICND2 v3.0 Experience” for everyone to share their experience after taking this exam.
Note for ICND2: There are no VRRP, GLBP, NetFlow and NAT questions (and they are not technologies learned in this exam).
Please share with us your experience after taking the ICND2 200-105 exam, your materials, the way you learned, your recommendations… But please DO NOT share any information about the detail of the exam or your personal information, your score, exam date and location, your email…