ICND1 – IP Routing 3
Note: The ICND1 exam requires candidates to understand basic knowledge of dynamic routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP, OSPF).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]When enabled, which feature prevents routing protocols from sending hello messages on an interface?
A. virtual links
B. passive-interface
C. directed neighbors
D. OSPF areas
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which routing protocol has the smallest default administrative distance?
A. IBGP
B. OSPF
C. IS-IS
D. EIGRP
E. RIP
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
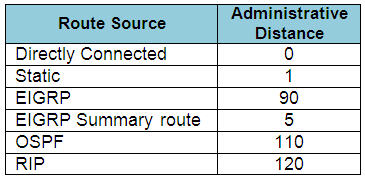
The Administrative Distance (AD) of popular routing protocols is shown below. You should learn them by heart:
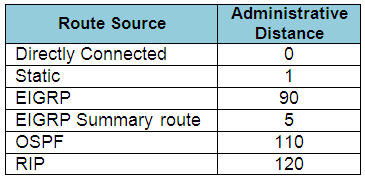
Note: The AD of iBGP is 200
The smaller the AD is, the better it is. The router will choose the routing protocol with smallest AD.
In this case EIGRP with AD of 90 is the smallest one.
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about static routes is true?
A. The source interface can be configured to make routing decisions.
B. A subnet mask is entered for the next-hop address.
C. The subnet mask is 255.255 255.0 by default
D. The exit interface can be specified to indicate where the packets will be routed.
Answer: D[/am4show]
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about routing protocols is true?
A. Link-state routing protocols choose a path by the number of hops to the destination.
B. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol.
C. Distance-vector routing protocols use the Shortest Path First algorithm.
D. IS-IS is a distance-vector routing protocol.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which dynamic routing protocol uses only the hop count to determine the best path to a destination?
A. IGRP
B. RIP
C. EIGRP
D. OSPF
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]A workstation has just resolved a browser URL to the IP address of a server. What protocol will the workstation now use to determine the destination MAC address to be placed into frames directed toward the server?
A. HTTP
B. DNS
C. DHCP
D. RARP
E. ARP
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
After resolving a browser URL to an IP address (via DNS server), the workstation must learn the MAC address of the server so that it can create a complete packet (a complete packet requires destination MAC and IP address, source MAC and IP address). Therefore the workstation must use ARP to find out the MAC address from the IP address.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What is the simplest way to configure routing between the regional office network 10.89.0.0/20 and the corporate network?
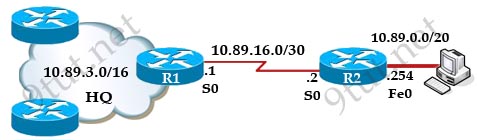
A. router1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.2
B. router2(config)#ip route 10.89.3.0 255.255.0.0 10.89.16.2
C. router1(config)#ip route 10.89.0.0 255.255.240.0 10.89.16.1
D. router2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.89.16.1
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
In this topology, R2 is a stub router with only one connection to the HQ network so the best way to configure routing is to set a static route (default route) to R1.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the output of the corporate router routing table shown in the graphic. The corporate router receives an IP packet with a source IP address of 192.168.214.20 and a destination address of 192.168.22.3. What will the router do with this packet?
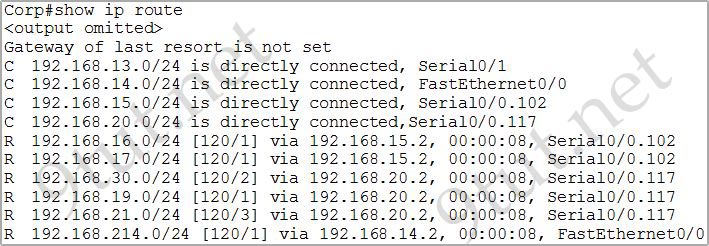
A. It will encapsulate the packet as Frame Relay and forward it out interface Serial 0/0.117.
B. It will discard the packet and send an ICMP Destination Unreachable message out interface FastEthernet 0/0.
C. It will forward the packet out interface Serial 0/1 and send an ICMP Echo Reply message out interface serial 0/0.102.
D. It will change the IP packet to an ARP frame and forward it out FastEthernet 0/0.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]The network administrator has found the following problem. The remote networks 172.16.10.0, 172.16.20.0, and 172.16.30.0 are accessed through the Central router’s serial 0/0 interface. No users are able to access 172.16.20.0. After reviewing the command output shown in the graphic, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
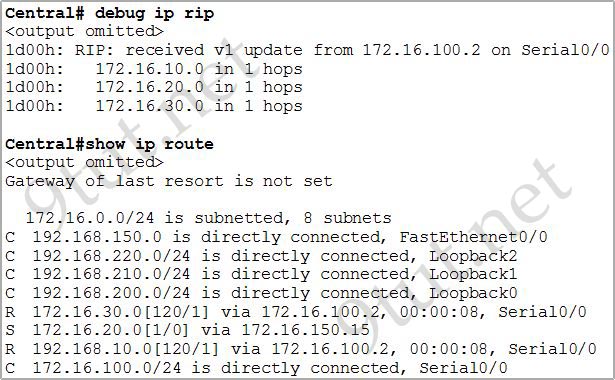
A. no gateway of last resort on Central
B. Central router’s not receiving 172.16.20.0 update
C. incorrect static route for 172.16.20.0
D. 172.16.20.0 not located in Central’s routing table
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 10
[am4show have=’p2;’]What information does a router running a link-state protocol use to build and maintain its topological database? (Choose two)
A. hello packets
B. SAP messages sent by other routers
C. LSAs from other routers
D. beacons received on point-to-point links
E. routing tables received from other link-state routers
F. TTL packets from designated routers
Answer: A C[/am4show]
Explanation
Link-state protocol uses hello packets to discover neighbors and establish adjacencies. After that, the routers begin sending out LSAs to every neighbor (each received LSA is copied and forwarded to every neighbor except the one that sent the LSA)
Question 11
[am4show have=’p2;’]A router has learned three possible routes that could be used to reach a destination network. One route is from EIGRP and has a composite metric of 20514560. Another route is from OSPF with a metric of 782. The last is from RIPv2 and has a metric of 4. Which route or routes will the router install in the routing table?
A. the OSPF route
B. the EIGRP route
C. the RIPv2 route
D. all three routes
E. the OSPF and RIPv2 routes
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
When one route is advertised by more than one routing protocol, the router will choose to use the routing protocol which has lowest Administrative Distance. The Administrative Distances of popular routing protocols are listed below:


Is this true “Note: The ICND1 exam requires candidates to understand basic knowledge of dynamic routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP, OSPF).”? I do not see in the Cisco list of topics for ICND1 neither EIGRP nor OSPF, just RIPv2 and Static routing
@h1 yes it is true. you do not need to know how to configure them but you do need to have a basic understanding on how they operate.