ICND1 – IP Routing 4
Note: The ICND1 exam requires candidates to understand basic knowledge of dynamic routing protocols (RIP, EIGRP, OSPF).
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Some routers have been configured with default routes. What are some of the advantages of using default routes? (Choose two)
A. They establish routes that will never go down.
B. They keep routing tables small.
C. They require a great deal of CPU power.
D. They allow connectivity to remote networks that are not in the routing table
E. They direct traffic from the internet into corporate networks.
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit, PC1 pings PC2. What three things will CORE router do with the data that is received from PC1? (Choose three)
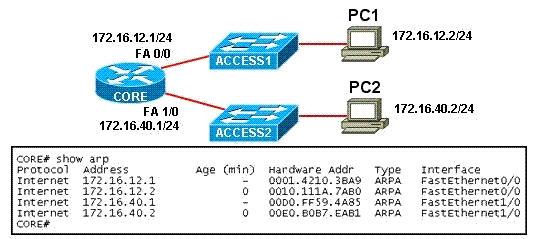
A. The data frames will be forwarded out interface FastEthernet0/1 of CORE router.
B. The data frames will be forwarded out interface FastEthernet1/0 of CORE router.
C. CORE router will replace the destination IP address of the packets with the IP address of PC2.
D. CORE router will place the MAC address of PC2 in the destination MAC address of the frames.
E. CORE router will put the IP address of the forwarding FastEthernet interface in the place of the source IP address in the packets.
F. CORE router will put the MAC address of the forwarding FastEthernet interface in the place of the source MAC address.
Answer: B D F[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which three statements are correct about RIP version 2? (Choose three)
A. It has the same maximum hop count as version 1.
B. It uses broadcasts for its routing updates.
C. It is a classless routing protocol.
D. It has a lower default administrative distance than RIP version 1.
E. It supports authentication.
F. It does not send the subnet mask in updates.
Answer: A C E[/am4show]
Explanation
A and E are correct according to the theory of RIP.
RIP version 1 updates are broadcasts, and RIP version 2 updates are multicast to 224.0.0.9 -> B is not correct.
RIP v1 is a classful routing protocol but RIP v2 is a classless routing protocol -> C is correct.
RIPv1 and RIPv2 have the same default administrative distance of 120 -> D is not correct.
RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol so it does send the subnet mask in updates -> F is not correct.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]A technician pastes the configurations in the exhibit into the two new routers shown. Otherwise, the routers are configured with their default configurations. A ping from Host1 to Host2 fails, but the technician is able to ping the S0/0 interface of R2 from Host1. The configurations of the hosts have been verified as correct. What is the cause of the problem?
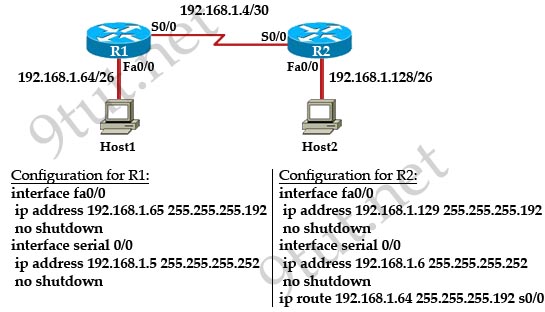
A. The serial cable on R1 needs to be replaced.
B. The interfaces on R2 are not configured properly.
C. R1 has no route to the 192.168.1.128 network.
D. The IP addressing scheme has overlapping subnetworks.
E. The ip subnet-zero command must be configured on both routers.
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
Host1 can ping the Serial interface of R2 because R1 has the network of 192.168.1.4/30 as directly connected route. But R1 does not know how to route to the network of Host2 (192.168.1.128/26) so R1 will drop that ping without trying to send it out S0/0 interface. To make the ping work, we have to configure a route pointing to that network (for example: ip route 192.168.1.128 255.255.255.192 s0/0 on R1).
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]After the show ip route command has been entered, the following routes are displayed. Which route will not be entered into the routing table of a neighboring router?
A. R 192.168.8.0/24 [120/1] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
B. R 192.168.11.0/24 [120/7] via 192.168.9.1, 00:00:03, Serial1
C. C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
D. R 192.168.5.0/24 [120/15] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:10, Serial0
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The route 192.168.5.0/24 currently has the metric of 15 so this router will add 1 hop count before sending out to its neighboring router. With RIP, a metric of 16 means that network is down -> it will not be installed in the routing table of the neighboring router.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. What value should be displayed in Box 1 of the ipconfig output of host A?
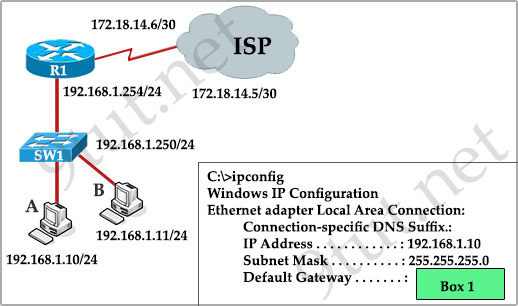
A. 172.18.14.5
B. 172.18.14.6
C. 192.168.1.10
D. 192.168.1.11
E. 192.168.1.250
F. 192.168.1.254
Answer: F[/am4show]
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]After you configure a default route to the Internet on a router, the route is missing from the routing table. Which option describes a possible reason for the problem?
A. The next-hop address is unreachable.
B. The default route was configured on a passive interface.
C. Dynamic routing is disabled.
D. Cisco Discovery Protocol is disabled on the interface used to reach the next hop.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
The passive interface only prevents routing updates from being sent and received on that interface. It does not affect the default route. But if we configure a default route like this:
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2
Then if the next-hop address is down (unreachable) then this default route would be removed from the routing table.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which information is used to install the best route to a destination in IP routing table?
A. the tunnel ID
B. the interface number
C. the prefix length
D. the autonoums system
Answer: C[/am4show]
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the administrative distance of connected routes?
A.1
B. 0
C. 10
D. 90
Answer: B[/am4show]


There is a question in https://www.9tut.net/final_flash/ICND1v3/All_Questions_3/quiz.html
(Question 11)
Which information is used to install the best route to a destination in IP routing table?
a: the Predix Length
b: the interface number
c: the autonomous system
d: the tunnel ID.
————————————-
the correct answer from the quiz is a: the prefix length.
however, my understanding is: prefix length decided the network mask, like /24 is the 255.255.255.0.
why not the answer b? my understanding is:
after configured, each interface has its IP address. the router will know which interface to send out the packet.
Thanks
Hi ,
Ques 5 I am unable to understand this ques .
question 5: After the show ip route command has been entered, the following routes are displayed. Which route will not be entered into the routing table of a neighboring router??
@sunil if you look there are 2 routes for the same network on s0/0. both are using RIP with a AD of 120 but the metric for the one route is 15 which means there is a higher cost to that route. There is some long math algorithm that computes this but f you look under the CCENT study guide you will see a good explanation of this.
@Anon if you reference the CCENT study guide under dynamic routing protocols you will see that routes first use AD to determine the best route and if they have the same AD they will then use the prefix length to send to the smallest network. check out https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_prefix_match
The question 5 states, that “… the following routes are displayed..”. But I cannot find the routes in below. @sharkguy / @Sunil, are you able see them?
The “routes displayed ” are referring to the list of answers, you have to choose from one of them.
Q8: Which information is used to install the best route to a destination in IP routing table?
a: the Prefix Length
b: the interface number
c: the autonomous system
d: the tunnel ID.
————————————-
the correct answer from the quiz is a: the prefix length.
but what is prefix length?
Sunil,
RIP has a max hop count of 15 hops, but DO NOT FORGET TO COUNT ‘0’ as a value (like binary), so 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15…..is…..16 hops.
anything more than 15 is dropped/Unreachable
so…0-14 is 15 hop max. If it said “R [120/14]” that would be valid still because 0-14 is 15 hop max..
Prefix lenght is just like subnet mask. in Ipv6 address the subnet mask is called prefix lenght. From my understanding, this question of one those trick questions.
Q8: Which information is used to install the best route to a destination in IP routing table?
A is right because of the following explanation :
Routers select best routes based on the following criteria:
Longest prefix match: Routers select routes with the longest match to the destination address in the forwarded packet. For example if a packet is destined to 192.168.12.1 and the router has 192.168.0.0/16 and 192.168.12.0/24 in its routing table, it will forward the packet using the 192.168.12.0/24 route.