ICND1 – Switch Questions 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit is showing the topology and the MAC address table. Host A sends a data frame to host D. What will the switch do when it receives the frame from host A?
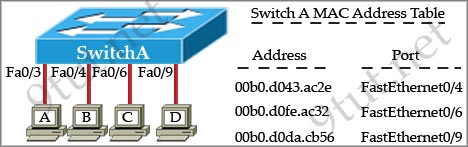
A. The switch will add the source address and port to the MAC address table and forward the frame to host D.
B. The switch will discard the frame and send an error message back to host A.
C. The switch will flood the frame out of all ports except for port Fa0/3.
D. The switch will add the destination address of the frame to the MAC address table and forward the frame to host D.
Answer: A[/am4show]
Explanation
In this case the destination MAC address has been learned so the switch just forwards the frame to the corresponding port. It also learn that the source MAC address of host A has not been existed in the MAC address table so it will add it (and port fa0/3) to its MAC address table.
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which statement about unicast frame forwarding on a switch is true?
A. The TCAM table stores destination MAC addresses
B. If the destination MAC address is unknown, the frame is flooded to every port that is configured in the same VLAN except on the port that it was received on.
C. The CAM table is used to determine whether traffic is permitted or denied on a switch
D. The source address is used to determine the switch port to which a frame is forwarded
Answer: B[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]Two hosts are attached to a switch with the default configuration. Which statement about the configuration is true?
A. IP routing must be enabled to allow the two hosts to communicate.
B. The two hosts are in the same broadcast domain.
C. The switch must be configured with a VLAN to allow the two hosts to communicate.
D. Port security prevents the hosts from connecting to the switch.
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
All ports on a Layer 2 switch are in the same broadcast domain. Only router ports separate broadcast domains.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]Configuration of which option is required on a Cisco switch for the Cisco IP phone to work?
A. PortFast on the interface
B. the interface as an access port to allow the voice VLAN ID
C. a voice VLAN ID in interface and global configuration mode
D. Cisco Discovery Protocol in global configuration mode
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
When you connect an IP phone to a switch using a trunk link, it can cause high CPU utilization in the switches. As all the VLANs for a particular interface are trunked to the phone, it increases the number of STP instances the switch has to manage. This increases the CPU utilization. Trunking also causes unnecessary broadcast / multicast / unknown unicast traffic to hit the phone link.
In order to avoid this, remove the trunk configuration and keep the voice and access VLAN configured along with Quality of Service (QoS). Technically, it is still a trunk, but it is called a Multi-VLAN Access Port (MVAP). Because voice and data traffic can travel through the same port, you should specify a different VLAN for each type of traffic. You can configure a switch port to forward voice and data traffic on different VLANs. Configure IP phone ports with a voice VLAN configuration. This configuration creates a pseudo trunk, but does not require you to manually prune the unnecessary VLANs.
The voice VLAN feature enables access ports to carry IP voice traffic from an IP phone. You can configure a voice VLAN with the “switchport voice vlan …” command under interface mode. The full configuration is shown below:
| Switch(config)#interface fastethernet0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode access Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 Switch(config-if)#switchport voice vlan 20 |
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which address type does a switch use to make selective forwarding decisions?
A. source IP address
B. destination IP address
C. source and destination IP address
D. source MAC address
E. destination MAC address
Answer: E[/am4show]
Explanation
When a switch receives a frame, it first checks for the destination MAC address and tries to find a matching entry in its MAC address table. If found, the switch then forwards that frame on the corresponding port associated with that MAC address. If no entry is found, the switch will flood that frame out of all (active) ports except the port that sent it.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]After the power-on self test (POST), the system LED of a Cisco 2950 switch turns amber. What is the status of the switch?
A. The switch has a problem with the internal power supply and needs an external power supply to be attached.
B. The switch has experienced an internal problem but data can still be forwarded at a slower rate.
C. The POST was successful.
D. POST failed and there is a problem that prevents the operating system of the switch from being loaded.
E. The switch passed POST, but all the switch ports are busy
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The system LED shows whether the system is receiving power and functioning properly. Below lists the LED colors and meanings:
| Color | System Status |
| Off | System is not powered up. |
| Green | System is operating normally. |
| Amber | System is receiving power but is not functioning properly. |
(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2950/hardware/installation/guide/hgovrev.html)
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which option is a invalid hostname for a switch?
A. 5witch-Cisco
B. Switch-Cisco!
C. 5witchCisc0
D. SwitchCisc0
Answer: B[/am4show]
Explanation
The “!” is an invalid letter for a hostname. The name is alphanumeric so it can begin with a number.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The ports that are shown are the only active ports on the switch. The MAC address table is shown in its entirety. The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives at the switch. What two operations will the switch perform when it receives this frame? (Choose two)
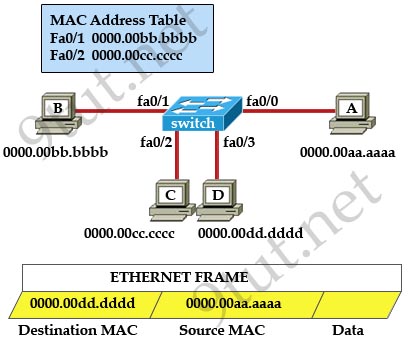
A. The MAC address of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be added to the MAC address table.
B. The MAC address of 0000.00dd.dddd will be added to the MAC address table.
C. The frame will be forwarded out port fa0/3 only.
D. The frame will be forwarded out fa0/1, fa0/2, and fa0/3.
E. The frame will be forwarded out all the active ports.
Answer: A D[/am4show]
Explanation
When a switch receives a frame, it first checks for the destination MAC address and tries to find a matching entry in its MAC address table. If found, the switch then forwards that frame on the corresponding port associated with that MAC address. If no entry is found, the switch will flood that frame out of all active ports except the port that sent it. In this case, the destination MAC address 0000.00dd.dddd has not been in the MAC address table so the switch will flood the frame out all of its ports except fa0/0 (the port that it received the frame) -> D is correct.
Also, the switch learns that the MAC address 0000.00aa.aaaa is received on fa0/0 -> the switch adds 0000.00aa.aaaa and its corresponding port fa0/0 to the MAC address table -> A is correct.
Question 9
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which table displays the MAC addresses that are learned on a switch?
A. FIB
B. ARP
C. TCAM
D. CAM
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
In short, TCAM (Ternary Content Addressable Memory) is used for faster IP look up while ARP table is Layer3 address to Layer2 address resolution so they are not correct.
The Content Addressable Memory (CAM) table on a switch keeps track of MAC addresses and on what port they appear, along with some other stuff like age. When a device that’s plugged into a particular port sends a frame to the switch, the switch makes note of the source MAC and the port and checks the CAM table. Notice that the CAM table is built on the source MAC addresses (while the destination MAC addresses are ignored).


“CAM table is built on the source MAC addresses” what does it mean? “source MAC address” is not a device
Source MAC addresses are attributes of the devices that communicate with switches. When devices connected to a switch attempt to comminicate through that switch (for multiple purposes), the switch will remember their MAC addresses. So no, “source MAC address” is not a device, but devices have (source) MAC addresses.
Which option is a invalid hostname for a switch?
A. 5witch-Cisco
B. Switch-Cisco!
C. 5witchCisc0
D. SwitchCisc0
Answer: B
Explanation
The “!” is an invalid letter for a hostname.
Please explain how I can configure all of those hostnames on my cisco switch.
configuration:
enable
config terminal
hostname 5with-Cisco etc
or to be more specific
R>enable
R#configurate terminal
R(conf)#hostname 5with-Cisco
5with-Cisco(conf)#
that’s how you will see it in your router CLI promt
he means he can config it with the “!” Natalie when it states its invalid.
In their naming conventions Will, they state this is wrong
can you reanswer on question no 4, it has the confusing answer
A configuration of which option is required on a Cisco switch for the Cisco IP phone to work?
A. PortFast on the interface
B. the interface as an access port to allow the voice VLAN ID
C. a voice VLAN ID in interface and global configuration mode
D. Cisco Discovery Protocol in global configuration mode
This sheet says “B” is the answer but I say “C” is the answer
Can I know why I don’t see any questions but only explananations?
Can someone send me the latest dumps for ICND1 to {email not allowed}
Can someone send me the latest dumps for ICND1 to rgillencost AT gmail.com
is the answer to number 8 should be A and C instead of D. It already has a destination MAC and it is available.
The link for question 6 is no longer working. It gives a 404 error as the 2950 switch is no longer supported.
@IDKanything,
What? There is no .dddd MAC address in the CAM table. A & D are correct, and if you think otherwise you’ll fail your Cisco exams.
Which option is a invalid hostname for a switch?
A. 5witch-Cisco
B. Switch-Cisco!
C. 5witchCisc0
D. SwitchCisc0
Answer: B
Explanation
The “!” is an invalid letter for a hostname.
But I can set hostnam with “!” ???
Switch>
Switch>ena
Switch>enable
Switch#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#hos
Switch(config)#hostname Switch-Cisco!
Switch-Cisco!(config)#