ICND2 – OSPF Questions 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]
Premium Member: You can test your knowledge with these questions first via this link.
[/am4show]
Note: If you are not sure about OSPF, please read my OSPF tutorial first.
Question 1
[am4show have=’p2;’]Which command is used to display the collection of OSPF link states?
A. show ip ospf link-state
B. show ip ospf Isa database
C. show ip ospf neighbors
D. show ip ospf database
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The output of the “show ip ospf database” is shown below:
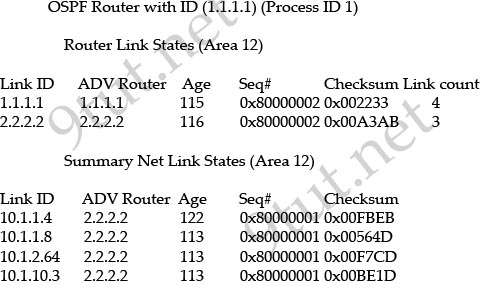
From the output above we can see LSA Type 1 (Router Link State) and LSA Type 3 (Summary Net Link State).
Question 2
[am4show have=’p2;’]What are two drawbacks of implementing a link-state routing protocol? (Choose two)
A. the sequencing and acknowledgment of link-state packets
B. the requirement for a hierarchical IP addressing scheme for optimal functionality
C. the high volume of link-state advertisements in a converged network
D. the high demand on router resources to run the link-state routing algorithm
E. the large size of the topology table listing all advertised routes in the converged network
Answer: B D[/am4show]
Question 3
[am4show have=’p2;’]
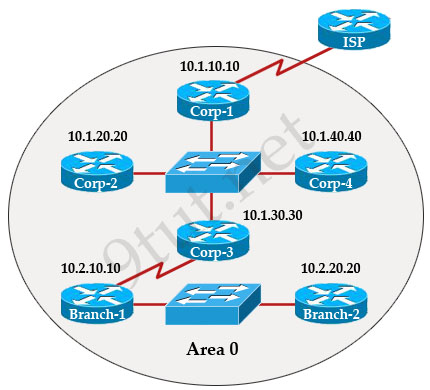
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic.
There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance.
As part of examining the router resources the OSPF DRs need to be known.
All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router.
Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two)
A. Corp-1
B. Corp-2
C. Corp-3
D. Corp4
E. Branch-1
F. Branch-2
Answer: D F[/am4show]
Explanation
There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40) & Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
Question 4
[am4show have=’p2;’]What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router?
A. 16
B. 2
C. unlimited
D. 4
Answer: D[/am4show]
Explanation
The default number of equal-cost paths that can be placed into the routing of a Cisco OSPF router is 4. We can change this default value by using “maximum-paths” command:
Router(config-router)#maximum-paths 2
Note: Cisco routers support up to 16 equal-cost paths
Question 5
[am4show have=’p2;’]RouterD# show ip interface brief

Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this router?
A. 10.1.1.2
B. 10.154.154.1
C. 172.16.5.1
D. 192.168.5.3
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The highest IP address of all loopback interfaces will be chosen -> Loopback 0 will be chosen as the router ID.
Question 6
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true about the loopback address that is configured on RouterB? (Choose two)
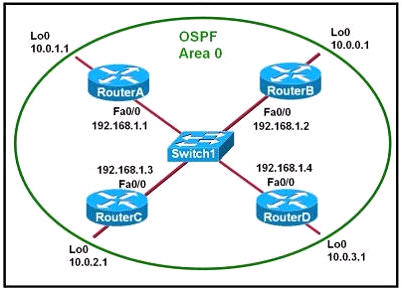
A. It ensures that data will be forwarded by RouterB.
B. It provides stability for the OSPF process on RouterB.
C. It specifies that the router ID for RouterB should be 10.0.0.1.
D. It decreases the metric for routes that are advertised from RouterB.
E. It indicates that RouterB should be elected the DR for the LAN.
Answer: B C[/am4show]
Explanation
A loopback interface never comes down even if the link is broken so it provides stability for the OSPF process (for example we use that loopback interface as the router-id) -> B is correct.
The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
+ The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
+ If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
-> The loopback interface will be chosen as the router ID of RouterB -> C is correct.
Question 7
[am4show have=’p2;’]Refer to the exhibit. The network associate is configuring OSPF on the Core router. All the connections to the branches should be participating in OSPF. The link to the ISP should NOT participate in OSPF and should only be advertised as the default route. What set of commands will properly configure the Core router?
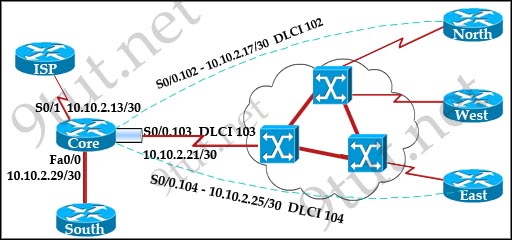
A. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
B. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.10.2.13 0.0.0.242 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
C. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
D. Core(config-router)#default-information originate
Core(config-router)#network 10.10.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0
Core(config-router)#exit
Core(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
Answer: C[/am4show]
Explanation
The question states that the link to ISP should not participate in OSPF -> answers A, B are not correct.
In answer D, the “network 10.10.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0” does not cover the IP address of S0/0.103 (10.10.2.21) -> D is not correct.
The default-information originate command advertises a default route to other routers, telling something like “please send me your unknown traffic”. So in this case, besides a full routing table, other routers will also receive a default route from Core router.
But please notice that Core router needs to have a default route in its routing table. That is why the command “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14” is added to Core router. By adding the “always” (after “default-information originate” command) the default route will be advertised even if there is no default route in the routing table of router Core.
Question 8
[am4show have=’p2;’]
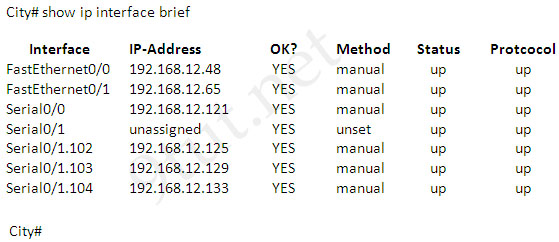
A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF.
Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three)
A. FastEthernet0/0
B. FastEthernet0/1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: B C D[/am4show]
Explanation
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63″ equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.168.12.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF -> B C D are correct.


Question 3 above is a duplicate of question 7 from ” New ICND2 – OSPF Questions “.
Hi, can someone explain question 7 please?
@aspire…
Q7 – you want all subnets in your network to be included in the “network” command, except for the 10.10.2.13/30 for the internet connection…
on Answer C, network 10.10.2.16 with a w/c mask of 0.0.0.15 (the same as a s/n mask of 255.255.255.240) includes all addresses from 10.10.2.16 – 10.10.2.31
Took ICND2 earlier today, 986 / 1000.
Questions 3 and 5 from this page were on there.
Thanks for all your input and test followup comments Mike!
hi all
subscribe to that channel http://www.youtube.com/user/Joynetworks for free
thanks
hi aspire,
q7 is subnetting at work. answer “c” encompasses the 2 networks of fa0/0 and s0/0.103. note that we have to exclude s0/1 as directed.
3 and were there
Passed today my ICND@2 by 1000. Got different configuration of the Eigrp & frame Relay labs where there were different DLCIs and IP addresses, but same process was used to get answers (show commands, show ip protocols, show ip interface brief ).
A question about GLBP and a question about netflow were on my test. You can find them here: http://www.examtut.com/2013/09/new-questions-in-ccna-200-120-hsrp-vrrp.html
Study 9tut and this guy i found him really helpful. He has unique way of teaching http://www.danscourses.com If you can do all his videos again and again. Trust me you will get the concept. Also one thing i learned today is if you don’t know the concept it’ll be hard for you in the exam.
All the best to every one in their path. Keep me in your good wishes.
Question 2.
D ok, but why B and not E?
Took the exam today. Pass 986/1000. Q3, Q5 were on there.
Thanks 9tut.
@izzarazzu
E. the large size of the >>topology table<< listing all advertised routes in the converged network
OSPF for IPv4 does not have topology tables. EIGRP is the interior gateway protocol that uses topology tables to determine a feasible successor.
Tested today, 8/20. #4, 5, 6 and 7 were on there.
took the exam today and pass with 907. Question 3 through 7 were on there, (#5 had only 1 loopback address).
location United States Florida.
test ICND 2
Thanks 9tut
Havent taken the test yet
Can someone explain question 8?
what does this statement mean: The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63″ equals to network 192.168.12.64/26??
Thank you.
Gary, ” Its the network range of 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63. So the Network is 192.168.12.64 and the Broadcast is 192.168.12.127 everything has to be in between 64 – 127. The 0.0.0.63 is the wildcard mask which OSPF uses. YOUTUBE Wildcard Mask for OSPF if you still dont get it.
FLO, Thanks, That makes sense!!
There’s a question on ospf where u not allowed to view configs but u must answer five questions on it please assist if someone so it
icnd 2
Easiest way to look at wildcard masks if you are familiar with your normal masks is to just subtract the number from 255.
So if we have 0.0.0.63 :
255
– 63
——–
=192
Now it looks likes a .192 mask, which we know has a 64 address subnet range (0-63, 64-127, 128-191, 192-255) When dealing with these familiar masks we can more easily determine the range of the subnet.
Look at another:
0.0.0.3 :
255
– 3
——-
=252
.252 mask has four addresses per subnet (0-3, 4-7, 8-11, 12-15, etc)
Hope this helps
What’s the difference between OSPF v2 & OSPF v3 ?
new Question .
Q2:
D – I get it;
B – Why??? Isn’t “E” a better answer?
@someone
You said that there is a new question :What’s the difference between OSPF v2 & OSPF v3 ?
Can you still remember some of the different options of your exam?
@Mateus_Ben
Someone already pointed out>>>topology table<<< is an eigrp thingy and in ospf context, it should called "ospf database"
Topology table is not like a registered trade mark of EIGRP, I am still thinking E is a better answer in a broad perspective.
B. the requirement for a hierarchical IP addressing scheme for optimal functionality
This sounds to me kind of a best practice for any routing routing protocol
Q 3,6 and 7 was there
Hi, please someone can explain me questions 8 ?
@Caudrick
for Q8 the advertised network is “City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0”
the wildcard mass 0.0.0.63 means to use increments of 64, so starting from 192.168.12.64 any IP with-in the next 64 bits will be advertised in OSPF. So 192.168.12.64 – 192.168.12.127 will be good because .128 will start the next subnet. It’s basically a part subnetting question.
A trick I learned from a CBTnuggets with Keith Barker. for using wildcard mass is to just subtract 1 away from the subnet masks increment
example: 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 (these are the increments for each subnet)
128 192 224 240 248 252 254 255 (these are all possible subnet mask)
if an ACL calls for us to only permit host 192.168.1.17 – 192.168.1.31 on 192.168.1.0/24 network
we will use access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.16 0.0.0.15 any
only 16 IP’s starting from 192.168.1.16 will be permitted. Hope this helped.
after I submitted the comment it re-formatted it a little so I’m just sending this for more clarity
128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 (these are the increments for each subnet)
128 192 224 240 248 252 254 255 (these are all possible subnet mask)
I had a question about the database exchange process: ExStart–>Exchange–>Loading–>Full
Q4: in the explanation it states “Note: Cisco routers support up to 6 equal-cost paths”. It should be 16, not 6.
@JB: Thanks for your detection. We have just updated it.
I got Q4, Q5, Q6, Q7 today in my ICND2 exam.
Thanks 9tut.
Got just Q4 today.
one question!!!
who can help me?
Given the show ip protocols how many ospf neighbors douse this router have?
HICKORY#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “ospf 1”
Sending updates every 0 seconds
Invalid after 0 seconds, hold down 0, flushed after 0
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is
Redistributing: ospf 1
Routing for Networks:
0.0.0.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
10.255.255.1 110 00:07:52
Distance: (default is 110)
guys download dumps with nuggets free from this following link
wurl. cc/dumps
Just took the test today – 980/1000 Altrhough I did not get any questions from this page Q7 with different values was one of the questions in the OSPF sim. Thanks 9tuts! Also got Frame Relay, EIGRP and OSPF labs
THERE IS NO NEED FOR ANY DUMPS – just study one book (Wendel or Todd) and the you tube lessons available free for visual knowledge. Along with 9tuts these are enough for 900 and over marks with ease.
But you MUST understand the concepts and not mug up the answer as they change the options and answers
Very good site for studying ccna. really good job
@all: We had to move all the questions and answers out of 9tut. We can only keep the explanation. You can download the questions and answers at: https://mega.co.nz/#!oIdESYbD!yyu33vygrfKPy4rcmcbV6qW2fxINNoTokuDM3CjA_og
why can’t I see the actual questions only the answers shown?
@Adan is exactly why so many people need to come here to find the answers. They won’t even take 2 seconds to look for an answer to their question that is RIGHT ABOVE THEIR POST.
Hey Guys,
Question 3 I thought was E & F, because its the highest IP Address is there any reason why its not? Can someone please explain. Thanks
@Anonymous,
There can only be one DR for EVERY SEGMENT. The key to this question is to realise that there are 2 (LAN) segments. The first consists of Corp1, 2, 3 and 4. The second segment consists of Branch 1 and 2.
Once you realise this, we can easily find out the DR for segment 1 is Corp-4 (highest IP in THAT segment) and the DR for segment 2 is Branch-2 (highest IP in THAT segment).
Hence, answers D and F are correct. Hope this helps.
Also been explained in the OSPF section of ICND1 if that helps. Good luck with your studies and exams!
@ someone in FEB. David answered your question in March over in OSPF Questions 1
What are two enhancements that OSPFv3 supports over OSPFv2? (Choose two.)
A. It requires the use of ARP.
B. It can support multiple IPv6 subnets on a single link.
C. It supports up to 2 instances of OSPFv3 over a common link.
D. It routes over links rather than over networks.
Answer: B, D
Passed with 894 today. One question involves why two OSPF neighbors are stuck in EXSTART state. The answer is the MTU settings mismatch.
why there is no question showing ?