OSPF Questions 2
Here you will find answers to OSPF Questions – Part 2
Note: If you are not sure about OSPF, please read my OSPF tutorial
Question 1
OSPF routing uses the concept of areas. What are the characteristics of OSPF areas? (Choose three)
A. Each OSPF area requires a loopback interface to be configured.
B. Areas may be assigned any number from 0 to 65535.
C. Area 0 is called the backbone area.
D. Hierarchical OSPF networks do not require multiple areas.
E. Multiple OSPF areas must connect to area 0.
F. Single area OSPF networks must be configured in area 1.
Answer: C D E
Explanation
C and E are correct according to the theory of OSPF. For answer E, it is a bit unclear but we can understand “Hierarchical OSPF networks do not require multiple areas” is correct because there are networks that are small enough to use only area 0 for the whole network.
Question 2
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a dynamic routing protocol for use in Internet Protocol (IP) networks.
If configuring all OSPF routers in a single area with the same priority value, what value does a router use for the OSPF router ID in the absence of a loopback interface?
A. the IP address of the first Fast Ethernet interface
B. the IP address of the console management interface
C. the highest IP address among its active interfaces
D. the lowest IP address among its active interfaces
E. the priority value until a loopback interface is configured
Answer: C
Question 3
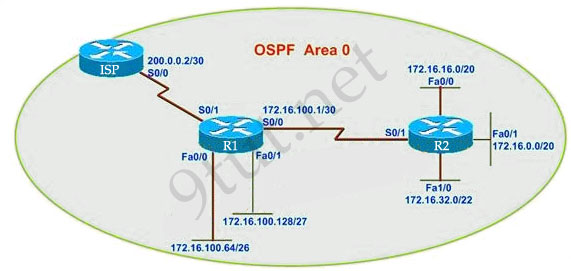
R1 routing commands:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0
router ospf 1
network 172.16.100.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 172.16.100.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
network 172.16.100.128 0.0.0.31 area 0
default-information originate
Assuming that all router interfaces are operational and correctly configured, that OSPF has been correctly configured on router R2, how will the default route configured on R1 affect the operation of R2?
A. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R1 will be dropped.
B. Any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in the routing table of router R2 will be directed to R1. R1 will then send that packet back to R2 and a routing loop will occur.
C. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately.
D. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately because of the lack of a gateway on R1.
Answer: B
Explanation
Please read the explanation of this question at http://www.9tut.com/ccna-ospf-questions (question 6)
Question 4
Border# debug ip ospf events
OSPF events debugging is on
Border#
*Nov 4 03:49:37477: OSPF: Rev hello from 10.10.3.3 area 0 from Serial0/3 192.168.255.18
*Nov 4 03:49:37.481: OSPF: End of hello processing
*Nov 4 03:49:37.641: OSPF: Rev hello from 10.10.1.1 area 0 from Serial0/1 192.168.255.22
“Nov 4 03:49:37.645: OSPF: Mismatched hello parameters from 192.168.255.22
*Nov 4 03:49:37.645: OSPF: Dead R 40 C 56, Hello R 10 C 14
What conclusion can be drawn from the output of the debug command presented in the exhibit?
A. The output represents normal OSPF operation.
B. A router is connected to interface Serial0/3 of the Border router.
The OSPF router ID of the connected router is the IP address of the connected interface.
C. The interfaces of two OSPF routers connected to the Border router are in the same subnet.
D. The OSPF router connected to interface Serial0/1 has NOT formed a neighbor relationship with the Border router.
Answer: D
Explanation
From the debug line “Mismatched hello parameters from 192.168.255.22” we learn that there is a mismatched parameter in the hello packet (Hello interval, Dead interval or AREA number).
Question 5
Which characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. provides common view of entire topology
B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
C. calculates shortest path
D. utilizes event-triggered updates
E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
Answer: A C D
Question 6
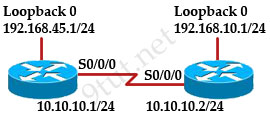
When running OSPF, what would cause router A not to form an adjacency with router B?
A. The loopback addresses are on different subnets.
B. The values of the dead timers on the routers are different.
C. Route summarization is enabled on both routers.
D. The process identifier on router A is different than the process identifier on router
Answer: B
Question 7
What is the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR election used for?
A. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which interface will be used to form a neighbor relationship with another OSPF router.
B. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which OSPF router will become the DR or BDR in a point-to-point network.
C. It is used with the OSPF priority values to determine which router will become the DR or BDR in a multiaccess network.
D. It is used to determine which interfaces will send Hello packets to neighboring OSPF routers.
Answer: C
Question 8
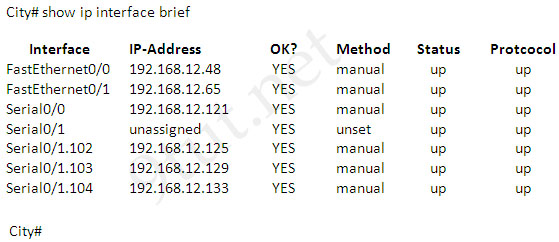
A network associate has configured OSPF with the command:
City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF.
Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three)
A. FastEthernet0/0
B. FastEthernet0/1
C. Serial0/0
D. Serial0/1.102
E. Serial0/1.103
F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: B C D
Explanation
The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63” equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:
+ Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)
+ Network address: 192.168.12.64
+ Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127
Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF -> B C D are correct.
Question 9
To maintain connectivity with neighboring routers, routers running OSPF will send some type of packets. What is the type of packets?
A. OSP packets
B. hello packets
C. LSU packets
D. dead interval packets
Answer: B
Question 10
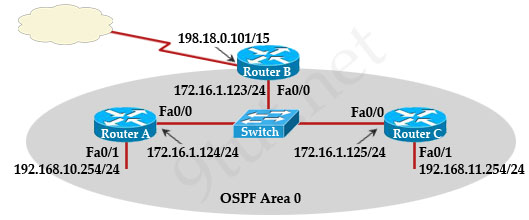
A network administrator is configuring the routers in the graphic for OSPF.
The OSPF process has been started and the networks have been configured for Area 0 as shown in the diagram.
The network administrator has several options for configuring RouterB to ensure that it will be preferred as the designated router (DR) for the 172.16.1.0/24 LAN segment.
What configuration tasks could be used to establish this preference? (Choose three)
A. Change the priority value of the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB to zero.
B. Configure the priority value of the Fa0/0 interface of RouterB to a higher value than any other interface on the Ethernet network.
C. Change the priority values of the Fa0/0 interfaces of RouterA and RouterC to zero.
D. Configure a loop back interface on RouterB with an IP address higher than any IP address on the other routers.
E. No further configuration is necessary.
Answer: B C D
Question 11
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a dynamic routing protocol for use in Internet Protocol (IP) networks, while EIGRP is short for Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. A large corporate which often integrates networks from newly acquired businesses has just decided to use OSPF to replace EIGRP as the corporate routing protocol.
Which two benefits will the corporation obtain by changing from EIGRP to OSPF? (Choose two)
A. the ability to automatically summarize networks
B. the ability to create a hierarchical design using areas
C. the ability to support multi-vendor routers
D. the ability to redistribute default and static routes
E. the ability to use VLSM
Answer: B C
Question 12
What are three characteristics of the OSPF routing protocol? (Choose three)
A. It converges quickly
B. OSPF is a classful routing protocol
C. It uses cost to determine the best route
D. It uses the DUAL algorithm to determine the best route
E. OSPF routers send the complete routing table to all directly attached routers
F. OSPF routers discover neighbors before exchanging routing information
Answer: A C F


Good
Hi All,
The Answer for Q1 Is different on http://www.9tut.com/ccna-ospf-questions Q5 ( the same question on the site for 640-802)
The way I understand it is OSPF networks that are small enough to not require multiple areas are not hierarchical. Hierarchical networks would by definition need to contain more than one area in order to have a hierarchy.
I may be wrong and this is a rather difficult question. I thought It would be answer B, but there is some doubt cast over this as well. Please see below.
I would advise anyone to look at both explanations as there is a Huge differance and until someone smarter than me can confirm this 100% draw your own conclusion.
Here is the explanation to this question in the other section:
I used to think the answers should be C D E and here is my explanation:
OSPF can use an active interface for its router ID, so a loopback interface is not a must -> A is incorrect.
OSPF Area is a 32-bit number so we can use up to 232 – 1 = 4294967296 – 1 (since Area 0 is the first area). Remember that only process ID is a 16-bit number and ranges from 1 to 65535 -> B is incorrect.
F is incorrect too because single area OSPF netwoks must be configured in Area 0, which is called the backbone area.
For answer D, it is a bit hard to guess what they want to say about “hierarchical” but we should understand “Hierarchical OSPF networks” as “OSPF networks”. D is correct bercause we can only have one area (area 0 – the backbone area) for our networks.
But TT commented on 01-11-2010:
Especially to note on choice B, D, and E:
Choice B: we all know that The areas can be any number from 0 to 4.2 billion and 1 to 65,535 for the Process ID. As choice B specifies ‘area’ (be aware, it’s not saying ‘process id), there is no reason to say that we cannot assign numbers from 0 to 65535 for area # (it is using ‘may be’, not ‘have to be’ or ‘ought to be’). Hence, we do not worry about assigning ’0′.
Choice E: as Area 0 is the backbone, we all understand that any areas in a OSPF network have to be connected to it. And actually this is implicitly saying that multiple areas form a hierarchical OSPF network, as Area 0 being a root and others being its leaves.
Choice D: when it specifies ‘Hierarchical’, at least 2 areas should be required to form such topology (of course that includes Area 0)
Although Choice B is not an absolutely accurate statement since it not only can be assigned up to 65535, it is still a correct answer. And again, it specifies ‘area’, not ‘process id’, so ’0′ can be included. Finally, it would be meaningless to call OSPF a hierarchical network if no more than one area is present.
—————————————————————————————————-
I reviewed the question and think it is a more suitable solution with choice B than choice D, surely it is a tricky question!
When I look at my comment above my first thought is TL:DR But please look at it, I feel it is a very important point.
@Mr Guy I’m going to have to agree with those that say we’re not able to actually assign an area as 0. That being the case, I believe B is incorrect and would go with 9tut’s answers. You’re right though, this question is tricky and it’s because of the wording. I wish it weren’t so vague.
I have an observation to make regarding Q10.
On RouterB, the highest IP is the 198.18.0.101. Which happens to be the highest of the ENTIRE network. The IP belongs to a WAN interface that is not a member of area 0 and no OSPF process has been configured for it.
However if we start the area 0 OSPF process, with the WAN link active (meaning line/protocol up, but without participating in OSPF) then RouterB will nevertheless get a RouterID of 198.18.0.101!
This means that if everything in the network has its default value (eg. priority=1) then RouterB has the highest ID and it will become the DR even if we leave the current configuration as it is.
That means answer E could be valid as well.
Any comments on that?
@GoingFor816: Yes, even the serial interface 198.18.0.101 is not in OSPF but router B will select it as the router ID so answer E could be valid too.
But because we have only 3 correct answers so we can’t choose E. It is the “weakest” correct answer.
Yeah, I was thinking along the same line. You’re probably right.
I think on question 2 its because of the default originate command and the route is not in the right direction
typo on Q1:
C and E are correct according to the theory of OSPF. For answer ***E***, it is a bit unclear but we can understand “Hierarchical OSPF networks do not require multiple areas” is correct because there are networks that are small enough to use only area 0 for the whole network.
Yea i’m french and i ve got to agree with both of the ideas that you have.
i find the 1 st question really strange. “Hierarchical OSPF networks do not require multiple areas.” doesn’t mean anything in regard of the ICND2 cisco book. Because they say a hierarchical OSPF network is supposed to have more than one area. And they say that as long as you got more than 50 routers, you’re in need of areas.
Q10 too is strange, considering that the highest Ip adress among the active interfaces is supposed to win! and Make da router become da DR
Oh sorry finally yes, the D question means something, tx for giving me 30 min more at the exam cause english is difficult sometimes
Q3 on my test today. still think it’s a bad question.
I think that in Q10 the answer E is more correct than D.
Let me explain my point of view:
1-In case routers have the same interface priority the second factor to break the tie is the router-id: highest loopbak address and only after that, is the ip address of any active routers interface.
2-So with answer D we are indirectly saying that to break the tie the ip address of loopback has the same value that ip address of any active interface and that is not true.
If option D was something like “Configure a loop back interface on RouterB with an IP address higher than any loopback IP address on the other routers.” I would accept this as correct answer.
I hope you can understand my point of view. What do you think?
@Joao: Yes, if there are no loopback interfaces on any routers than answer E should be more suitable than D. In fact, this is an unclear question because it doesn’t mention anything about loopback interface.
Q1. Answer B is correct according to exam cram, CCNA (640-802) Practice questions 3rd Editicon by Jeremy Cioara. The tear-out cram sheet in the front states under ospf “Areas may be assigned any number from 0 to 65536”. Exactly the same answere given under B. How can this be Wrong.
IN addition the OSPF questions in the CCNA area of this site confirm this. see question 5; Exactly the same Question stack but the Asnweres are B, C and E. I’m guessing now that this is an error to this page.
Passed ICND2 today with 944!! I had questions #2 #3 #5 #9 #12 on my test today
Very Helpful WKC Thanks. I’m cramming like a tetris games. A few gaps here and there but mostly together.
Question1 , Explination typo ( For answer E, it is a bit unclear but we can understand )Should be for answer D!Thank to 9tut and everyone!!!
WKC thanks for the info
Q# 12 in my exam
For Q1, the answer is B C E according to the following sites.
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/20343
http://www.certprepare.com/forum/index.php?showtopic=1470
Passed with 944 mark. Q1, Q11 and Q12 were on my exam.
Passed ICND2 today with 986/1000 🙂
none of these were there
Could you explain me the question the Q5? I think A B D is correctly.
Q1 – the correct answers are C and E. Answer B is not correct. If you log into a router and enter the following command, you will see you can configure many more areas than 65535:
R1(config-router)#area ?
OSPF area ID as a decimal value
A.B.C.D OSPF area ID in IP address format
Answer E is pretty clear to me. It says “Multiple OSPF areas must connect to area 0.” That is true. ALL areas must connect to the backbone (area 0).
Agreed. Thankyou!
lol yeah Q1 answer B is “technically” correct because 0-65535 range is included. But I agree a better wording is preferred. And yes I’m confused with answer D too. By saying hierarchical it means at least an area attached to the backbone area 0, so at least two area. But, if the main point is OSPF itself, regarding of its hierarchical nature, the network can only consists of area 0 only itself. Again, wording issue.
Hi anh! My understand is that link-state routing protocol send routing updates to neighbors, i.e. a route change in the original router’s routing table, not exchanging routing tables with neighbors.
Hi there, can anyone please give me a hand to understand Q8? The way that I see it is that 0.0.0.63 wildcard should be translated as 255.255.255.192, right? And therefore, a 64 increment would apply and IPs from 193-254 could be used.
This is obviously wrong because there are no options available within the answers provided.
Any help would be highly appreciated. Cheers
@darko
nope 🙂
network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
*advertise network* *that starts at 192.168.0.64* *and goes for another 63 IPs* *on area 0*
you must make sure that the start point is equal to (wildcard number+1)
please solve this on your own now:
network 10.0.0.64 0.0.0.31 area 6
Thanks for your quick reply Xalax.
I´m still a bit confused. I´ve read a few articles about how to translate wildcards to subnet masks. This 0.0.0.63 should be translated to 255.255.255.192, right?
(since 255-63=192)
What I don´t get, from your previous command, is these lines:
network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
*advertise network* *that starts at 192.168.0.64* *and goes for another 63 IPs* *on area 0*
If the network is 192.168.12.64, why do you say *that starts at 192.168.0.64*and modify the 3rd octet? I really don´t understand it. Cheers.
@darko
typo, starts at 192.168.12.64
im only human 🙂
yes, 0.0.0.63 corresponds to a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192.
if you like long and boring subnet math please read here: http://blog.ine.com/2008/11/03/binary-math-part-ii/
Q3 today! R1 “default-information originate” means asking neighbor R2 to use R1 as the default gateway, so R2 will route packet to R1 if no match. R1 will then send the packet back to R2 via S0/0 because of the default route. As a result looping occurs.
Good morning, the friends; j ‘ai passing my exam yesterday, favour has this site; thank you really for your help and especially the contribution for this site!!!!!! good chance has all those who get ready in exam!! that the good God assists you how it m ‘avait assisted!!!
guezmajo@yahoo.fr or
guez_carrine@yahoo.fr
Q1 answer must be B, C, and E……..
correct me if i’m wrong.
Becz B says (An area “MAYBE” assigned a number from 0 to 65535) which is true for “Maybe”
Q10, in the configuration shown there are no loopback interfaces, so how can we assign an IP address, so option D is incorrect, and E is the correct one,.. correct me if im wrong n explain plz..?
I agree that the wording of Q1 is really bad! The actual area range is 0-4294967295. 0 to 65535 does fall within that range. But the wording makes it look like 0 to 65535 is the entire range, which it is not. If you notice 1-65535 is the process ID range. Perhaps Cisco’s way of confusing people? I found this on another site and it said B was correct though? http://www.aiotestking.com/cisco/2011/08/what-are-the-characteristics-of-ospf-areas/
And another debate on the question is here. http://www.sadikhov.com/forum/index.php?/topic/180535-ospf-tricky-question/
Most people agree that C and E are correct. I want to say D is correct because you can have a Hierarchical network in 1 area. That’s my 2 cents.
@MalikCCNA A Loopback interface is a logical interface and you can configure as many as you want on any single router, the question doesn’t have to specify there is a Loopback interface because you can create one regardless, so D is the correct answer
I’m having a problem with Q1 answer. I think we need multiple areas to have a hierarchical design. Any suggestions ?
Question 1 is tricky but its CORRECT based on the fact that you CANT assign OSPF a process ID of 0. The Valid process ID ranges are 1 – 65535.
Go ahead and Try assign ospf a process ID 0f 0 in packet tracer and see if you wont get an error.
Hope this Ends the debate..
(: From Jamaica representing to the World 🙂
Question 1 is correct. The ospf process id is 1 – 65k but the area id is a 32 dotted decimal value. ie area 0 is really area 0.0.0.0
Passed 640-816 today..888. Pass is a pass…
Go through all 9tut’s pages…really helped.
Dion
South Africa
Oh yes, I forgot to mention, double check 9tut answers against study guide. 9tut just prepares you for the level of questions on the exams.
Used: Wendell Odom’s CCNA – 640-816 3rd Edition and CBT Nuggets videos. Very good combo.
Q. 1 is correct. The answer is c, D, & E. Answer B is incorrect. Is the Same question as what Mr. Guy stated.
The Answer for Q1 Is different on http://www.9tut.com/ccna-ospf-questions Q5 ( the same question on the site for 640-802).
Please read the explanations correctly on the link. It clearly stated that answer B is incorrect. They just had the answer typo.
However, Area 0 is called the backbone.
JL
Question 12 on todays test.
Taking the INCD2 on March 4th…
Thanks for all the great input and this informative site… this site is well worth my donation.
If anyone has the latest/newest dumps please email them to me @ ( unvmm@yahoo.com).
Thanks in advance!
Had questions 3 and 12 today.
Question 3 was on today’s exam. April 15.
hey folks doing exam 16 may If anyone has the latest/newest dumps please email them to me @ ( carog@sky.com).
Thanks in advance!
Marks: –/1
The speed of all serial links is E1 and the speed of the all other links is 100Mb/s. A static route will be established on the Manchester router to direct traffic toward to the internet over the most direct path available. What configuration of the Manchester router will establish a route toward to the internet for traffic from workstation on the Manchester LAN?
2, 3, 6, 9 and 12 where on exam today
Q still valid Thanks 9tut passed today with 944. i had question 3,8,12 in the exam
good luck
For question 1:
OSPF routing uses the concept of areas. What are the characteristics of OSPF areas? (Choose three)
A. Each OSPF area requires a loopback interface to be configured. – NO
F. Single area OSPF networks must be configured in area 1. – NO
C. Area 0 is called the backbone area. – YES
E. Multiple OSPF areas must connect to area 0. – YES
B. Areas may be assigned any number from 0 to 65535.
D. Hierarchical OSPF networks do not require multiple areas.
These last two are tricky – Hierarchical OSPF networks do not REQUIRE multiple areas, as technically area 0 sits at the top of the hierarchy. However, if additional areas were introduced, a second area IS REQUIRED. In my opinion, The lack of additional areas defines a lack of hierarchy, so I consider this answer INCORRECT.
Areas may be assigned any number for 0 to 4 trillion in OSPFv2, but perhaps OSPFv1 or earlier IOS versions had a more restrictive policy regarding these values. Additionally, the values provided are contained within this larger range, so the emphasis is that this answer is NOT INCORRECT, and so should be considered MORE CORRECT.
Just wrote my ICND2 today, and i got 902/1000.. Question 6 was in the exam.. Thanks to the 9tut team..
I guys, can someone please send me the latest dumps? timrnorman@yahoo.com
thanks
@9tut, according to the question 5 from ospf in ccna section question 1 on this page has wrong answers
Q1 and Q3 in ICND2 today
when configuring the single OSPF protocol. Area is always area 0. Between 2 router always hello time and dead time is the same together router
Reference CCNA R & S (CCNA5.0) OSPF routing configuration site:
http://thietbivienthongbachkhoa.com/Default.asp?mod=News&action=list&NewsID=330&temp=Vertuvn_vn&Object=1&ItemID=83&Language=vn
Q 12 on today’s exam. Nailed it with 888/1000. Thanks to 9tut, CBT Nuggets, CiscoPress, HeavyMod.
Can someone please explain to me the answer for Question 6?
There’s no show commands nor are the routers even named…confusing.
zibbo merda
helpul
like your answers